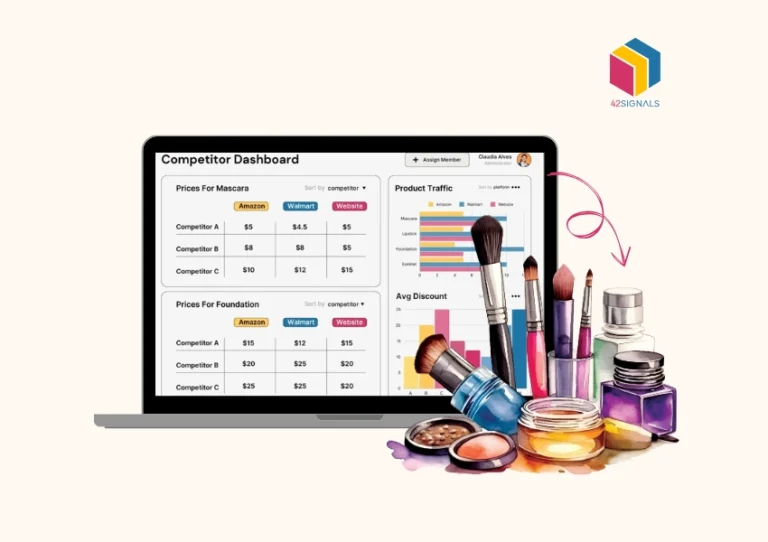
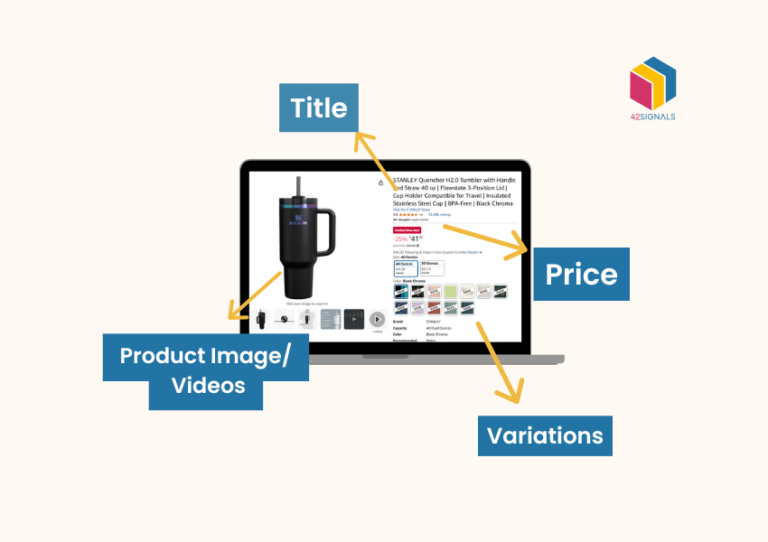
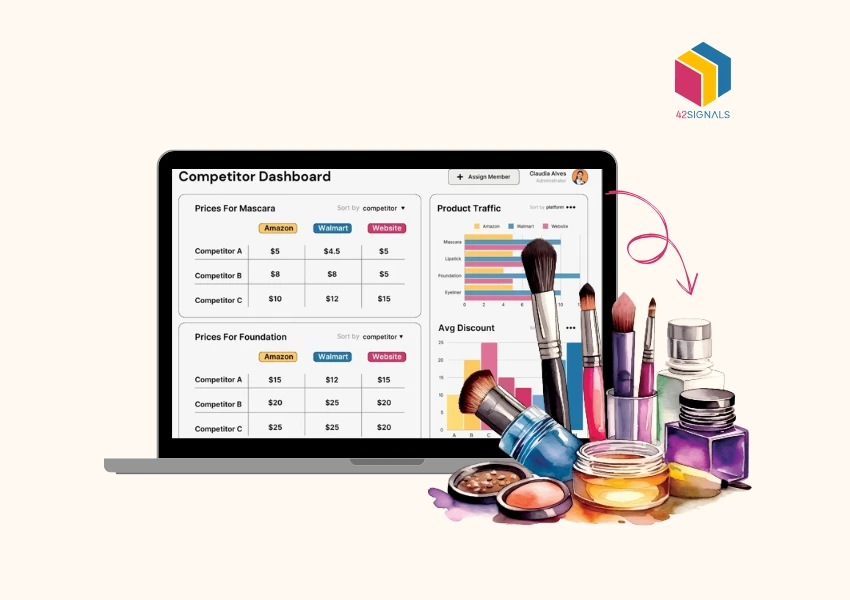
Beyond merely assigning numerical values to products, pricing serves as a strategic tool that can profoundly influence a company’s profitability. An exceptionally effective approach in this regard is incorporating retail pricing analytics.
