Half of the retail executives, according to Deloitte, predict that consumers will place greater emphasis on price than brand loyalty by 2024, highlighting a significant change in buyer behavior. Given this transformation, price parity has become a key aspect affecting customers’ judgment and choices. On one hand, consistent pricing throughout all sales channels bolsters customer trust, simplifies pricing methods, and strengthens brand identity.
On the other hand, rigid implementation of price parity introduces possible downsides, such as decreased pricing versatility and tighter profit margins for retailers. Navigating a balanced connection between price consistency and refined pricing analytics is imperative for companies seeking growth in the expanding, cutthroat digital commerce sector.
This article aims to examine the idea of price parity, its relevance to online retailers, and efficient techniques to manage the interplay between price uniformity and adaptable pricing tactics.
Price Parity in Retail
Retail price parity entails establishing unified pricing for products across diverse sales channels, meaning identical prices apply regardless of whether goods are purchased online, in physical stores, or via third-party platforms. The benefits include:
- Maintaining brand integrity by avoiding customer confusion over varying prices
- Simplifying pricing strategies and inventory management for retailers
- Encouraging customer loyalty through transparent and consistent pricing
However, such a strategy may also limit a retailer’s ability to:
- Engage in competitive pricing strategies that could target specific markets or demographics
- Implement dynamic pricing based on specific sales channels’ demand and supply conditions
- Tailor promotions and discounts to different retail environments securing strategic advantages
Therefore, while price parity promotes fairness, it may reduce a retailer’s flexibility in pricing tactics.
Price Parity and Its Importance for Online Retailers
Uniform pricing, frequently referred to as price parity, holds great importance for online retailers. Essentially, this practice entails establishing identical prices for items across multiple platforms, ranging from a retailer’s own site to popular marketplaces such as Amazon and eBay.
By doing so, retailers prevent customers from encountering conflicting prices during their shopping experience across diverse sales channels.
Moreover, price parity helps in upholding the value of products, preventing the devaluation that might result from inconsistent pricing strategies.
The Benefits of Price Parity
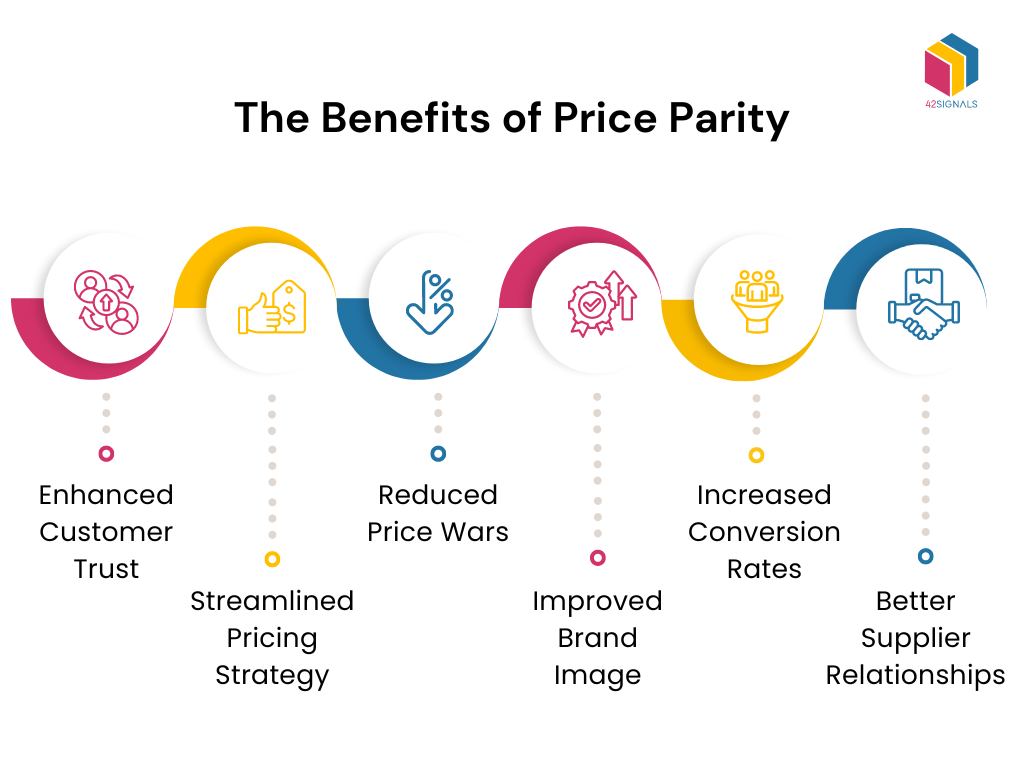
• Enhanced Customer Trust
Price parity assures customers they’re getting the best deal across all channels, building trust and loyalty towards the ecommerce platform.
