A single pricing misstep can cost brands millions. Imagine this: A customer is about to purchase your flagship product on Amazon but spots an identical item listed 20% cheaper on Walmart. They abandon their cart, opting for the competitor. Multiply this scenario by thousands, and suddenly, your revenue plummets while rivals gain ground. This isn’t hypothetical—it’s the daily reality for brands that overlook ecommerce price scraping, a critical component of retail pricing analytics and digital shelf analytics.
Price scraping isn’t just about tracking numbers—it’s about arming your brand with actionable insights to outmaneuver competitors, protect margins, and dominate search rankings.
Let’s explore why this tool is indispensable for ecommerce success.
What Is Ecommerce Price Scraping?

Image Source: Radware
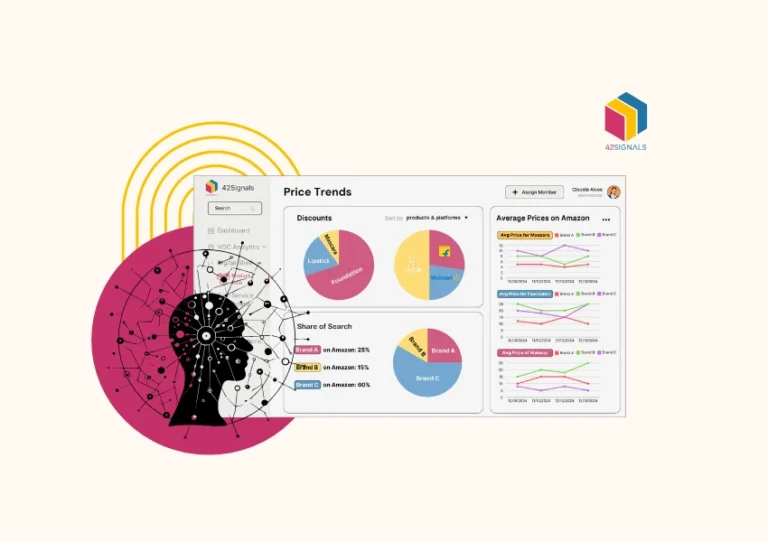
Ecommerce price scraping involves using automated tools to extract real-time pricing data from competitors’ websites, marketplaces, and third-party seller platforms. Unlike manual price checks, advanced scraping tools collect millions of data points daily, analyzing trends across regions, product categories, and sales cycles. This data feeds into pricing analytics, helping brands:
- Track competitor price changes
- Identify MAP (Minimum Advertised Price) violations
- Optimize pricing strategies based on demand fluctuations
- Monitor stock availability and delivery costs
For example, a tool might scrape Walmart’s product pages hourly to detect if a rival slashed the price of a best-selling blender during Prime Day. Without this intel, brands risk losing sales to aggressive discounting or missing opportunities to adjust prices dynamically.
Why Price Scraping Is the Secret Weapon for Competitive Pricing?
1. Real-Time Pricing Intelligence Prevents Revenue Leakage
Competitors adjust prices multiple times daily, often using algorithms to exploit market trends. Without scraping, brands operate blindly. Consider a cosmetics brand that noticed a 15% sales drop for its serum.
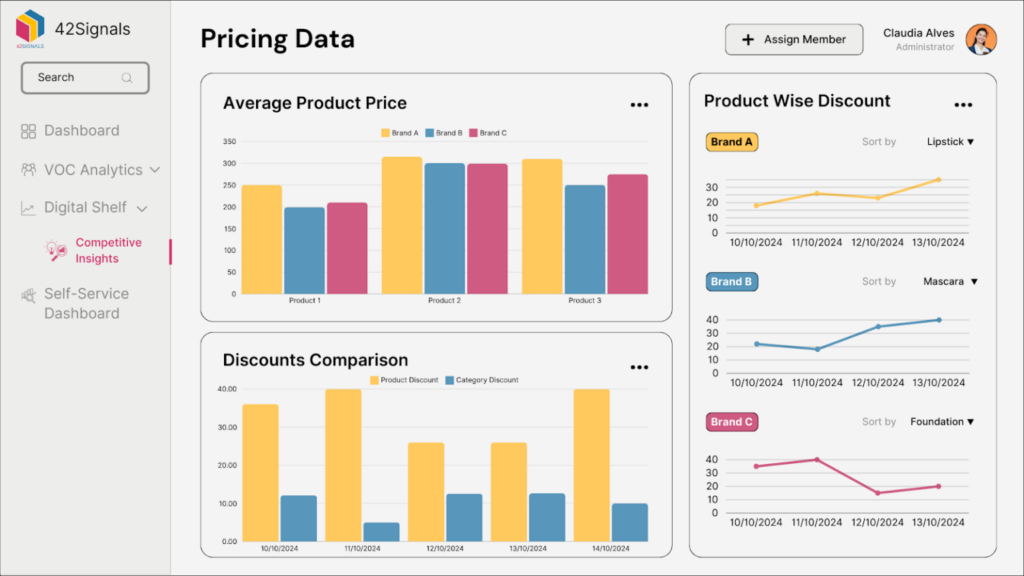
Product data and ecommerce price scraping revealed a competitor had discounted a similar product by 25% on Target.com. By responding with a timed 10% promo (without eroding margins), the brand regained market share within days.