Through the utilization of data and advanced analytics methodologies, retailers can refine their pricing strategies.
This helps them attract a larger customer base, enhancing sales, and ultimately elevating their overall profitability.
How Pricing Analytics Can Boost Profits
Examining pricing trends, market demand, competition, and customer behavior constitutes the essence of pricing analytics.
The utilization of retail pricing data offers retailers valuable avenues to elevate their profitability through the following strategies:
Improved Pricing Accuracy
Historical Sales Data Analysis:
By examining past sales data, retailers can identify patterns and trends that influence pricing decisions. For example, they can determine how seasonal demand, promotions, or economic conditions affect sales volumes and revenue.
Example: A retailer selling winter apparel can analyze sales data from previous years to set optimal prices for jackets and sweaters during peak winter months.
Market Trend Insights:
Retailers can leverage external data sources (e.g., industry reports, and economic indicators) to understand broader market trends. This helps them anticipate changes in consumer behavior or supply chain disruptions that may impact pricing.
Outcome: Retailers avoid underpricing (which erodes margins) or overpricing (which deters customers), ensuring they capture maximum revenue.
Dynamic Pricing
Real-Time Market Monitoring:
Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices in real time based on factors like demand fluctuations, competitor pricing, and inventory levels. Retailers can use algorithms and machine learning to automate this process.
Example: An e-commerce platform can increase the price of umbrellas during a sudden rainstorm or lower the price of overstocked items to clear inventory.
Demand Sensitivity:
By analyzing how price changes affect demand, retailers can identify the “sweet spot” where price and demand intersect to maximize revenue.
Outcome: Retailers stay competitive and responsive to market conditions, ensuring they don’t lose sales to competitors or miss out on higher margins.
Aligning Prices with Customer Value
Perceived Value Analysis:
Pricing analytics helps retailers understand how customers perceive the value of their products. This involves analyzing customer feedback, reviews, and purchasing behavior.
Example: A luxury brand may find that customers are willing to pay a premium for high-quality materials and exclusive designs, allowing them to justify higher prices.
Value-Based Pricing:
Instead of relying solely on cost-plus pricing, retailers can adopt value-based pricing strategies that reflect the benefits and experiences customers associate with the product.
Outcome: Prices resonate with customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction, loyalty, and willingness to pay.
Identifying Pricing Opportunities
Product Category Analysis:
Retailers can use pricing data to identify underperforming or overperforming product categories. This helps them focus on areas where price adjustments can drive higher profitability.
Example: A grocery store might discover that organic products have higher margins and lower price sensitivity, allowing them to increase prices without losing customers.
Price Elasticity Insights:
By understanding how sensitive customers are to price changes (price elasticity), retailers can identify products where small price increases won’t significantly impact sales volume.
Outcome: Retailers capture additional margins without risking a decline in sales, boosting overall profitability.
Competitive Analysis
Competitor Price Tracking:
Retailers can use pricing analytics tools to monitor competitor pricing in real time. This helps them stay informed about market trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Example: An electronics retailer can track competitors’ prices for the latest smartphone model and offer a slightly lower price or additional perks to attract customers.
Benchmarking and Positioning:
By comparing their pricing strategies with competitors, retailers can identify gaps and opportunities. For instance, they may discover that they can position themselves as a premium brand or a budget-friendly alternative.
