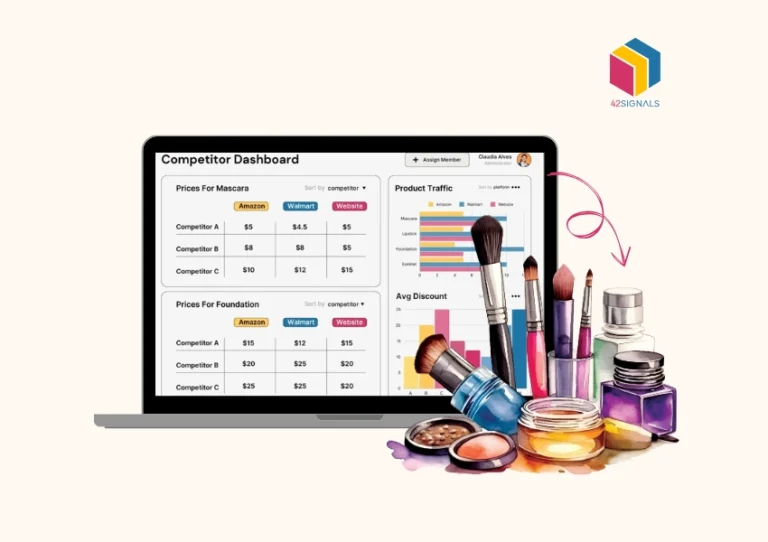
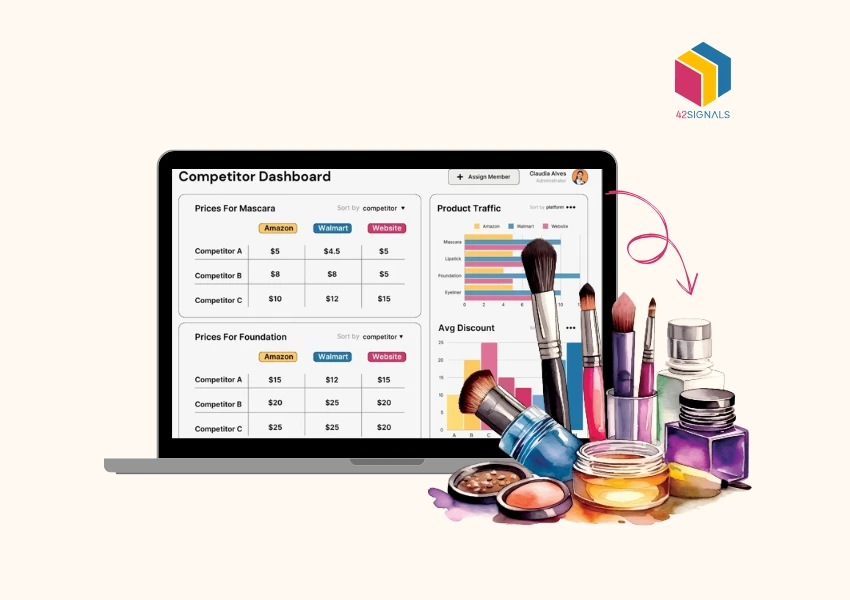
Introduction to GTM
Tailoring GTM strategies to align with specific consumer groups has become paramount in retail. Customization in product offerings, marketing, and customer experience enables retailers to connect more effectively with their target audiences.
Personalizing Go-to-Market aka GTM retail strategies involves understanding the unique preferences, behaviors, and needs of distinct consumer segments, and crafting tailored approaches to engagement and conversion.
Adapting initiatives for varied demographic, psychographic, and geographic profiles, this strategic angle seeks to heighten relevance and drive sustained retail success.
