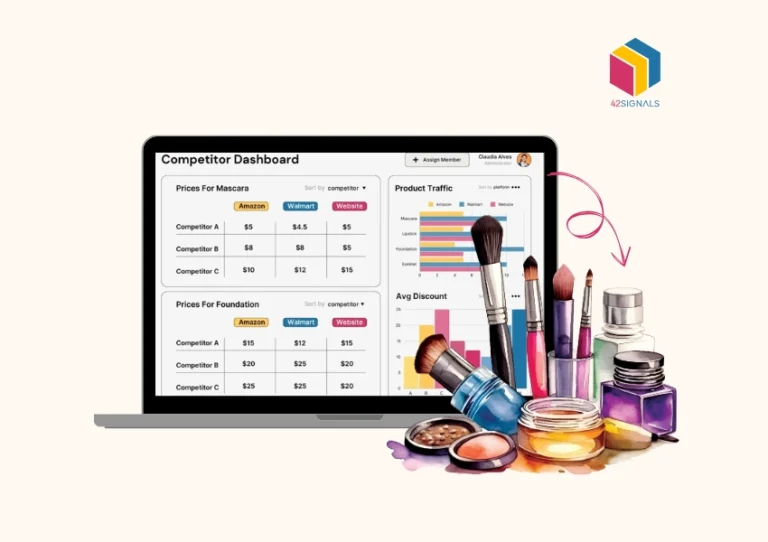
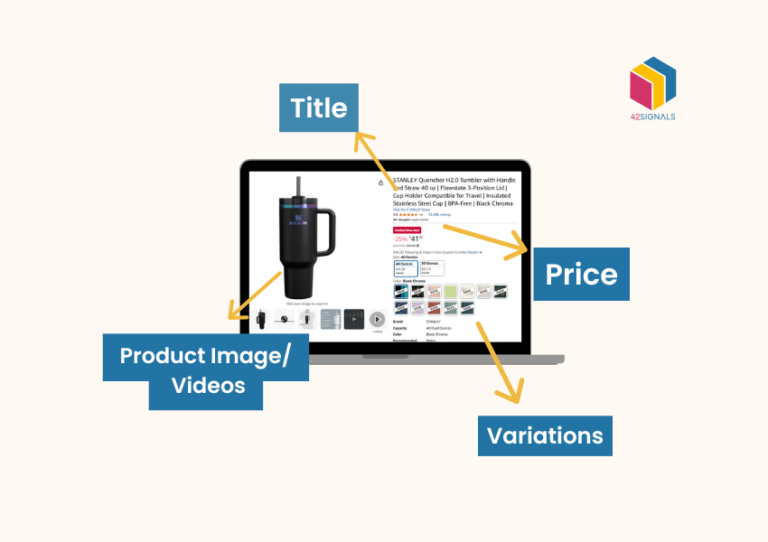
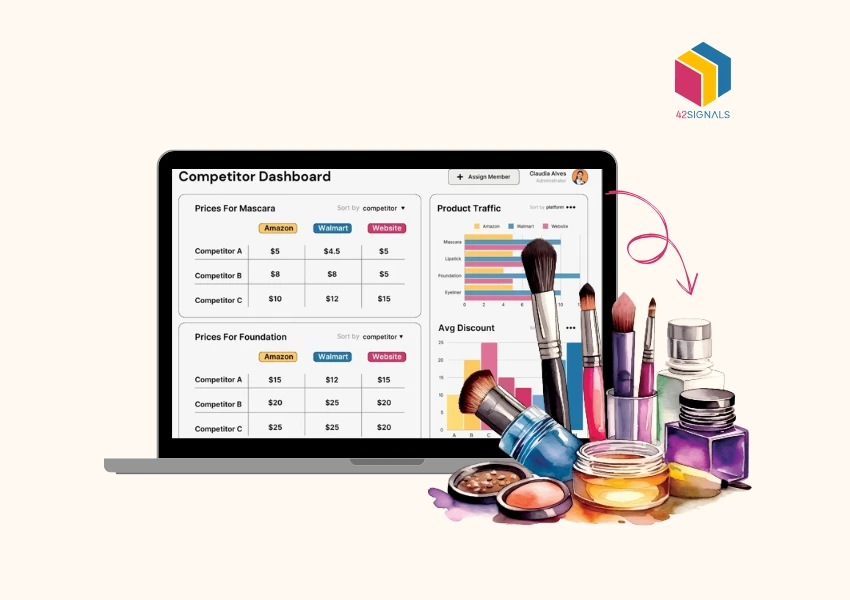
The Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policy essentially sets the lowest price that retailers can promote for a product, a benchmark determined by brands or manufacturers. This measure is put in place to ensure a level playing field among authorized retailers.
