Consider a scenario in which a renowned electronics manufacturer meticulously crafts a comprehensive Minimum Advertised Price Violations (MAP) policy, aiming to maintain fair competition and preserve brand value.
However, amidst the hustle of the online marketplace, various retailers start advertising their products at shockingly low prices, undercutting the carefully set standards. This isn’t just an oversight; it’s a clear case of MAP violation, leading to a cascade of implications for both the manufacturer and the retailers involved.
In this blog, we embark on an exploration of the intricate world of minimum advertised price violations. Whether you’re a seasoned industry leader or a fresh contender in the market, come along as we embark on a journey to uncover the strategies that sustain equitable competition and uphold the integrity of your brand within the digital marketplace.
The Definition of Minimum Advertised Price (MAP)
Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) is the lowest price at which a manufacturer allows a retailer to publicly advertise its products. The manufacturer establishes this price to create a fair marketplace for retailers, preventing them from engaging in price undercutting. It’s important to note that the MAP is distinct from the actual selling price; instead, it represents the price that retailers can advertise to potential customers.
By implementing a MAP policy, manufacturers aim to protect the value and reputation of their brands. By setting a minimum advertised price, manufacturers can prevent retailers from engaging in a price war that may devalue the product or damage the brand’s image.
Understanding Minimum Price Advertised Violations
Minimum advertised price violations happen when a retailer promotes a product at a price lower than the minimum advertised price established by the manufacturer. Minimum advertised price violations can be either deliberate or inadvertent. Deliberate violations may be driven by the desire to secure a competitive edge, lure more customers, or expand market presence. On the flip side, unintentional violations can result from a lack of awareness or a failure to promptly adjust pricing and promotional strategies.
MAP violations can damage the relationship between a manufacturer and its retailers. When retailers consistently advertise products below the MAP, it creates an imbalance in the marketplace, leading to unfair competition and a potential loss of trust among retailers.
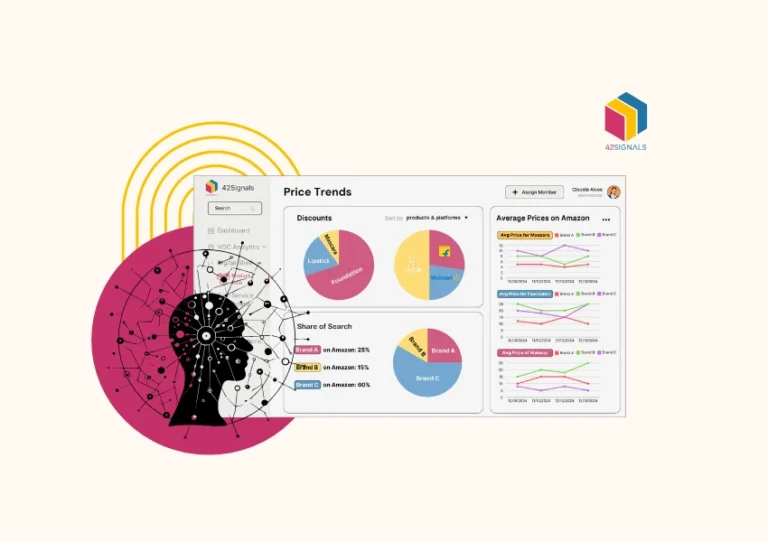
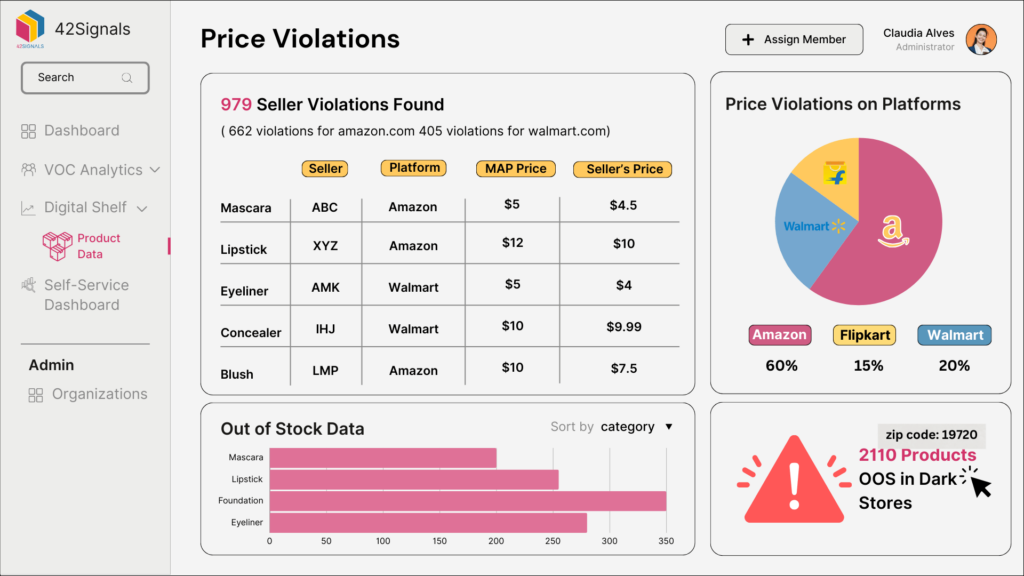
Let’s understand this better with an example: In the world of cosmetics, where brands fiercely compete, GlamourGlow has always stood out. Renowned for their quality and allure, their products have cultivated a dedicated fan base. However, variations in product pricing threatened to tarnish their image. They had set minimum advertised prices (MAP) to maintain integrity and ensure consistent pricing across retailers, including Amazon. Yet, their e-commerce analytics partner uncovered 764 instances of price violations on Amazon, causing serious repercussions for GlamourGlow.
