Price sensitivity refers to the degree to which the price of a product affects consumers’ purchasing decisions. The more sensitive consumers are to price, the more likely they are to change their buying habits in response to price changes. This phenomenon is an essential aspect of pricing strategy, guiding businesses in setting prices that attract customers while maintaining profitability.
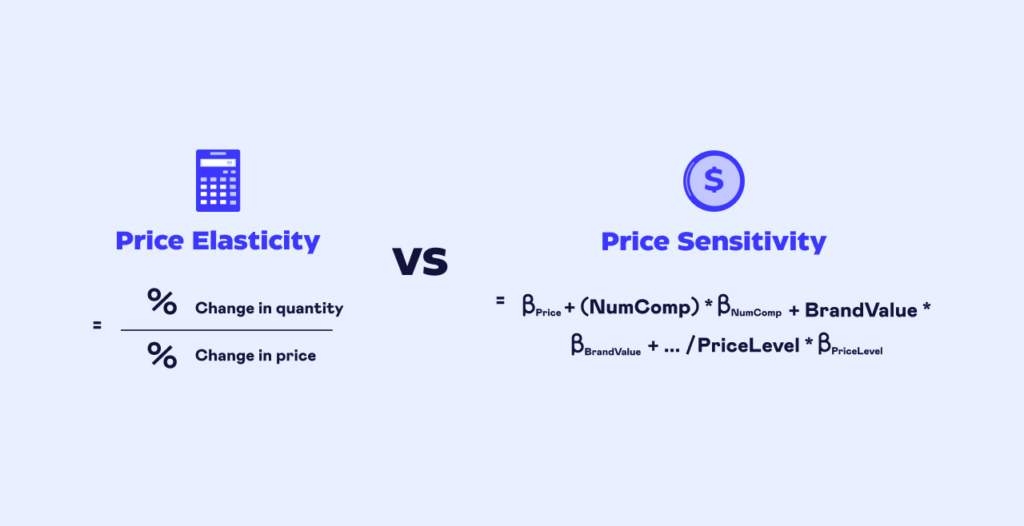
Image Source: Symson
However, adjusting prices is not a straightforward task. Companies must balance between staying competitive, preserving brand value, and avoiding product cannibalization—a situation where a new product eats into the sales of an existing one. To navigate these challenges, companies rely on sophisticated pricing strategies informed by customer behavior, product availability, and inventory management.
What is Price Sensitivity?
Price sensitivity varies across different customer segments, products, and market conditions. Several factors influence how sensitive customers are to price changes:
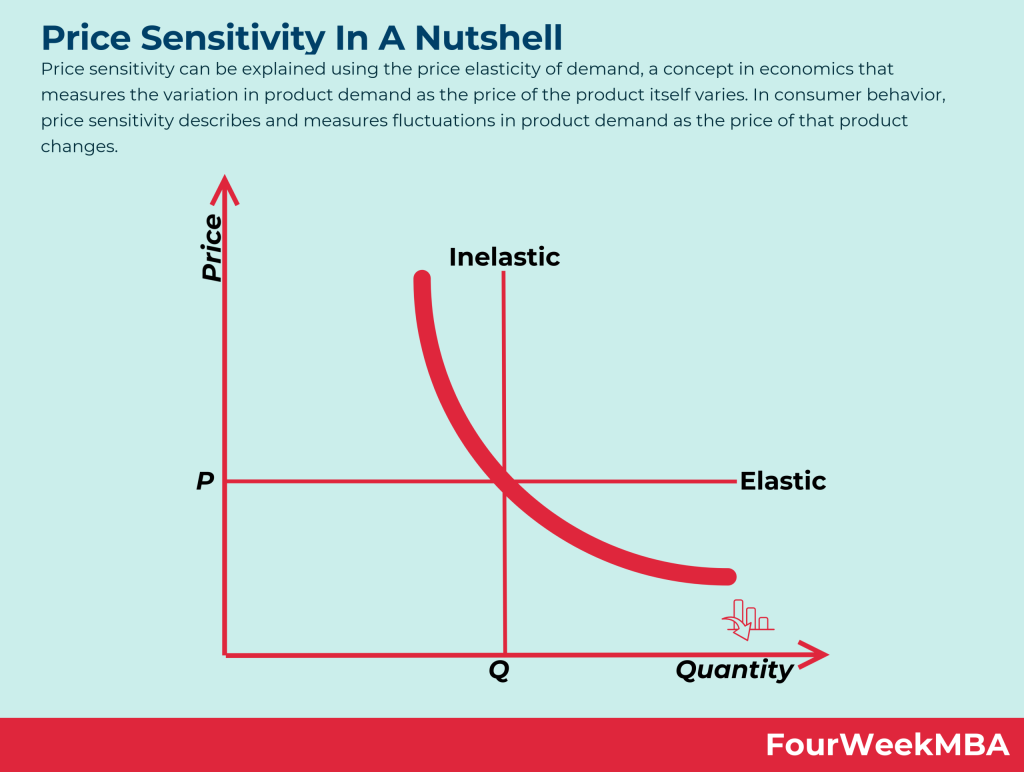
Image Source: Four Week MBA
1. Perceived Value
If customers perceive a product as unique or superior, they are often less sensitive to its price. For example, Apple’s iPhones maintain high demand despite premium pricing, due to the brand’s strong reputation for quality and innovation.