Identify and Define Consumer Segments
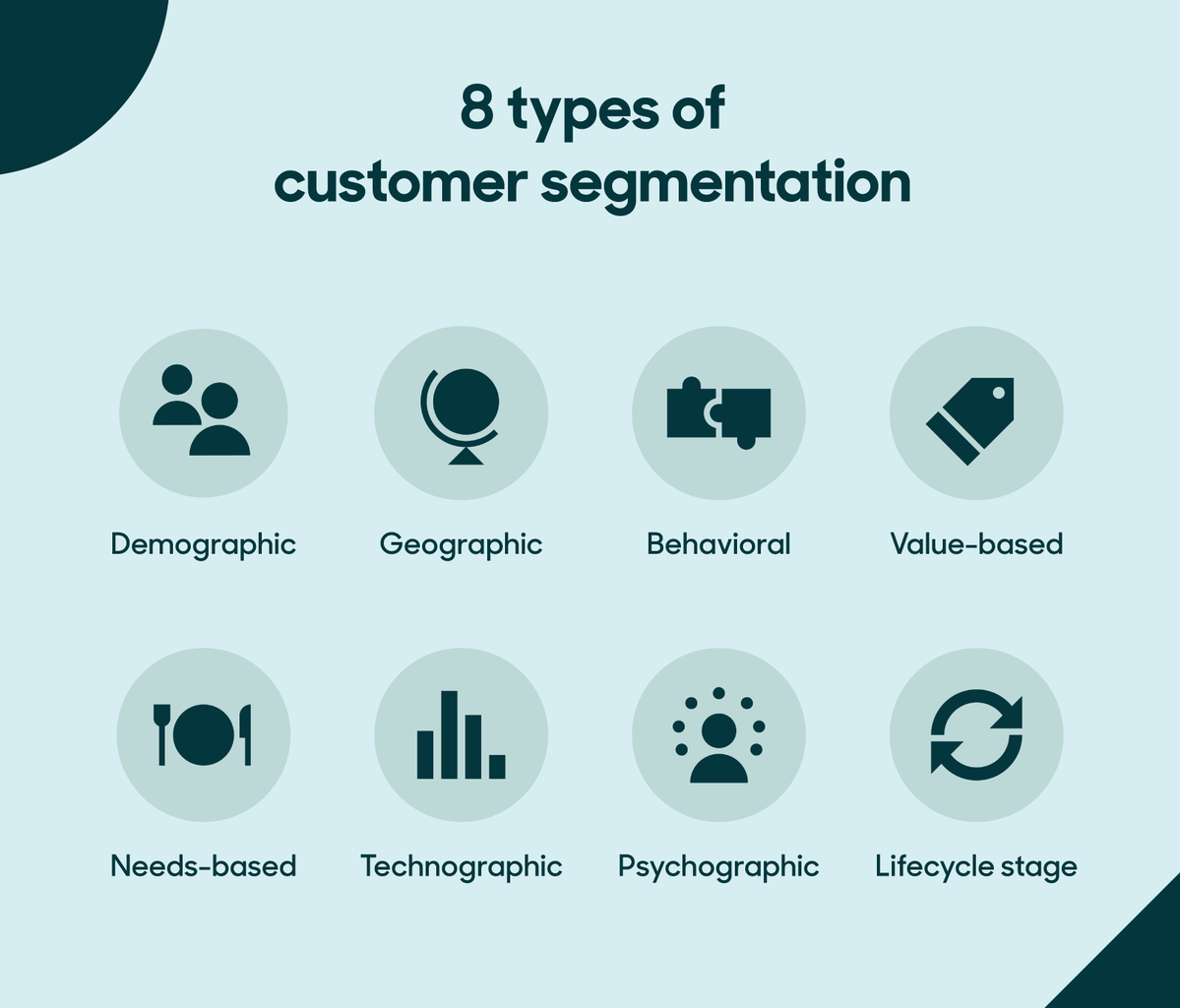
Image Source: Customer segmentation: Guide to types, tips, and strategy
In personalizing GTM retail strategies, understanding and defining consumer segments is crucial. To start with, retailers gather information related to customers’ demographics, psyche, and behaviors. Specifically, they consider aspects such as age, gender, earnings, and educational background in their demographic analysis.
Moreover, retailers examine individuals’ way of life, principles, and hobbies through psychographic profiling. Behavioral aspects consider purchase history, product usage, and brand interactions.
- Demographics: Who the customers are
- Psychographics: Why they buy
- Behavior: How they engage
Through segmentation, retailers can customize their strategies, making their marketing initiatives more applicable and productive. By distinguishing separate clusters, retailers are able to create focused promotional campaigns that align with the unique requirements, tastes, and behaviors of each group.
