Table of Contents
ToggleEvery successful company that ever exists, has used competitive benchmarking at least once in their existence. It could be in the product development phase or the launch phase, or when certain features or products fail to land well.
In all these scenarios, competitive benchmarking – comparing your company’s performance against industry leaders or competitors, is vital to ensure success.
Let’s understand how it helps.
Tips for Successful Competitive Benchmarking
1. Identify Your Goals and Metrics
Before starting any benchmarking process, it’s vital to identify what you want to accomplish. Are you looking to improve customer service, increase sales, reduce costs, or enhance product quality? Once you have clear goals in mind, determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to those objectives. These could include metrics such as conversion rates, average order value, net promoter score, or return on investment.
Step 1: Brainstorm with your team to list potential areas for improvement.
Step 2: Prioritize these areas based on strategic importance and feasibility.
Step 3: Select appropriate Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for each area identified.
2. Choose the Right Companies to Compare With for Competitive Benchmarking
Select companies similar to yours in terms of size, market share, products offered, target audience, etc., but also consider aspirational organizations known for their best practices. Be sure not to limit yourself only to direct competitors; sometimes, businesses outside your immediate field can offer valuable insights into innovative approaches and strategies.

Image Source: HubSpot Blog
Step 1: Research industry leaders and aspiring organizations.
Step 2: Create a list of potential comparison companies based on factors like size, market share, products offered, target audience, etc.
Step 3: Validate your choices by discussing them with internal experts or consulting external resources.
3. Gather Data Systematically
Collect data systematically from multiple sources like annual reports, financial statements, press releases, social media platforms, online reviews, and industry surveys. Use automated tools where possible to streamline the data collection process, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Regularly update your database so that your comparisons remain current.
Step 1: Define a consistent data collection process.
Step 2: Assign tasks to team members responsible for different aspects of data collection.
Step 3: Utilize automation tools wherever possible to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
Step 4: Store collected data securely in a central location accessible to authorized personnel only.
4. Analyze Data Thoroughly
Analyzing collected data is just as important as gathering it. Look beyond raw numbers and percentages to understand trends, patterns, correlations, and anomalies. Consider using statistical analysis techniques, visualization tools, and machine learning algorithms to extract meaningful insights from complex datasets. Remember, context matters: Understand the story behind each data point before concluding.

Image Source: Zapier
Step 1: Clean and preprocess the dataset to remove inconsistencies or errors.
Step 2: Apply statistical analysis techniques to discover trends, patterns, and correlations.
Step 3: Use visualization tools to represent findings graphically for easy understanding.
Step 4: Interpret results in the context of your organizational goals and industry landscape.
5. Draw Actionable Insights for Competitive Benchmarking
Translate findings into actionable recommendations tailored to your organization’s unique situation. For example, if a competitor offers faster delivery times, analyze how they do it and explore whether implementing similar methods makes sense for your business. Avoid copying blindly; instead, adapt successful competitor strategies creatively within your operational constraints.
Step 1: Identify strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors.
Step 2: Translate analytical findings into practical recommendations tailored to your organization.
Step 3: Evaluate proposed changes considering resource availability, timelines, and potential impact.
6. Communicate Results Clearly
Present results clearly and concisely, focusing on implications rather than details. Make sure all stakeholders understand the purpose of the study, its methodology, major findings, and recommended actions. Visual aids like charts, graphs, infographics, and dashboards can facilitate comprehension and engagement.
Step 1: Design presentations using simple language and engaging visuals.
Step 2: Tailor content according to the audience’s background and interests.
Step 3: Provide ample opportunity for questions, discussions, and clarifications.
Step 4: Summarize key takeaways and next steps in follow-up communications.
7. Implement Changes Strategically
Implement changes strategically, monitoring progress closely to ensure desired outcomes are achieved. Continuously review KPIs and adjust tactics accordingly based on real-time feedback loops. Keep track of ongoing improvements and communicate successes back to the team to maintain motivation and momentum.
Step 1: Develop detailed implementation plans, including milestones, responsibilities, and contingency measures.
Step 2: Allocate necessary resources and obtain required approvals.
Step 3: Monitor progress regularly through established feedback loops.
Step 4: Adjust the course as needed based on real-time feedback and changing circumstances.
8. Establish a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Competitive benchmarking should be part of an ongoing effort toward continuous improvement, not a one-off exercise. Encourage employees at all levels to participate in identifying areas for improvement, setting targets, collecting data, analyzing results, and suggesting solutions. Foster a culture where constructive criticism and open dialogue lead to innovation and growth.