To illustrate, envision a brand establishing a MAP of $100 for a highly sought-after pair of sneakers. No authorized retailer can publicly promote them below that price, whether in online listings, flyers, or social media posts. Importantly, while retailers can sell below MAP in-store, advertising such discounts is a violation.
What are MAP Violations?
Imagine a “no-sell-below” price tag set by a brand. When a store advertises below that price, it’s a MAP violation. Sometimes, mistakes like computer glitches or confusion cause this. But other times, stores go lower on purpose to win customers, leading to price wars and hurting the brand’s image. Following the rules (MAP policy) helps everyone play fair and keeps things healthy in the market.
Here’s a video that explains what MAP Policies are:
Here are some common types of MAP violations:
- Online listings: Advertising below MAP on e-commerce platforms or marketplace websites.
- Flyers and brochures: Distributing physical marketing materials offering products below the minimum price.
- Social media promotions: Advertising discounted prices on social media channels.
- Bundling and price stacking: Combining products with the targeted product to effectively offer it below MAP.

Image Source: Metrics Cart
Challenges in Enforcing MAP Policies
MAP enforcement presents several challenges:
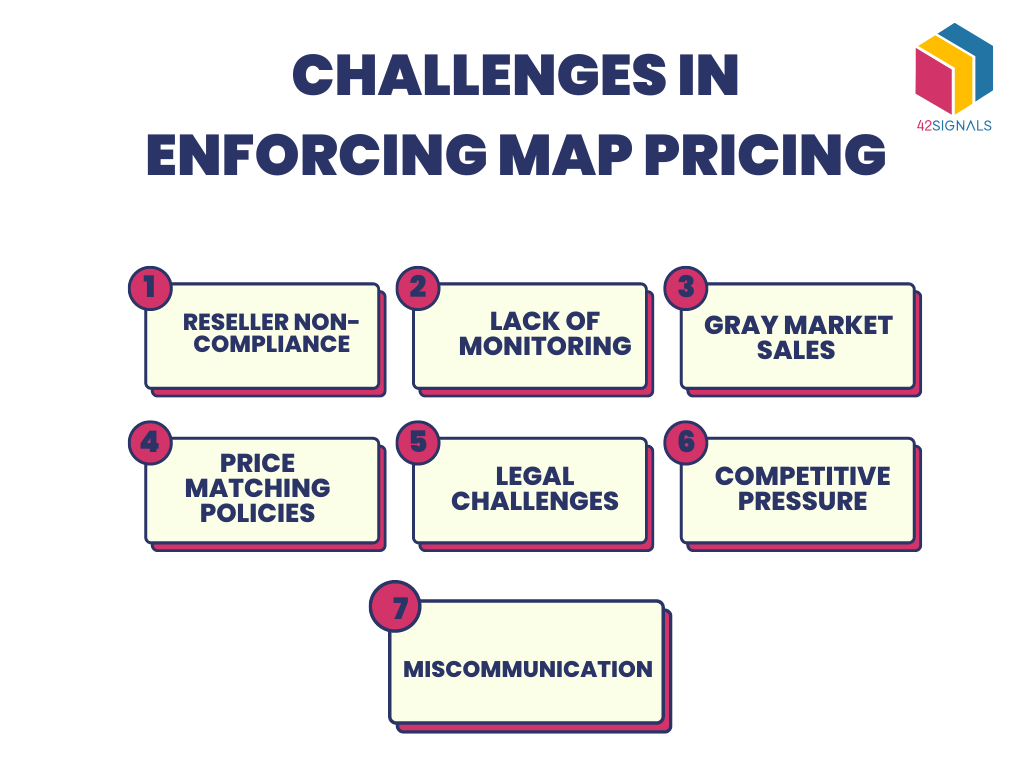
Image Source: How to Enforce MAP Pricing: Best Practices and Strategies
Complexity and ambiguity
MAP policies can be complex and open to interpretation, leading to confusion and unintentional violations.