Their best-selling Kajal had a MAP of ₹356, but Retailers A and D advertised it for ₹346 and ₹348, respectively. Meanwhile, Retailer C marked it at an exorbitant ₹495, and Retailer B listed it at ₹390. Similar violations extended to other popular products, including the Gift Kit, Hair Styling Gel, and Sunscreen. Retailer A consistently priced these products below MAP, eroding profit margins and damaging the brand’s premium image.
The Implications of Minimum Advertised Price Violations
Minimum advertised price violations can have significant implications for both manufacturers and retailers. Here are some key consequences of non-compliance with MAP policies:
1. Brand Erosion
Mechanism: Chronic below-MAP advertising trains consumers to perceive the product as a “discount item” rather than a premium offering. This commoditization erodes the brand’s aspirational value and premium positioning.
Long-Term Impact: Diminished brand equity makes it harder to command premium prices anywhere, stifles new product launches, and damages relationships with retailers who invested in showcasing the brand’s premium image. Luxury and innovation-driven brands are particularly vulnerable.
Consumer Psychology: Creates price anchoring, where consumers permanently reset their perception of the product’s “fair” price to the discounted level, making future full-price sales difficult.
2. Loss of Profit
Retailer Impact: Price wars triggered by violations squeeze margins for all retailers, even compliant ones, forced to match prices to stay competitive. This disproportionately harms smaller retailers lacking the volume to absorb thin margins.
Manufacturer Impact: Reduced retailer profitability discourages investment in sales staff training, in-store displays, marketing support, and inventory depth. Manufacturers may see volume shift to lower-margin channels or competitors, and face pressure to lower wholesale prices, further compressing their own margins.
Race to the Bottom: Creates a vicious cycle where the primary competitive lever becomes price, not value, service, or brand experience.
3. Strained Retailer Relationships Due to Minimum Advertised Price Violations
Trust Breakdown: Violations signal disrespect for the agreement and the manufacturer’s brand strategy. Compliant retailers feel betrayed and unfairly disadvantaged.
Concrete Consequences: Manufacturers must act to protect the policy’s integrity. Punishments escalate: warnings → withholding co-op/MDF funds → delayed shipments → restricted access to hot new products → termination of the partnership.
Channel Conflict: Creates animosity between authorized retailers, damaging the overall channel cohesion and brand experience.
4. Legal Ramifications
Enforcement Actions: Manufacturers can pursue breach of contract claims against authorized retailers who signed MAP agreements. Remedies include injunctions (court orders to stop violations) and monetary damages.