Develop Unique Value Propositions for Each Segment | GTM Strategy
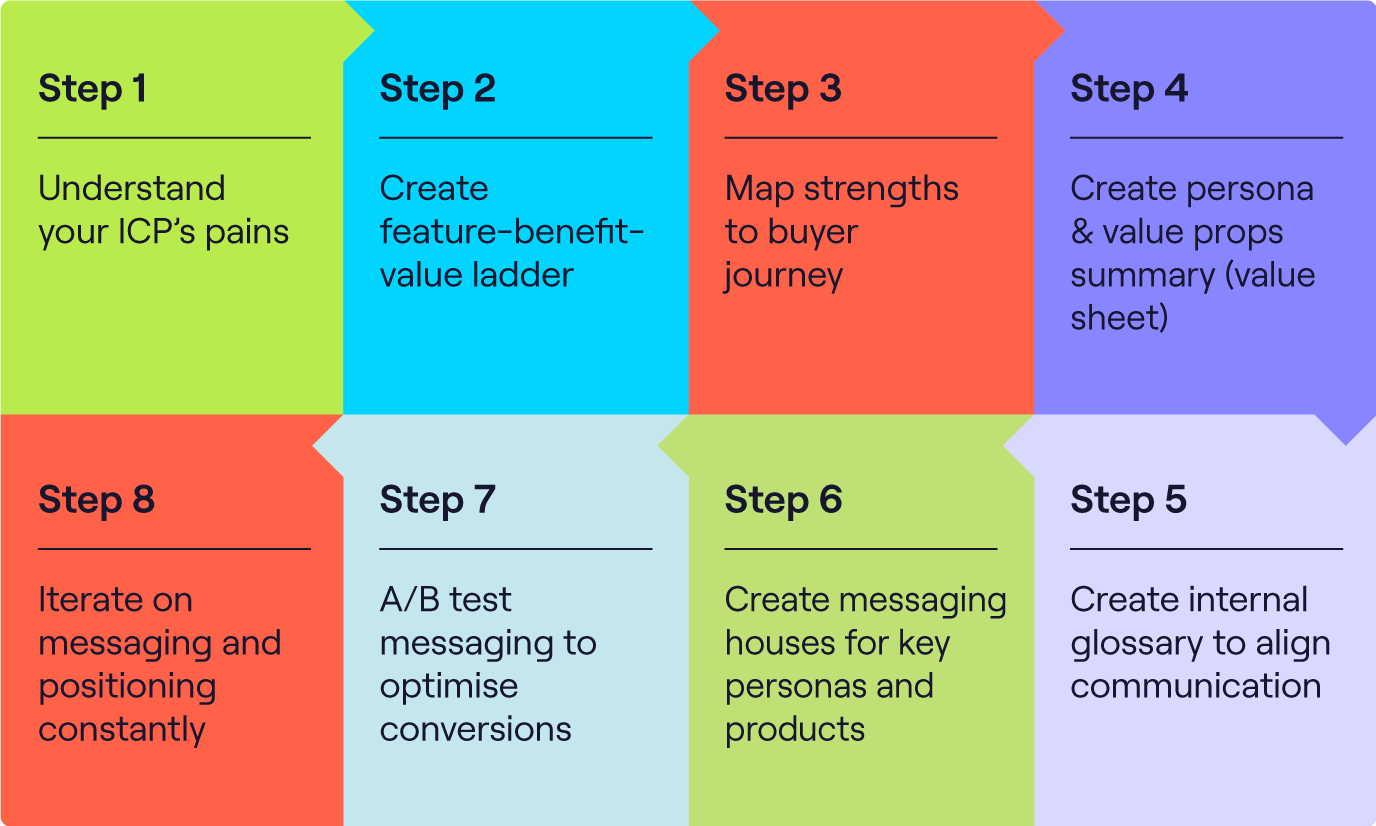
Image Source: What is a Go-to-Market Strategy? Guide for Enterprises
A successful personalization of a GTM retail strategy requires businesses to create customized value offerings that appeal to particular consumer categories. By designing targeted communication that emphasizes the advantages of a product or service for individual clusters, companies can greatly improve their relationship and loyalty among customers. This process involves:
- Identifying Consumer Needs: Understanding the unique needs and desires of each target segment is crucial for creating a compelling value proposition.
- Customization of Benefits: Align the product’s features with the identified needs to showcase direct benefits to the consumer segment.
- Communicative Clarity: Ensure that the value proposition is communicated clearly, avoiding any potential confusion or misinterpretation.
- Differentiation from Competitors: Highlight what sets the product apart, vital for segments surrounded by competing choices.
- Consistent Reinforcement: Reinforce the value proposition at every customer touchpoint to build a strong, recognisable brand association within each segment.
Customized Pricing Strategies

Image Source: Everything you need to know about pricing strategy | Upmetrics
To effectively personalize their GTM strategies, retailers ought to make use of data in order to create tailored pricing models. Through the analysis of particular customer groups’ purchasing habits and price sensitivity, companies can modify retail pricing strategies that will have a more personal impact. For example:
- Tiered Pricing: Creates a sense of exclusivity and caters to different spending thresholds.
- Dynamic Pricing: Adjusts prices in real-time based on demand, inventory, and customer profiles.
- Promotional Bundling: Offers value to customers seeking a deal by grouping related products at a reduced price.
- Geographic Pricing: Tailors prices according to regional economic factors and competitive landscapes.
These tactics can help retailers target consumer groups more effectively, maximizing profits while maintaining customer satisfaction.
