In the realm of retail, pricing stands as a pivotal factor influencing a product’s market success. A widely embraced pricing strategy is the Minimum Advertised Price (MAP). This guide aims to furnish you with a comprehensive understanding of Minimum Advertised pricing—its definition, advantages, challenges, and effective implementation and enforcement strategies.
What is MAP Pricing?
MAP pricing is a policy instituted by manufacturers or brand owners that delineates the minimum advertised price for their products by retailers. Notably, Minimum Advertised pricing concentrates on the advertised price rather than the actual selling price. Retailers possess the freedom to sell the product at any price, provided it aligns with or exceeds the predetermined MAP price.
The primary aim of minimum advertised price violation pricing is to uphold price uniformity and safeguard the brand’s perceived value. By preventing the advertisement of products below the established MAP, this strategy mitigates the risk of price erosion and excessive competition among retailers. The result is a fair and equitable marketplace for all sellers.
The Benefits of MAP Pricing
Implementing a pricing strategy offers several benefits for both manufacturers and retailers. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:

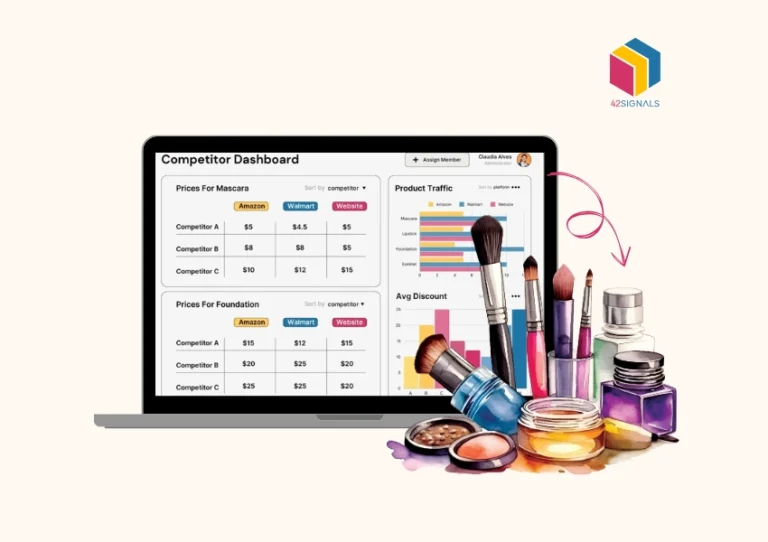
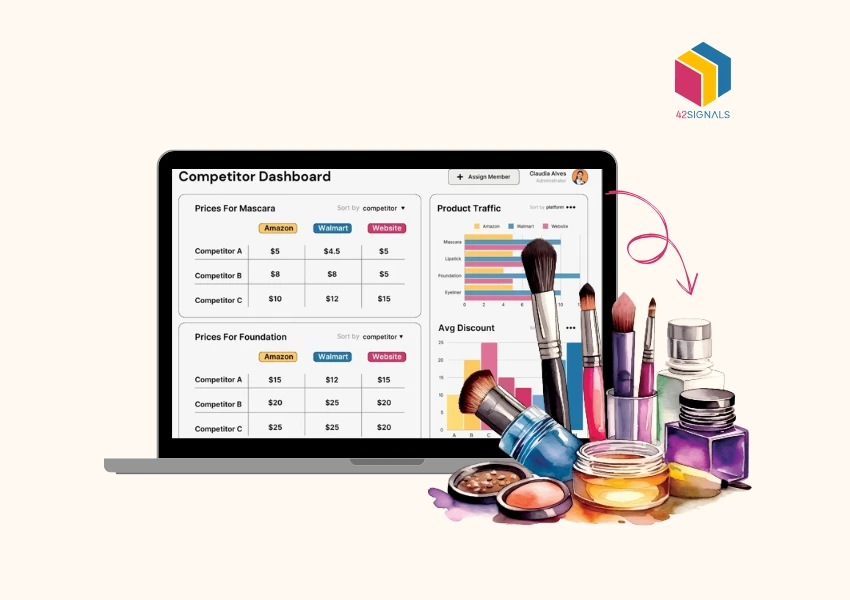
Image Source: Metrics Cart
Price Stability
Minimum Advertised pricing ensures that all retailers are advertising the product at a consistent price. This stability helps to avoid price competition, protecting the brand’s image and perceived value.