Gray Market/Unauthorized Sellers: MAP is harder to enforce against unauthorized sellers, but manufacturers can use trademark infringement claims if sellers imply unauthorized affiliation or sell diverted/gray market goods.
Antitrust Caution (US Focus): MAP governs advertised prices, not final selling prices. Manufacturers must avoid language or actions implying control over the retailer’s final selling price (Resale Price Maintenance – RPM), which can be illegal under antitrust laws (though legal nuances exist, like the Colgate doctrine). Policies must be unilateral and enforced uniformly. Legal counsel is essential for policy drafting and enforcement strategy.
Tips for Ensuring Compliance with MAP Policies
Complying with MAP policies is essential for maintaining positive relationships with manufacturers and protecting the value of your brand.
1. Clearly Communicate MAP Policies
Detail: Specify exact MAP prices, covered products (SKUs), advertising channels (online marketplaces, websites, social media, flyers, email), and calculation rules (shipping, bundles, coupons).
Access: Maintain a dedicated, easily accessible portal (e.g., partner portal) with the current policy, FAQs, and updates. Include the policy in all retailer agreements.
Onboarding: Integrate MAP policy review into the new retailer onboarding process.
2. Monitor Pricing Regularly
Scope: Monitor all relevant online channels (e-tailers, marketplaces like Amazon/Walmart.com, price comparison engines, affiliate networks, Google Shopping) AND offline channels (print ads, circulars, in-store signage – where feasible).
Technology: Invest in specialized MAP Monitoring Software (e.g., PriceSpider, TrackStreet, PROS, IntelligenceNode). These tools automate 24/7 scanning, provide alerts, track historical pricing, identify unauthorized sellers, and generate violation reports.
Frequency: Real-time or daily monitoring is essential in fast-paced e-commerce environments.
3. Educate Retailers on Minimum Advertised Price Violations
Beyond Policy Docs: Conduct webinars, create video tutorials, and host Q&A sessions. Explain the “why” – how MAP protects their profitability, the brand’s health (which drives customer demand), and a level playing field.
Channel-Specific Guidance: Provide clear examples of compliant vs. non-compliant advertising for different platforms (e.g., Amazon “List Price” vs. “Your Price”, handling automatic platform markdowns).
Open Dialogue: Establish a clear point of contact for retailers to ask compliance questions before launching promotions.
4. Enforce Consequences
Defined Escalation Path: Create a clear, written enforcement protocol (e.g., 1st Violation: Warning & Education; 2nd Violation: Temporary suspension of MDF/Co-op; 3rd Violation: Shipment delays/restrictions; 4+ Violations: Account suspension/termination). Apply this uniformly to all retailers.
Swift Action: Address violations promptly (within agreed timeframes in the policy, e.g., 24-48 hours to correct).
Thorough Documentation: Meticulously log every violation, communication, and action taken. This is critical for legal defensibility and demonstrating consistent enforcement.
5. Implement E-commerce Analytics Tools
Utilize e-commerce analytics tools to monitor and track pricing across various platforms. These tools can provide real-time alerts for any violations, allowing for immediate action.
- Integration: Use MAP monitoring tools not just for alerts, but to generate comprehensive compliance reports, track retailer performance over time, and identify repeat offenders or systemic issues.
- Automated C&D (Cease & Desist): Some platforms integrate with marketplaces to automatically generate and send standardized violation notices upon detection.
- Unauthorized Seller Identification: Utilize tools to track down and take action against unauthorized sellers who frequently violate MAP and damage brand integrity.
- Data-Driven Insights: Analyze violation data to identify patterns (e.g., specific regions, channels, product categories more prone to violations) and refine strategies or policy language.