• Streamlined Pricing Strategy
Maintaining consistent pricing simplifies the pricing strategy for sellers, preventing pricing conflicts and confusion among consumers.
• Reduced Price Wars
Ensures a level playing field among sellers, preventing undercutting that can lead to destructive price wars and reduced profit margins.
• Improved Brand Image
Price consistency enhances the brand’s reputation by upholding values of fairness and equality in the marketplace.
• Increased Conversion Rates
A consistent pricing approach can lead to higher conversion rates as consumers are less likely to abandon their carts in search of better deals.
• Better Supplier Relationships
Vendors appreciate consistent pricing as it protects their brand value and helps maintain a stable market for their products.
The Drawbacks of Maintaining Price Parity

• Limited Pricing Flexibility
Price parity agreements restrict businesses from adjusting prices based on changing market conditions or implementing dynamic pricing strategies.
• Reduced Competitive Edge
With uniform pricing, retailers lose the ability to stand out by offering lower prices online, which could attract price-sensitive customers.
• Potential Legal Issues
Price parity clauses can sometimes conflict with antitrust or competition laws, potentially exposing businesses to legal risks.
• Consumer Dissatisfaction
Customers might feel discontent if they discover the same product is priced identically across all platforms, negating the benefits of shopping around.
• Smaller Margins for Retailers
Strict price parity can squeeze retailer margins, particularly if they need to absorb higher costs of selling online, such as shipping and handling.
Strategies for Ecommerce Sites to Balance Price Parity
Ecommerce sites must leverage retail pricing analytics to maintain price parity while staying competitive. They can employ several strategies:
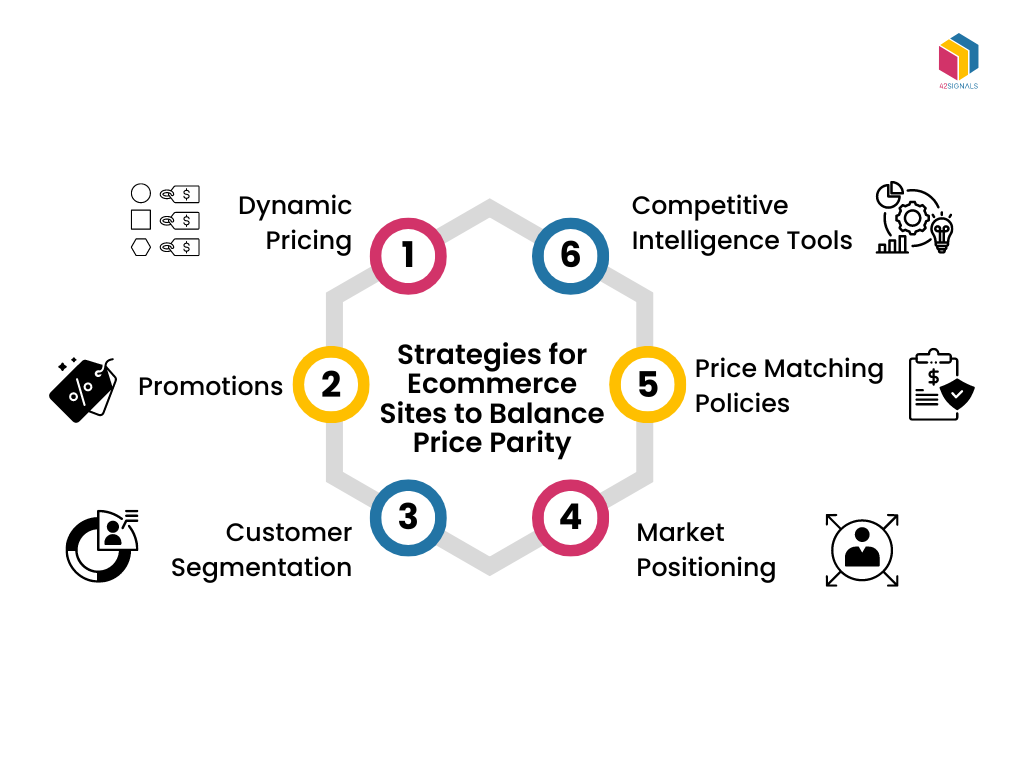
• Dynamic Pricing
Implement algorithms that adjust prices in real-time based on market conditions and competitor pricing.
