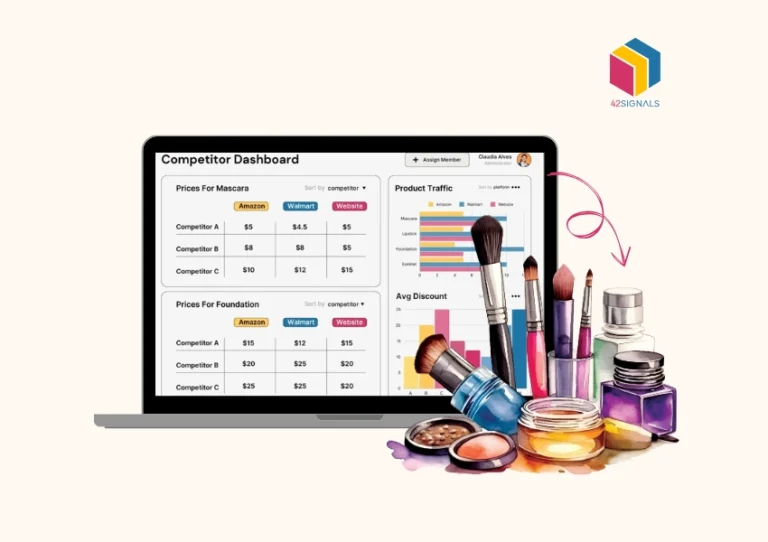
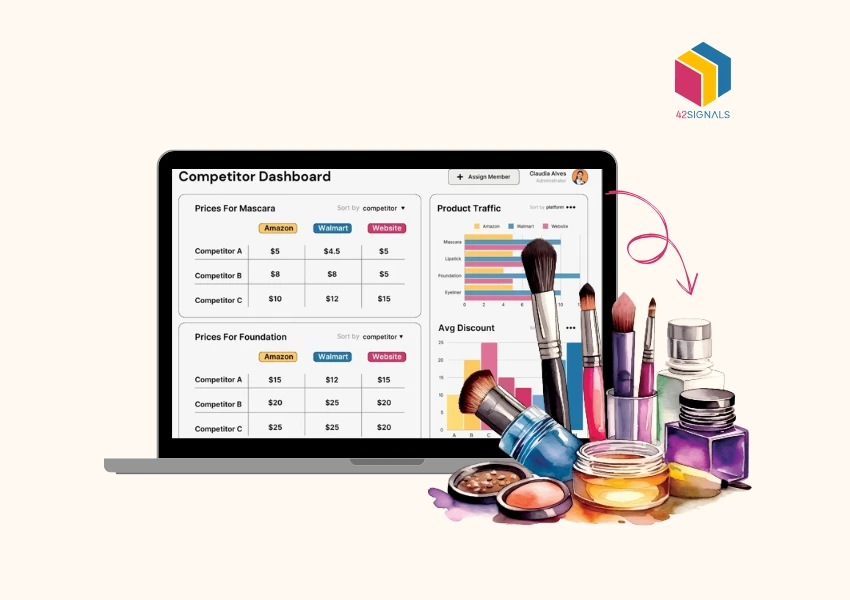
What is Quick Commerce?
Quick commerce or q-commerce is an e-commerce platform that focuses solely on quick deliveries. This means an order is usually delivered within 15-30 minutes or less than an hour.
With customer behavior slowly shifting towards quick shopping and instant deliveries, quick commerce has risen in popularity in big cities.
Let’s see how different strategies can contribute to higher customer satisfaction.
Strategies to Improve Customer Satisfaction in Quick Commerce
1. Efficient Supply Chain and Inventory Management
- Localized Micro-Warehouses: Utilizing dark stores or micro-fulfillment centers strategically placed across the city allows companies to store high-demand products closer to customers. This reduces delivery time and ensures that popular items are always in stock.
- Demand Forecasting: Leveraging AI and data analytics to predict peak demand and seasonal trends ensures inventory aligns with customer needs, reducing stockouts or delays.
2. Seamless Technology Integration
- User-Friendly Mobile Apps: An intuitive and quick-to-navigate interface helps customers place orders effortlessly. Features like saved preferences, one-click reorder, and real-time tracking enhance the shopping experience.
- Real-Time Tracking: Providing live updates on order status builds trust and allows customers to plan around their delivery.