Select Appropriate Marketing Channels per Segment
It is essential to identify and make use of appropriate marketing channels in order to successfully customize your GTM retail strategies. Here’s how to align channels with targeted consumer segments:
- For young, tech-savvy audiences, prioritize digital channels like social media, email marketing, and influencer partnerships.
- With professionals, leverage LinkedIn for networking and tailored content, and use email for direct communication.
- For value-driven shoppers, coupon sites, discount apps, and email campaigns highlighting promotions can be highly effective.
- The family-oriented segment often responds well to community event sponsorships, local advertising, and family-friendly content on social platforms.
- For luxury buyers, high-end publications and exclusive event invitations through personal concierge services can build a strong connection.
When retailers match their marketing channels to fit customers’ preferences, they are able to interact more successfully with different customer groups.
Omnichannel Integration
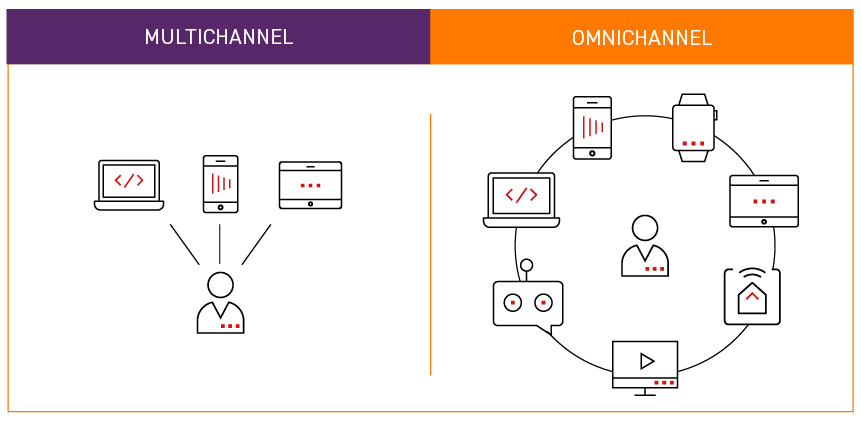
Image Source: Behind the Scenes of Omnichannel Integration
Developing effective personalized Go-To-Market (GTM) retail strategies requires the integration of omnichannel strategies as a key component. This involves gathering data from all possible consumer interaction points, be it online or offline platforms. The gathered data enables retailers to recognize and comprehend customer behavioral tendencies, inclinations, and buying practices across diverse channels.
Providing a uniform brand encounter, regardless of whether the client is shopping in-store, via a mobile application, or on a desktop site, is crucial. With such an approach, particular consumer segments get customized marketing content and merchandise suggestions, thereby enhancing involvement and boosting sales. A smooth combination of several channels empowers retailers to construct a harmonious and specialized shopping adventure for each distinct customer.
Metrics and Analysis
To successfully customize go-to-market (GTM) approaches, retailers need to examine data-based measurements that provide insights into customer behaviors. Critical measures of success (KPIs) may consist of the following:
- Consumer Demographics: Age, location, income levels.
- Purchase Patterns: Frequency, average spend, category preferences.
- Channel Effectiveness: Conversion rates of different sales channels.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Projected revenue a customer will generate.
- Engagement Metrics: Time spent on website, email open rates, social media interactions.
By utilizing sophisticated analytical techniques like predictive modeling, retailers can forecast upcoming trends and consumer preferences. Periodically examining these analytics enables businesses to customize their products and promotional content for particular consumer groups, resulting in greater pertinence and improved customer interactions.
Anticipating and Planning for Market Changes
In tailoring Go-To-Market (GTM) retail strategies for specific consumer groups, retailers must proactively anticipate and adjust to market changes. This involves:
- Continuous Market Research: Keeping abreast of trends, interests, and economic shifts that influence consumer behavior.
- Adaptive GTM Frameworks: Flexibility in strategies allows quick responses to unanticipated market developments.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing data to predict future consumer needs and preferences to stay ahead of the curve.
- Collaborative Planning: Engaging with suppliers and partners to ensure the supply chain can adapt to market dynamics.
- Contingency Plans: Having backup plans to mitigate risks from sudden market upheavals.
Through the incorporation of these methods, retailers can more adeptly adapt to fluctuations in the market, thereby maintaining applicable and successful go-to-market (GTM) approaches.
Conclusion | Leveling-Up Your GTM Strategy
A successful GTM retail strategy relies on incorporating customized and flexible solutions based on customer segment data.
It’s essential to invest in advanced technologies that support real-time analytics and focused marketing campaigns. Cross-departmental collaboration contributes to consistent messaging, which boosts customer interaction and loyalty.