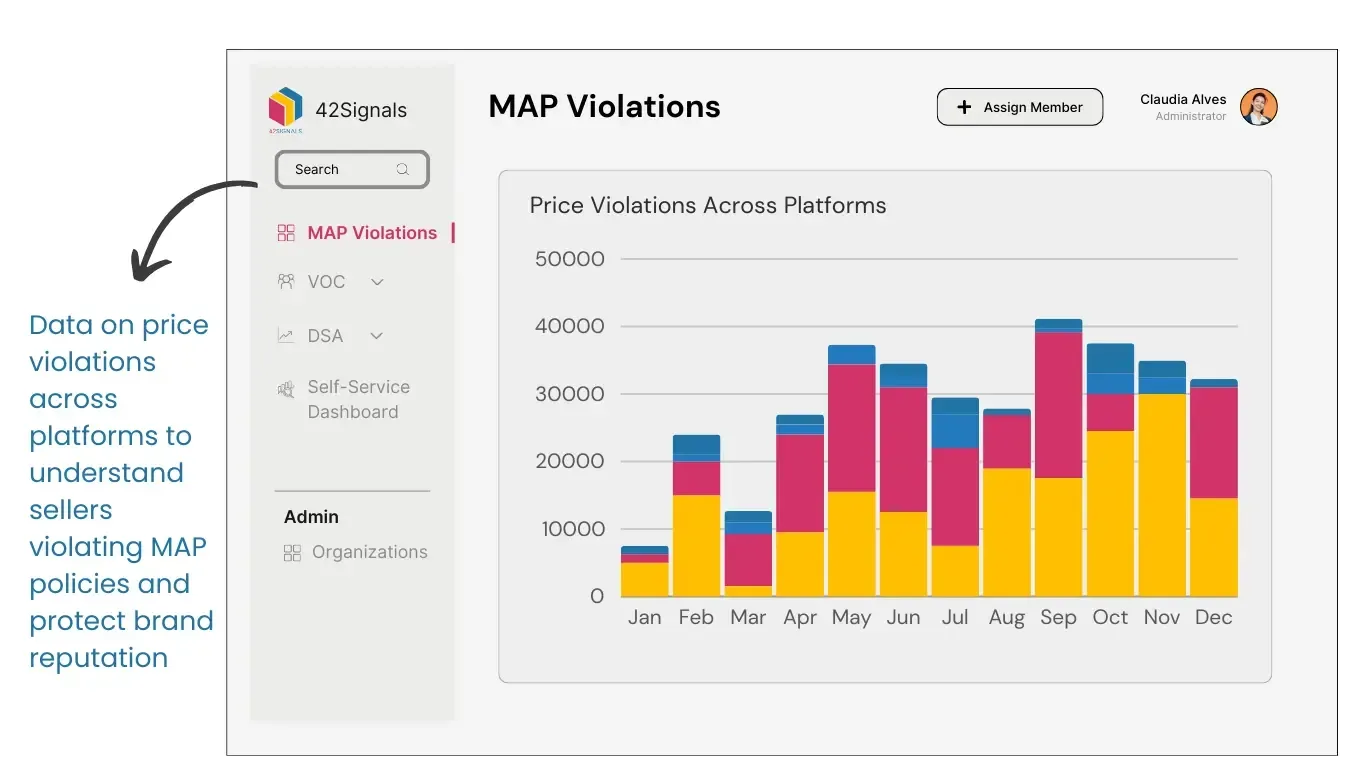
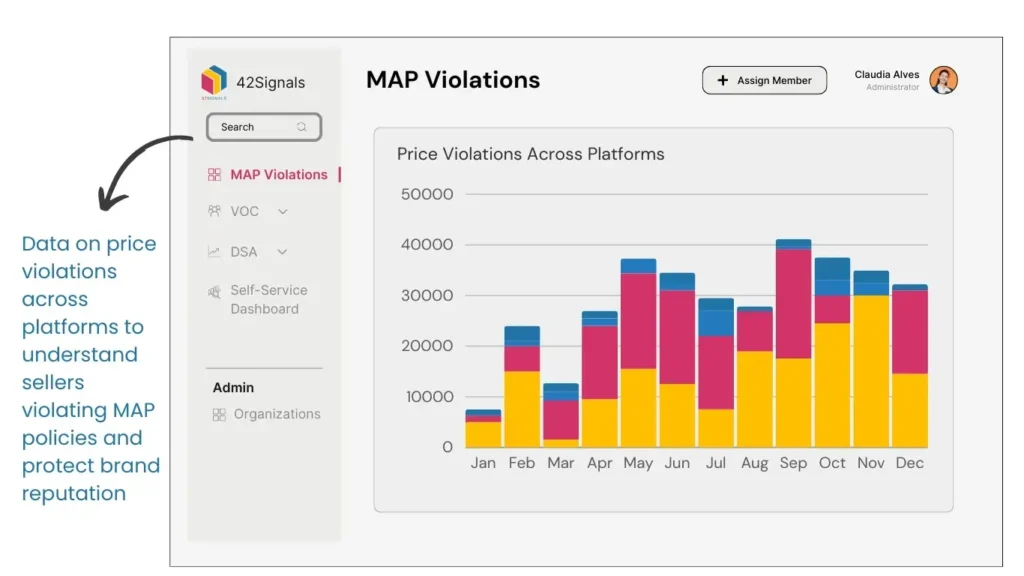
MAP Violation Tracking
Tracking Minimum Advertised Price violations can be made more efficient and effective with the use of e-commerce analytics tools. These tools can help identify pricing discrepancies, monitor multiple online platforms simultaneously, and automate the violation reporting process. By utilizing these tools, manufacturers can ensure timely action against violators and maintain better control over the pricing integrity of their products.
Navigating the basics of Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) violations is essential for both manufacturers and retailers. Understanding the definition of MAP, the implications of violations, and implementing strategies for compliance are crucial for maintaining brand value, fair competition, and successful retailer relationships. By prioritizing MAP compliance, manufacturers and retailers can create a level playing field that benefits all stakeholders in the e-commerce landscape.
Get expert assistance in dealing with minimum advertised price violations by partnering with 42Signals. Contact us today at sales@42signals.com.
Frequently Asked Questions on MAP Violations
What is a minimum advertised price violation?
A Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) violation happens when a reseller or retailer advertises a product for sale at a price lower than the minimum set by the manufacturer or brand owner. This doesn’t restrict the actual selling price — only the publicly displayed advertised price (online listings, print ads, etc.).
For example, if a brand sets the MAP at $199 for a product, but a retailer lists it online for $179 in a Google ad or on their website, that’s a MAP violation. These violations can lead to penalties such as warnings, loss of distribution rights, or even legal action from the brand.
What is the minimum advertised price competition law?