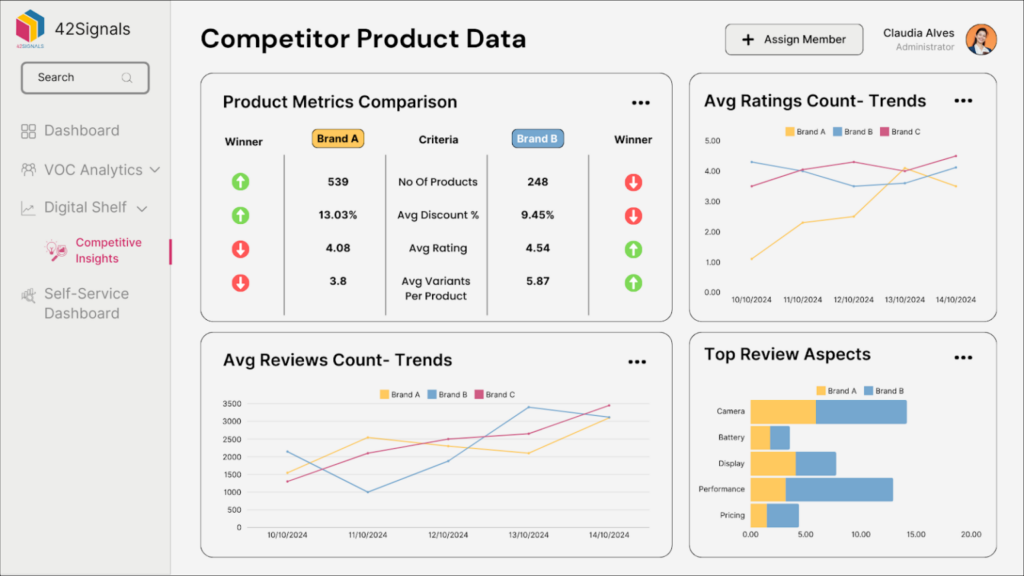
Key Insight: Price scraping integrates with digital shelf analytics to show not just competitor prices but also how your product listings compare in titles, images, and specs. A unified digital shelf ensures customers aren’t lured away by cheaper or better-presented alternatives.
2. Dynamic Pricing Maximizes Profit Margins
Static pricing is a relic. Retailers like Amazon change prices every 10 minutes based on demand, inventory, and competitor actions. Price scraping enables retail pricing analytics to fuel dynamic strategies:
- Surge Pricing: Raise prices during peak demand (e.g., holiday toys).
- Discount Optimization: Offer limited-time deals in regions with low competition.
- Bundle Pricing: Pair slow-moving products with popular items if competitors are out of stock.

A home appliance brand used ecommerce price scraping data to discover competitors were inflating prices of air purifiers during wildfire season. By capping their own price increases at 10% (vs. the industry’s 25%), they boosted customer loyalty and sales volume.
3. Unmask Competitor Strategies with Precision

Ecommerce price scraping reveals patterns invisible to the naked eye:
- Do competitors undercut prices every Thursday?
- Which products do they discount first during sales?
- Are they testing “decoy pricing” to steer customers toward premium items?
A pet supplies retailer analyzed scraped data to find a rival that consistently discounted dog food mid-month, coinciding with payroll cycles.
They launched targeted Facebook ads for budget-conscious buyers during this window, increasing click-through rates by 40%.
4. Enforce MAP Policies and Protect Brand Value
Unauthorized sellers often violate MAP policies, eroding brand prestige. Price scraping tools flag these violations instantly. One luxury watch brand detected a seller on eBay listing products 30% below MAP. By reporting the seller and redirecting customers to authorized partners, they maintained premium positioning.
Pro Tip: Pair scraping with product data monitoring to ensure counterfeiters aren’t using stolen images or descriptions to sell knockoffs.
5. Optimize for the Digital Shelf with Cross-Channel Insights
Your product’s digital shelf isn’t just its price—it’s the entire shopping experience. Scraping tools can identify:
- Competitors using superior keywords in titles (e.g., “4K HDMI cable” vs. “HD cable”).
- Missing product specs are hurting your search rankings.
- Inaccurate stock levels lead to cart abandonment.