• Promotions
Offer exclusive online discounts or bundled products to provide value without directly undercutting in-store prices.
• Customer Segmentation
Analyze customer data to offer personalized pricing, targeting different customer segments with strategic discounts.
• Market Positioning
Position products uniquely online, justifying any price differences with added value or exclusive features.
• Price Matching Policies
Adopt policies that reassure customers they are getting the best price, whether they shop online or in-store.
• Competitive Intelligence Tools
Use software solutions to monitor competitor pricing and ensure alignment with market trends without breaching parity agreements.
Conclusion
Navigating the ever-changing ecommerce environment requires careful attention to price parity maintenance, presenting both prospects and difficulties for businesses. To keep pace with competitors and sustain a cutting edge, continuous surveillance of competitor pricing and market patterns is imperative.
Technological advancements empower merchants with refined instruments for instantaneous pricing modifications; nevertheless, the threat of price disputes persists, posing a risk to profitability.
Building consumer trust relies heavily upon consistent pricing practices, especially considering the increasing overlap between physical and virtual shopping experiences. Embracing these complexities demands nimbleness and forward-thinking, propelling companies toward triumph in a competitive industry driven by price openness and clarity.
FAQs
What is parity pricing?
Parity pricing denotes a pricing technique wherein the price of an item or service corresponds to its production expenses, unbiased by competitor quotations. Its objective is to guarantee sustainability and ongoing profitability, irrespective of shifts in demand or rivalry. Contrasting with competitive pricing tactics, parity pricing aims to uphold financial stability whilst maintaining affordable and appealing offers.
What are price parities?
Price parities signify diverse pricing contrasts amongst alternative commodities, services, or venues. Comparative analyses occur frequently—for instance, examining hotel room tariffs inside one urban area or evaluating flight fares along specific travel routes. Awareness of price parities empowers customers during decision-making and assists enterprises in strategic planning, tailoring offerings suitably, and responding effectively to shifting market trends.
How do you calculate parity price?
To determine the parity price, first ascertain complete production expenditures before calculating the average expense per unit through division. Subsequently, apply a predetermined profit margin percentage to derive the ultimate selling price. Assuming an average expense per unit of $50 and pursuing a 20% net revenue, adding $10 results in a retail price of $60 per unit. Regularly revisit these computations due to evolving circumstances involving inflation, fluctuating material expenses, and alterations in supply-demand balances.
What is the market parity price?
Market parity price indicates the balanced juncture when all stakeholders involved consent upon a fair product or service worth in a distinct marketplace. Buyer expectations align with seller provisions, enabling optimal utilization of resources devoid of substantial disruptions to supply-demand ratios. Dynamic negotiations between transacting parties formulate market parity prices via continuous response towards ever-changing contextual variables. Economic theories strive to anticipate market parity prices but encounter challenges owing to intricate, real-life factors impacting actual trading scenarios.