2. Substitute Products
The availability of substitute products significantly impacts price sensitivity. If a cheaper alternative offers similar benefits, customers are likely to switch, increasing price sensitivity.
3. Income Levels
Higher-income consumers tend to be less price-sensitive because price changes represent a smaller portion of their disposable income.
4. Purchase Frequency
For frequently purchased items, customers are more likely to notice and react to price changes, leading to higher price sensitivity.
How to Adjust Prices Based on Customer Behavior
Understanding these factors allows companies to adjust prices effectively. Here are some strategies businesses use to align pricing with customer behavior:

Image Source: Inflow Inventory
1. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices in real time based on market demand, competitor pricing, and other factors. This strategy is prevalent in industries like e-commerce, airlines, and hospitality, where prices fluctuate frequently. For example, Amazon uses sophisticated algorithms to adjust prices throughout the day, ensuring competitive pricing and maximizing profits.
2. Price Discrimination
Price discrimination involves charging different prices to different customer segments for the same product. This strategy is often used in services like airlines and utilities, where customers are segmented based on factors such as age, location, or purchase timing. For instance, airlines offer cheaper fares for customers who book well in advance compared to last-minute bookings.
3. Bundling and Unbundling
Companies can adjust prices by offering products in bundles or selling them separately. Bundling can reduce price sensitivity by offering perceived value, while unbundling allows customers to purchase only what they need, which can attract price-sensitive buyers.
4. Promotional Pricing
Short-term promotions and discounts can stimulate demand among price-sensitive customers. However, companies must be careful not to overuse promotions, as this can lead to customers expecting lower prices and becoming more price-sensitive in the long term.
Why Is Product Cannibalization a Major Concern for Brands?
While adjusting prices can attract more customers, it also carries the risk of cannibalizing sales of existing products. Product cannibalization occurs when a new product eats into the sales of an existing product within the same company, reducing overall profitability.
Understanding Cannibalization
Cannibalization is a natural concern when launching new products or adjusting prices. It is especially problematic when the new product is similar to existing ones in the company’s portfolio. For example, when Apple introduced the iPhone SE, a lower-cost version of its flagship phone, there was concern it might cannibalize sales of the more expensive models.
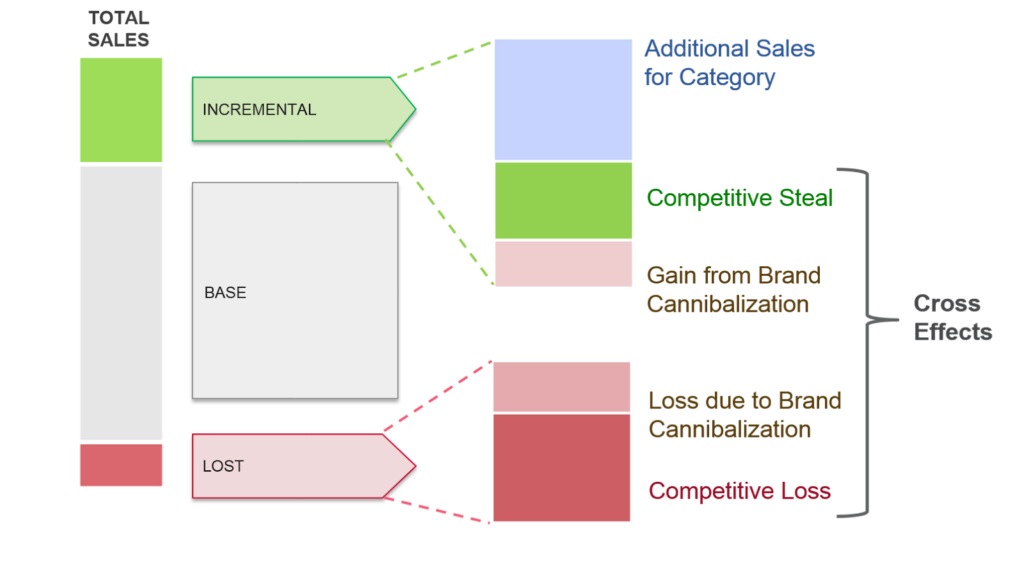
Image Source: Ashok Chakran
Cannibalization is not always negative; it can be part of a strategic decision to capture a new market segment or phase out older products. However, companies must carefully analyze the potential impact on overall sales and profitability.