Brand Protection
Minimum Advertised pricing safeguards the integrity and value of the brand. By establishing a minimum price, brand owners can maintain control over how their products are perceived in the market.
Fair Competition
MAP pricing creates a fair and level playing field for all retailers. It prevents a situation where some retailers engage in aggressive price cutting to the detriment of others, ensuring healthy competition within the market.
Margin Protection in Understanding What is MAP Pricing
Minimum Advertised pricing helps to protect retailers’ profit margins. By setting a minimum advertised price, retailers can avoid selling products at incredibly low prices, allowing them to maintain profitability.
The Challenges of Establishing MAP Policy
While Minimum Advertised pricing offers significant advantages, it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the challenges include:
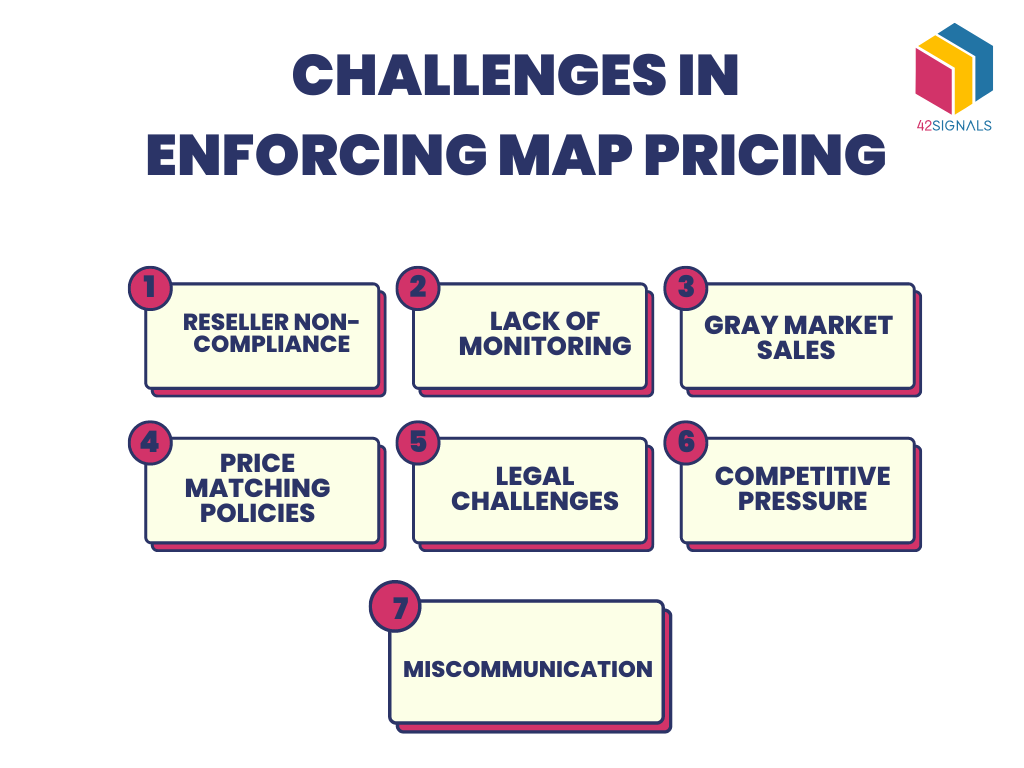
Enforcement Difficulties
Ensuring compliance with Minimum Advertised pricing policies can be challenging, particularly when dealing with a large number of retailers spread across different regions.
Price Monitoring
Constantly monitoring prices across various online and offline platforms can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, making it difficult to promptly identify price violators.
Reseller Resistance
Some retailers may resist implementing Minimum Advertised pricing policies, as they believe it restricts their ability to set competitive prices and attract customers.