MAP policies themselves are legal in many countries, including the United States, but they exist in a gray area under competition (antitrust) law. Here’s the breakdown:
- MAP policies are legal as long as they are unilateral, meaning the brand sets the terms without entering into formal price-fixing agreements with retailers.
- They aim to protect brand value and price consistency across channels, especially online.
- However, if MAP policies are used to collude or restrict competition, they could violate antitrust laws, particularly under the Sherman Act in the U.S. or EU Competition Law in Europe.
Brands must be careful to enforce MAP policies in a consistent and non-coercive manner.
Is it illegal to advertise the wrong price?
It can be, depending on the intent and context. Advertising a wrong or misleading price — especially one that is deceptively low to lure customers — can violate consumer protection laws.
In most jurisdictions:
- Honest mistakes (e.g., a pricing typo) may require correction but are not typically prosecuted.
- Intentionally misleading prices (known as “bait-and-switch” tactics) can lead to legal penalties, including fines and lawsuits.
- For businesses under MAP agreements, incorrectly advertising below the minimum price may breach contractual obligations, even if it’s not illegal per se.
So while not every pricing error is illegal, it’s a serious issue in both compliance and brand trust.
What is an example of a minimum advertised price?
Let’s say a premium headphone brand sets a MAP of $299 for one of its models. This means all authorized retailers can sell it for more, less, or exactly $299, but they cannot advertise it for less than $299 — whether it’s in an online ad, email campaign, or on their website.
Even if a retailer wants to give a secret discount in-store or at checkout, they can do that, as long as the advertised price seen by the public remains at or above $299. That’s the essence of a MAP policy: controlling how low a product’s price is publicly promoted, not how it’s sold behind the scenes.