Monitoring challenges
Effectively monitoring online and offline advertising across all retailers can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Enforcement disparities
Consistent enforcement across all retailers is crucial, but varying degrees of commitment and capabilities can create loopholes.
Legal constraints
Legal restrictions concerning price fixing and competition laws can limit the scope and severity of enforcement actions.
Strategies for Addressing MAP Violations
Despite these challenges, several strategies can be employed to address MAP violations effectively:
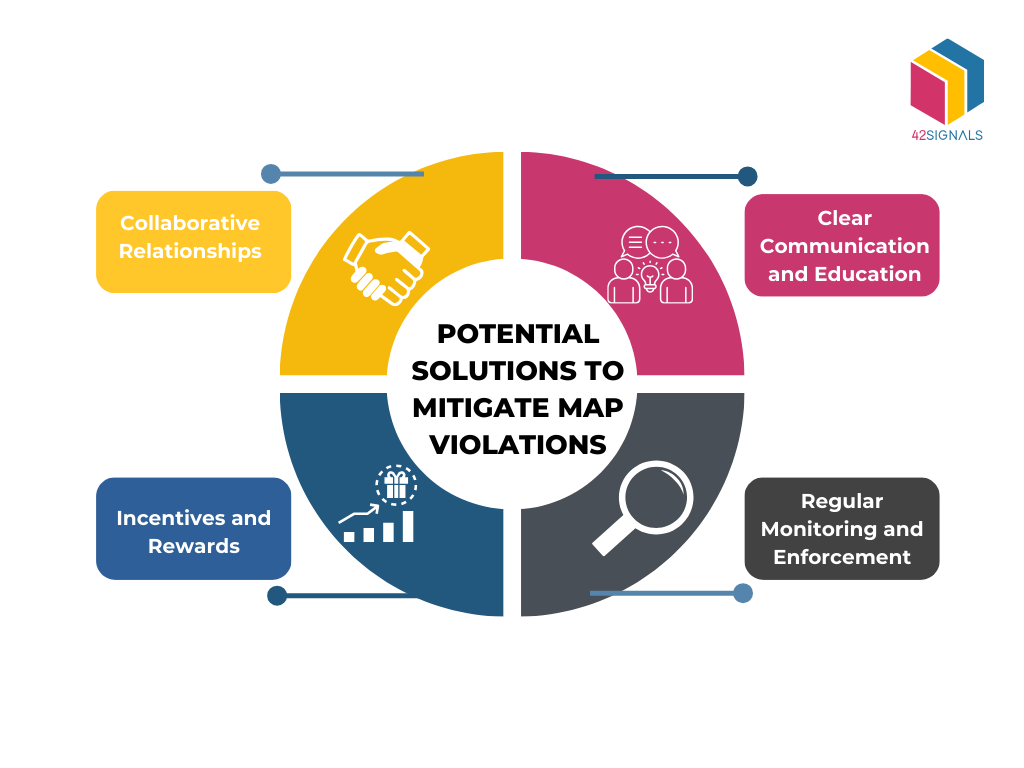
Image Source: The Impact of MAP Violations on Retailer-Brand Relationships: Risks and Solutions
Clear and concise policies
Develop well-defined, easily understandable MAP policies that clearly state the rules and potential consequences.
Regular communication
Communicate the MAP policy effectively to all authorized retailers, including regular updates and training materials.
Monitoring and detection
Utilize appropriate tools and processes to actively monitor online and offline advertising channels for potential violations.
Graduated enforcement
Implement a tiered approach to enforcement, starting with warnings and educational resources before escalating to more severe measures.
Legal guidance
Seek legal counsel to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations related to MAP policy enforcement.
Collaboration and industry action
Collaborate with other manufacturers and industry organizations to promote consistent MAP enforcement practices.
Conclusion
MAP policies represent a valuable asset for brands and manufacturers aiming to uphold price uniformity and brand identity. Nonetheless, grappling with MAP violations and ensuring robust policy enforcement poses distinctive hurdles. Through grasping these obstacles and deploying holistic approaches, brands can manage violations equitably and consistently, fostering a more regulated and enduring online retail landscape.