Channel Conflict
Implementing a MAP pricing policy can create tension between manufacturers and retailers, especially if some retailers choose not to comply.
Factors Influencing MAP Policy
Several factors influence the determination of minimum advertised prices. These factors may vary depending on the industry, product type, and brand positioning. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Brand Positioning: Companies with premium brands may set a higher MAP price to maintain a perception of exclusivity and quality.
- Product Differentiation: Products with unique features or innovations may command a higher MAP price to reflect their value proposition.
- Competitor Pricing: Monitoring competitors’ pricing strategies is crucial when determining Minimum Advertised pricing. It helps ensure that the MAP price remains both competitive and profitable.
- Market Demand: Understanding consumer demand and willingness to pay for the product is vital in determining an optimal MAP price.
Implementing Pricing Strategies
To implement a successful Minimum Advertised pricing strategy, consider the following steps:
- Establish Clear Policies: Clearly outline your MAP policies and communicate them to all retailers. Ensure that all parties understand the consequences of non-compliance.
- Secure Retailer Agreement: Obtain a written agreement from each retailer to adhere to the MAP policy. This agreement should include consequences for violators.
- Educate Retailers: Provide training and educational materials to retailers to help them understand the benefits and importance of minimum advertised prices.
- Regular Price Monitoring: Regularly monitor prices across various channels to identify any violations or pricing discrepancies.
- Provide Incentives: Consider offering incentives or rewards to retailers who consistently comply with your MAP policy.
Monitoring MAP Violations

Image Source: Intelligence Node
To effectively monitor MAP violations, consider these strategies:
- Automated Price Monitoring Tools: Utilize automated tools that can continuously track prices across multiple platforms, allowing for immediate identification of violations.
- Mystery Shopping: Conduct periodic mystery shopping exercises to assess whether retailers are adhering to the Minimum Advertised policy.
- Online Brand Protection Services: Engage third-party services that specialize in monitoring and enforcing MAP pricing policies across various online marketplaces.
Dealing with MAP Violators
Handling MAP violators requires a systematic approach. Here are some steps to follow:
- Document Violations: Maintain a record of all instances where violations occur, including screenshots, emails, or any other evidence.
- Contact the Violator: Reach out to the violator, informing them of their non-compliance, and provide an opportunity to rectify the situation.
- Take Appropriate Action: If the violator fails to rectify the violation or repeats offenses, impose the agreed-upon consequences as outlined in the retailer agreement.
Conclusion, What is MAP Pricing?
MAP pricing is a powerful tool that ensures consistency and fair competition in the retail industry. By setting a minimum advertised price, manufacturers and brand owners can protect their brand value and provide a level playing field for retailers.
While implementing and enforcing Minimum Advertised pricing policies may present challenges, the benefits outweigh the difficulties. With tools like 42Signals, it’s easier than ever to track violations and take the right action at the right time.
To know more about our solution, visit our pricing page or schedule a demo.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is MAP vs MSRP?
MAP (Minimum Advertised Price) is the lowest price that a retailer is allowed to publicly advertise for a product, as determined by the manufacturer. It’s a guideline aimed at maintaining fair competition among retailers and ensuring the product’s perceived value is not undermined by extreme discounts.
MSRP (Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price), on the other hand, is the price at which the manufacturer recommends that retailers sell the product. While retailers can sell products below the MSRP, they must adhere to the MAP when advertising prices.
Is MAP pricing illegal?
No, MAP pricing is not illegal. Manufacturers are allowed to set guidelines for how their products are advertised, including minimum prices. However, MAP agreements cannot dictate the price at which a product is sold, only the advertised price. This practice is legal in many countries, including the United States, but it’s important to comply with antitrust laws to avoid any appearance of price-fixing or coercion.
Who sets MAP pricing?
Manufacturers set MAP pricing as part of their distribution agreements with retailers. It is a way for manufacturers to protect the perceived value of their brand and ensure consistency across various sales channels. Retailers who agree to sell the manufacturer’s products must also agree to adhere to MAP guidelines when advertising the products.