A baby gear brand found its strollers ranked lower than competitors on Buy Buy Baby’s site due to incomplete size specifications. Updating their product data improved visibility by 50%.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Price Scraping Strategy
Step 1: Choose the Right Tools
Not all ecommerce price scraping tools are equal. Look for:
- Cross-Platform Coverage: Amazon, Walmart, Shopify, niche sites.
- Real-Time Alerts: Notifications for price drops, stockouts, or MAP breaches.
- Integration: Compatibility with your CRM, ERP, or analytics platforms.
Tools like 42Signals offer customizable dashboards to track KPIs like “price position” (your price vs. the market average).
Step 2: Legal and Ethical Compliance
Web scraping operates in a legal gray area. Avoid pitfalls by:
- Respecting robots.txt files
- Scraping public data only (no login-required pages).
- Use proxies to prevent IP bans.
Consult legal experts to ensure compliance with regional regulations like GDPR.
Step 3: Automate and Integrate
Merge scraped data with ecommerce analytics platforms to:
- Adjust prices automatically via repricing software.
- Update product descriptions based on competitor SEO tactics.
- Alert your team about emerging trends (e.g., a sudden spike in yoga mat prices).
Step 4: Test, Learn, Iterate
Run A/B tests to gauge how price changes affect conversions. For instance, an electronics retailer tested a 5% price hike on headphones during the back-to-school season. Despite the increase, sales rose 12% because competitors were out of stock—an insight revealed by scraping.
The Cost of Ignoring Price Scraping
Brands that dismiss price scraping risk:
- Lost Sales: 56% of shoppers compare prices across at least three sites before purchasing.
- Eroded Trust: Inconsistent pricing or stockouts drive customers to rivals.
- Missed Trends: Competitors capitalize on seasonal demand shifts while you lag.
A sporting goods brand ignored scraping and failed to notice a competitor’s stealth price drop on hiking boots. The result? A 22% decline in quarterly revenue.
Conclusion on ECommerce Price Scraping
In ecommerce, pricing isn’t just a number—it’s a signal of value, quality, and urgency. Price scraping arms brands with the intelligence needed to stay agile, protect margins, and dominate the digital shelf. By integrating pricing analytics, competitor strategies, and product data insights, businesses transform raw data into revenue.
The question isn’t whether you can afford to invest in price scraping—it’s whether you can survive without it.

Ready to Improve Your Pricing Strategy with 42Signals? Schedule a demo with 42Signals today and turn competitor data into your most powerful asset.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is price scraping illegal?
Price scraping is not inherently illegal, but its legality depends on how it’s done, what data is being accessed, and the terms of the website being scraped.
- Public data scraping (like prices visible on a website) is generally legal if done ethically and without violating the terms of service.
- Illegal or risky scraping includes:
- Bypassing paywalls or login credentials
- Overloading servers (denial of service)
- Ignoring “robots.txt” rules
- Violating copyright, trademark, or privacy laws
Bottom line: Scraping public pricing data is often legal, but always check the website’s terms of use and consult legal counsel for large-scale projects.
Is scraping eCommerce websites legal?
Scraping eCommerce websites is legal only if the data being scraped is publicly available and the scraping does not violate intellectual property laws or the site’s terms of service.
- What’s generally allowed:
- Public product listings, prices, and descriptions
- When done with rate limits and respect for site performance
- What’s risky or prohibited:
- Scraping user account information or reviews protected by login
- Ignoring legal warnings or anti-bot measures
- Using scraped data in ways that compete unfairly with the original site
Major platforms like Amazon, Walmart, and BestBuy have strict anti-scraping clauses, and violations could lead to IP bans or legal notices.
What is scraping in eCommerce?
Scraping in eCommerce refers to the use of automated tools (also called bots or crawlers) to collect product data from online retail websites. This includes:
- Prices and discounts
- Product titles, images, descriptions
- Stock availability
- Seller and shipping information
Why companies use it:
- Competitive price tracking
- Market research and assortment analysis
- Monitoring unauthorized sellers
- MAP compliance enforcement
Ethical scraping supports business intelligence—but doing it responsibly is crucial to avoid legal or ethical issues.
Can you scrape Amazon for prices?
Technically, yes—you can scrape Amazon for prices, but Amazon’s terms of service explicitly prohibit it, and they actively monitor and block unauthorized bots.
- Amazon has anti-bot technology and may block your IP, user agent, or take legal action if scraping is aggressive or violates their rules.
- Some businesses use Amazon’s Product Advertising API, which allows structured, legal access to price and product data—but only with proper permissions and under Amazon’s usage policies.
Recommendation:
If you’re a brand, seller, or analytics provider, use authorized APIs or tools (like 42Signals or Helium 10) to get Amazon data legally and reliably.