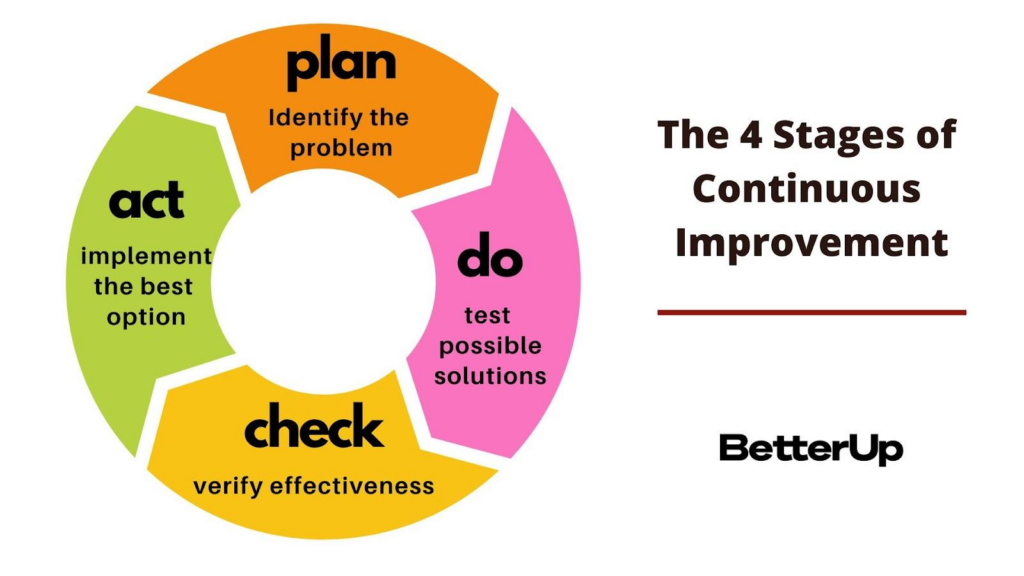
Image Source: BetterUp
Step 1: Encourage employee participation in benchmarking activities.
Step 2: Recognize and reward contributions made towards continuous improvement efforts.
Step 3: Incorporate lessons learned from past experiences into future planning and decision-making processes.
9. Respect Ethical Guidelines
When conducting competitive benchmarking, always respect ethical guidelines related to confidentiality, privacy, fairness, and legality. Never engage in espionage or deceptive practices, which could damage your reputation and expose you to legal risks. Always seek permission when using proprietary information belonging to others, even if publicly available.
Step 1: Familiarize yourself with applicable laws and regulations governing competitive intelligence.
Step 2: Ensure transparency and honesty throughout the benchmarking process.
Step 3: Seek explicit consent whenever utilizing proprietary information belonging to others.
10. Learn From Failures
Not every benchmarking initiative will yield positive results. Don’t shy away from acknowledging failures; instead, use them as opportunities to learn and grow. Reflect on why certain initiatives didn’t work out, what could have been done differently, and how to avoid similar pitfalls in future endeavors. Embrace failure as a natural step toward long-term success.
Step 1: Conduct post-mortem analyses to identify reasons behind failed initiatives.
Step 2: Document lessons learned for future reference.
Step 3: Share insights gained from failures across the organization to promote collective wisdom.
Step 4: Maintain a positive attitude towards experimentation and risk-taking despite setbacks.
Conclusion on Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking is necessary with the competition that exists today. If you’re interested in a platform that provides clear and actionable insights on competitors, schedule a demo with 42Signals today.
Your answers are on us!
Frequently Asked Questions on Competitive Benchmarking
What is competitive benchmarking?
Competitive benchmarking is the process of comparing your business performance, strategies, or products against your direct competitors to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
It helps you answer key questions like:
- How do we rank in price, service, or quality compared to our top competitors?
- What are industry leaders doing better than us?
- Where can we gain a competitive advantage?
Common benchmarking areas include pricing, digital shelf performance, product features, customer reviews, SEO visibility, and fulfillment efficiency.
What are comparative benchmarks?
Comparative benchmarks are data points used to compare the performance of one entity against another, often across industries or market segments.
Unlike competitive benchmarks (which focus on direct rivals), comparative benchmarks may include:
- Industry averages
- Global best practices
- Peer groups with similar size, structure, or audience
- Adjacent or non-competing brands for inspiration
These benchmarks help companies understand where they stand in a broader context, not just against their rivals.
What is the difference between functional and competitive benchmarking?
The difference lies in who you compare yourself to and why:
- ✅ Competitive Benchmarking – Compares performance against direct competitors offering similar products or services.
Purpose: To identify gaps and outperform rivals in your own market. - ✅ Functional Benchmarking – Compares your processes or functions to companies in different industries that excel in specific areas.
Purpose: To adopt best practices and innovative ideas beyond your industry.
Example:
- A retail brand may competitively benchmark against Zara or H&M.
- The same brand may functionally benchmark Amazon’s fulfillment system to improve delivery speed.
Is benchmarking between competitors illegal? What are the dangers of benchmarking?
Benchmarking between competitors is legal, as long as the data is collected ethically and lawfully — through public sources, third-party tools, or market research (not through collusion or confidential disclosures).
❗ Dangers of unethical benchmarking include:
- Violating antitrust laws if companies share sensitive pricing or strategy info directly
- Inaccurate data leading to poor decisions if benchmarks are outdated or misinterpreted
- Over-focus on competitors, which can stifle innovation or lead to copycat strategies
Best practice: Use public data or reputable intelligence platforms like 42Signals, SimilarWeb, or SEMrush — and never engage in direct price-fixing or confidential data sharing.
Who should be on the benchmark competitor list?
Your benchmark competitor list should include a mix of:
- Direct competitors – Brands offering similar products to the same target market
- Indirect competitors – Businesses solving the same problem with different products
- Category leaders – Industry frontrunners known for innovation, customer loyalty, or operational excellence
- Emerging disruptors – Startups or new players gaining traction quickly
- Aspirational brands – Companies you want to emulate for customer experience, branding, or digital strategy
Ideally, choose 3–8 companies that reflect a range of competition and inspiration, and update the list periodically based on market shifts.