- AI-Driven Personalization: Recommending products based on user behavior creates a customized experience, increasing satisfaction and repeat purchases.

Image Source: Finch
A customer looking to buy a product would significantly benefit from detailed information on the item, looking at an example of a skincare product, having scientifically rigorous product information can help the buyer understand the ingredients not only at a summary level but also knowing its impact on the skin can be tremendously helpful.
3. Optimized Delivery Logistics
- Hyperlocal Delivery Networks: Partnering with local delivery agents or maintaining an in-house fleet ensures timely deliveries. Leveraging route optimization software helps minimize delays.
- Dynamic Dispatching Systems: Using smart dispatch systems to assign orders to the nearest available rider reduces waiting times and ensures efficiency.
- Eco-Friendly Delivery Options: Offering options like bicycle or electric vehicle deliveries can appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
4. Focus on Product Quality in Quick Commerce
- Secure Packaging: High-quality packaging prevents damage to products during transit, ensuring items arrive in pristine condition.
- Temperature-Controlled Logistics: For perishables or temperature-sensitive items, ensuring they remain fresh is vital for customer trust.
5. Customer Service Excellence
- 24/7 Support Channels: Providing round-the-clock customer service through chatbots, calls, or social media channels ensures timely resolution of queries for quick commerce orders.
- Proactive Communication: Sending proactive updates about delays or order substitutions minimizes frustration.
- Flexible Return Policies: Hassle-free return options encourage customers to trust the platform for future purchases.

Image Source: Shopify
6. Loyalty and Reward Programs
- Subscription Models: Offering perks like free deliveries or exclusive discounts through subscription packages incentivizes customer retention.
- Point-Based Systems: Allowing customers to earn points for each purchase and redeem them for discounts or freebies fosters brand loyalty.
7. Community and Sustainability Initiatives
- Support for Local Brands: Partnering with local vendors or producers can appeal to customers who value community-driven businesses.
- Sustainability Commitments: Using recyclable packaging and reducing carbon footprints demonstrates social responsibility, which resonates with conscious consumers.
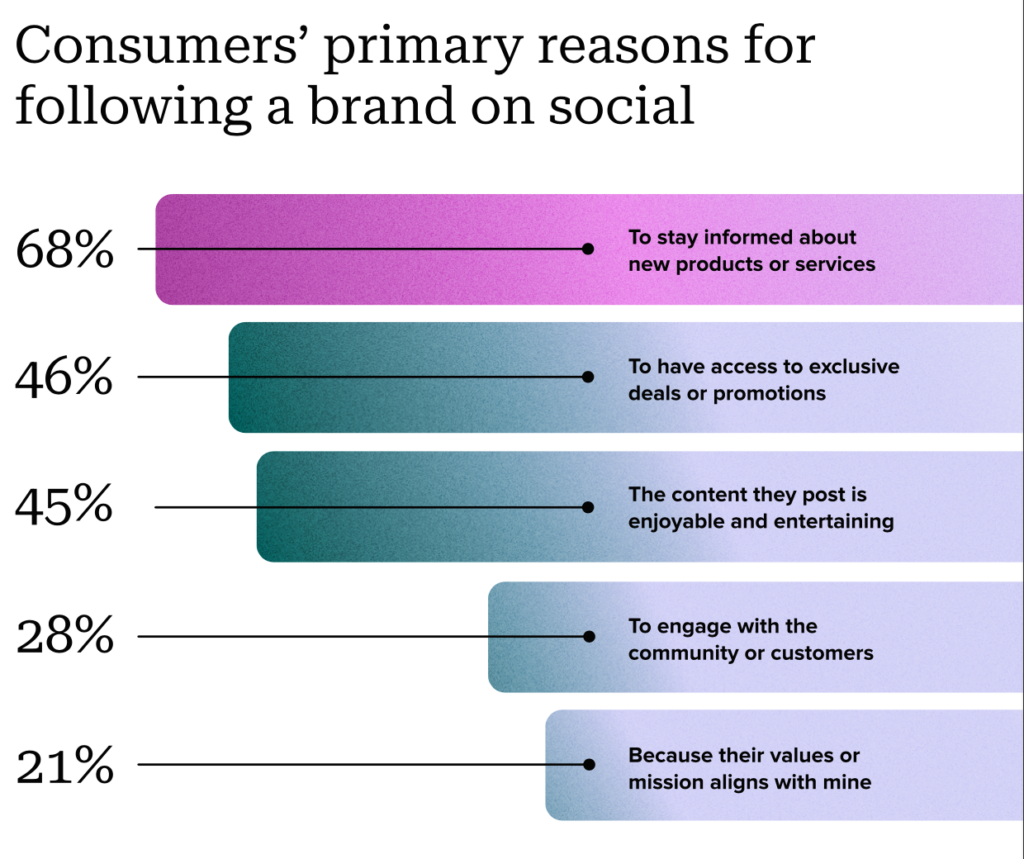
Image Source: LinkedIn
If a user tweets a brand asking for advice on which type of coffee maker to buy, the brand’s prompt response to the tweet suggesting a few models that fit the user’s budget and preferences can make the user into a customer. As you can see 28% of people follow a brand to engage with the community.
