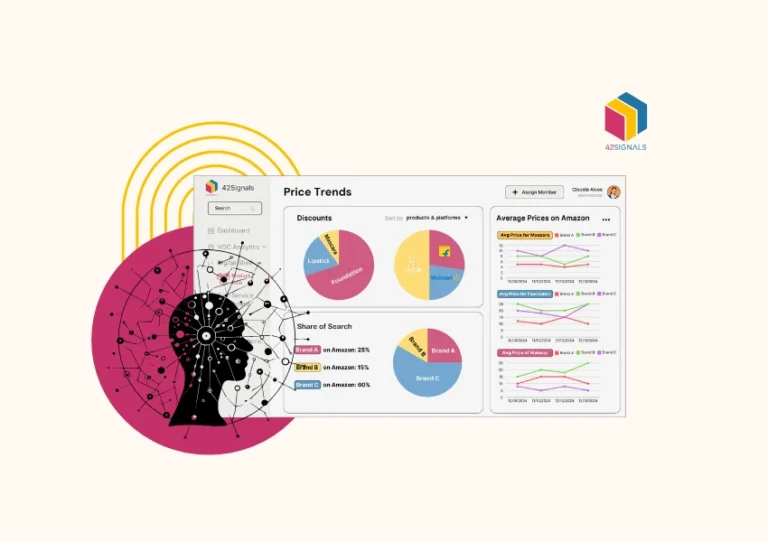
Why is Category Management Important in E-commerce?
Let’s understand the need for a category management process.
Imagine walking into a store and finding products scattered all over, without any rhyme or reason. It would be nothing but an overwhelming, confusing, and annoying experience, wouldn’t it? Similarly, in e-commerce, a well-thought-out and structured arrangement of products within categories is crucial for customer engagement and conversion.
However, it’s more than just arranging products neatly; it’s about creating a shopping experience that guides customers seamlessly through their journey. In e-commerce, where customer preferences change quickly, relying on gut feelings or assumptions can be risky.
Data-driven insights from digital shelf analytics help e-commerce brands overcome this challenge by helping them understand customer behavior, identify trends, and refine strategies. This leads to optimized digital shelves that cater to customers and drive sales.
In this blog, we’ll look at the 8-step category management process, each step’s significance, and how digital shelf analytics can help e-commerce businesses with category management.
The 8-Step Category Management Process

Image Source: Retail Dogma
1. Define The Categories
When deciding how to organize products or services into clear categories, a practical method is to group them based on their shared purpose. This involves looking at the characteristics of the items and how they fulfill customer needs.
To accommodate varying profitability and customer preferences, it’s a good idea to establish sub-categories within broader categories.
This approach lets businesses create customized strategies for each category and it is necessary in the category management process.
For example, they can group items near the checkout zone into a single category, which then can be further split into different segments.
2. Assess The Role of Each Category
Once products are sorted into categories, the next step is to define the role of each category within the larger product lineup of the business.
Different categories can serve distinct functions, like drawing in footfall or encouraging spontaneous purchases.
This phase may also entail identifying potential suppliers and evaluating them before bringing them on board as category suppliers
3. Assess Current Performance
Examining how each category performs involves using key performance indicators (KPIs) to guide decisions on pricing, promotions, placement, and product variety strategies. Regular performance assessments also serve as benchmarks for other categories.
For instance, testing strategies like placing mints at check-out counters and offering buy-one-get-one promotions or coupons at check-out can provide insights into their impact on sales.
4. Set a Scorecard for Each Category
Developing a category scorecard means setting out specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for each category.
This scorecard allows businesses to track indicators such as net sales, volume sales, market share, product assortment, and customer satisfaction.
Similarly, they can establish a scorecard for suppliers to align their efforts with the broader category goals in the category management process.
5. Devise Strategies
To meet scorecard goals, it’s important to devise tailored strategies for each category. These strategies may encompass goals such as increasing market share, sales, traffic, return on investment, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
6. Set Tactics to Implement Your Strategies
Once the category strategies are established, the next step is to create tactics for putting them into action. These tactics cover areas like pricing, promotions, market expansion, and product variety. The brand can determine the extent, frequency, and timing of each tactic.
7. Implement
After outlining the objectives, strategies, and tactics for each category, it’s time to implement an execution plan that outlines how the entire process will unfold. This plan should assign responsibilities among team members and specify target completion dates for each tactic. Visual aids like planograms can effectively communicate project goals.
8. Review
The final phase of the category management process involves analyzing, measuring, and reviewing outcomes, followed by necessary adjustments. Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of different strategies ensures that categories stay aligned with market trends and remain financially viable. This step may involve assessing supplier relationships and potentially renegotiating contract terms when required.
How Digital Shelf Analytics Helps with Category Management Processes
Achieving success in the category management process demands more than intuition – it requires data-driven precision. This is where Digital Shelf Analytics comes in.
By providing insights into product performance, consumer behavior, and market trends, digital shelf analytics guides e-commerce businesses through the process of category management. Here’s how digital shelf analytics helps in category management:
- Informed Decision-Making
- Optimized Product Assortment
- Dynamic Pricing Strategies
- Personalized Shopping Experiences
- Enhanced Visual Merchandising
- Competitive Advantage
- Data-Driven Insights
Driving E-commerce Excellence Through Category Management Processes
Through this 8-step category management process, we’ve journeyed from understanding market nuances and consumer behavior to meticulously curating assortments, optimizing pricing, and fine-tuning promotions.
As the curtains draw on this overview, it’s crucial to recognize that category management is not a one-time affair but a continuous journey toward growth and success.
This journey is incomplete without its guiding force- data! With every click, scroll, and purchase, digital shelf analytics unveils valuable patterns and trends, guiding you to make informed decisions for continuous improvement.
Check out 42Signals Digital Shelf Analytics which will help you track, manage, and optimize your product performance across online channels.
For more details, contact our sales team at sales@42signals.com