How to Avoid Cannibalization
Avoiding cannibalization requires a thoughtful approach to product development and pricing strategy.

Image Source: Chisel Labs
Here are some strategies companies can employ:
1. Differentiation
Clearly differentiate new products from existing ones to target different customer segments. This could involve varying features, quality, or price points. For example, automobile manufacturers often release multiple models with distinct features and price ranges to appeal to different demographics, reducing the risk of cannibalization.
2. Tiered Pricing
Implementing a tiered pricing strategy allows companies to offer multiple products at different price points, catering to various levels of price sensitivity. This approach can prevent cannibalization by clearly positioning each product for a specific customer segment.
3. Controlled Rollout
Gradually introducing new products allows companies to monitor their impact on existing products and make adjustments if necessary. A controlled rollout can help minimize the risk of cannibalization by enabling the company to fine-tune its strategy based on early results.
4. Market Research and Testing
Before launching a new product, conducting thorough market research and testing can help identify potential cannibalization risks. Companies can use focus groups, surveys, and pilot programs to gauge customer reaction and make data-driven decisions.
Product Cannibalization Analysis
Conducting a product cannibalization analysis is essential for companies that frequently launch new products or adjust prices. This analysis involves assessing the potential impact of a new product on existing ones and determining whether the benefits outweigh the risks.
Steps in Product Cannibalization Analysis
1. Market Segmentation
Begin by segmenting the market to understand which customer groups are most likely to purchase the new product and how it overlaps with existing products.
2. Sales Forecasting
Estimate the sales of the new product and the potential decline in sales of existing products. This involves analyzing historical sales data, customer preferences, and market trends.
3. Profitability Analysis
Assess the profitability of the new product, taking into account the potential loss of sales from existing products. This includes calculating the contribution margin and overall impact on company revenue.
4. Scenario Planning
Use scenario planning to explore different outcomes based on various pricing strategies and market conditions. This helps in understanding the potential risks and benefits of introducing the new product.
5. Monitor and Adjust
After launching the product, continuously monitor sales data to identify any signs of cannibalization. If cannibalization occurs, be prepared to adjust pricing, marketing, or product positioning to mitigate its impact.
The Role of Product Availability and Inventory Management
Price sensitivity and product cannibalization are closely linked to product availability and inventory management. Effective inventory management ensures that the right products are available at the right time, which is crucial for minimizing lost sales due to stockouts or overstock situations.
1. Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is essential for aligning inventory levels with expected sales, particularly when adjusting prices. For instance, if a company plans to lower prices to attract more price-sensitive customers, it must ensure sufficient inventory to meet the anticipated increase in demand.
2. Inventory Optimization
Companies must optimize their inventory levels to balance the cost of holding stock against the risk of stockouts. Techniques such as just-in-time inventory, safety stock calculations, and automated reordering systems can help maintain optimal inventory levels.
3. Product Lifecycle Management
Understanding the lifecycle of products helps in managing inventory effectively. For example, as a product nears the end of its lifecycle, companies might reduce prices to clear inventory, while also being cautious of cannibalization risks.
Conclusion
Price sensitivity is a critical factor in determining the success of a product in the market. By understanding customer behavior and adjusting prices accordingly, companies can optimize their pricing strategies to attract and retain customers. However, the process is complex and requires careful consideration of factors such as product cannibalization, product availability, and inventory management.
By employing strategies to avoid cannibalization, conducting thorough product cannibalization analysis, and ensuring effective inventory management, companies can navigate the challenges of price sensitivity.
Ready to optimize your pricing strategy and master price sensitivity? Schedule a demo today to discover how our advanced analytics can help you avoid product cannibalization, manage inventory effectively, and boost your market success.