8. Marketing and Promotions on Quick Commerce Platforms
- Targeted Campaigns: Tailored marketing strategies based on customer demographics or purchasing patterns can drive engagement and satisfaction in quick commerce.
- Limited-Time Offers: Time-sensitive promotions encourage impulse buying and increased app engagement.
- Referral Incentives: Offering discounts or rewards for referrals helps expand the customer base while retaining existing ones.
9. Continuous Feedback Loop
- Customer Feedback Mechanisms: Actively soliciting feedback through post-purchase surveys or app ratings helps identify areas for improvement.
- Iterative Improvements: Using feedback to continuously refine operations, product offerings, and service quality ensures evolving customer needs are met.

Quick commerce is booming worldwide. A fun and positive shopping experience on quick commerce applications can change customer behavior making them loyal shoppers.
E-commerce insights on product availability and understanding what items are selling faster can help avoid stockouts and improve customer experience.
If you would like to know more about e-commerce analytics, schedule a demo with us today.
Why Q-Commerce Thrives in Big Cities
Urban areas with dense populations and high mobile penetration are ideal for q-commerce. Factors such as traffic congestion, the need for convenience, and a growing preference for digital solutions make q-commerce platforms indispensable for city dwellers.
Furthermore, the cultural shift towards instant gratification aligns perfectly with the promise of ultra-fast delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a quick commerce channel?
A quick commerce channel refers to a type of e-commerce model that focuses on delivering products to customers in the shortest time possible, often within minutes or hours.
This is achieved through the use of advanced technology such as artificial intelligence and machine learning for inventory management, order processing, and real-time tracking.
Additionally, these channels typically have a network of local fulfillment centers or dark stores located close to high population density areas, which enables faster delivery times compared to traditional e-commerce models.
Quick commerce channels cater primarily to essential items like groceries, household supplies, personal care products, and meals from restaurants. The goal of these channels is to provide convenience and instant gratification to consumers who want their orders fulfilled quickly and efficiently without having to leave their homes or offices.
What is the difference between Q-commerce and ecommerce?
E-commerce (Electronic Commerce):
Definition: E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods or services over the Internet. It encompasses a wide range of online transactions, including retail sales, digital downloads, subscriptions, and more.
Channels: E-commerce operates primarily through websites, mobile apps, and online marketplaces.
Examples: Online retail stores like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify fall under the e-commerce umbrella.
Payment Methods: E-commerce platforms accept various payment methods, such as credit cards, digital wallets, and bank transfers.
Delivery: Products are typically shipped to the customer’s address.
Business Models: B2C (Business-to-Consumer), B2B (Business-to-Business), and C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer) models are common in e-commerce.
Q-commerce (Quick Commerce):
Definition: Q-commerce is an evolution of e-commerce that focuses on ultra-fast delivery of goods. It aims to provide near-instantaneous delivery, often within minutes.
Speed: Q-commerce platforms prioritize speed and convenience. They leverage local micro-fulfillment centers and couriers to achieve rapid delivery.
Product Range: Q-commerce typically offers a limited selection of essential items, such as groceries, pharmaceuticals, and convenience goods.
Examples: Grocery delivery services like Instacart, food delivery platforms like Uber Eats, and on-demand convenience stores fall into the Q-commerce category.
Business Model: Q-commerce relies on hyper-local logistics and real-time inventory management.
Customer Expectations: Customers expect lightning-fast delivery, often within an hour or less.