Outcome: Retailers gain a competitive edge by offering better value, attracting price-sensitive customers, or differentiating themselves in the market.
Key Metrics for Pricing Analytics
Image Source: Business Wire
In order to conduct a thorough analysis and enhance the efficiency of retail pricing, it is essential to take into account specific crucial metrics.
These metrics offer valuable perspectives on the efficacy of pricing strategies and aid in pinpointing areas that may benefit from improvement.
Here are a few key metrics for retail pricing analysis:
Gross Margin
Definition and Importance:
Gross margin is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS), expressed as a percentage of revenue. It reflects how efficiently a retailer converts sales into profit.
Example: If a product sells for 100 and the COGS is 60, the gross margin is 40%.
Product Profitability Analysis:
By calculating gross margins for individual products or categories, retailers can identify high-margin items that drive profitability and low-margin items that may need reevaluation.
Actionable Insight: A retailer might discover that accessories (e.g., phone cases) have higher margins than the main products (e.g., smartphones) and focus on upselling them.
Pricing Adjustments:
If a product’s gross margin is too low, retailers can consider increasing the price, reducing costs, or discontinuing the product. Conversely, high-margin products can be promoted more aggressively.
Outcome: Retailers maximize profitability by focusing on products that contribute the most to their bottom line.
Price Elasticity
Understanding Price Sensitivity:
Price elasticity measures how changes in price affect customer demand. Products with high elasticity see significant demand changes with price fluctuations, while low-elasticity products are less sensitive.
Example: Luxury goods often have low elasticity (customers are less price-sensitive), while everyday items like groceries have high elasticity (customers are more price-sensitive).
Optimizing Revenue:
By understanding elasticity, retailers can set prices that balance volume and margin. For highly elastic products, small price reductions can lead to significant sales increases, while inelastic products can sustain higher prices.
Actionable Insight: A retailer might lower the price of a popular snack by 10%, leading to a 20% increase in sales and overall higher revenue.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies:
Elasticity insights enable retailers to implement dynamic pricing, adjusting prices based on demand fluctuations, competitor actions, or inventory levels.
Outcome: Retailers achieve optimal pricing that maximizes both sales volume and profitability.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Definition and Calculation:
CLV represents the total revenue a retailer can expect from a customer over the entire duration of their relationship. It factors in repeat purchases, average order value, and retention rates.
Impact of Pricing Decisions:
Pricing strategies directly influence CLV. For instance, offering discounts to first-time customers can increase acquisition rates, but retailers must ensure these customers return at full price to maintain profitability.
Actionable Insight: A subscription-based business might offer a discounted trial period to attract customers, knowing that the long-term CLV will offset the initial discount.
Customer Retention:
By analyzing CLV, retailers can identify high-value customers and tailor pricing strategies (e.g., loyalty programs, and personalized discounts) to retain them.
Outcome: Retailers build long-term customer relationships, driving sustained revenue growth.
Market Share
Definition and Importance:
Market share represents the portion of total sales in a market that a retailer captures. It’s a key indicator of competitiveness and customer preference.
Pricing and Value Perception:
Market share is closely tied to pricing strategies. If customers perceive a retailer’s products as offering better value (quality, features, or price), they are more likely to choose that retailer over competitors.
Actionable Insight: A retailer might lower prices on key products to attract more customers and increase market share, even if it temporarily reduces margins.
Competitive Benchmarking:
By monitoring market share, retailers can assess the effectiveness of their pricing strategies relative to competitors. A growing market share indicates that their pricing is resonating with customers.
Outcome: Retailers gain a competitive edge by aligning their pricing with customer expectations and market dynamics.
The Role of Technology in Pricing Analytics
ECommerce analytics tools like 42Signals provide retailers with the capabilities to collect, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of pricing data.

These tools offer features such as:
- Historical pricing data analysis: Retailers can gain insights from their past pricing strategies and their impact on sales and profitability.
- Competitive pricing analysis: Retailers can track competitor pricing strategies, allowing them to make informed pricing decisions and stay competitive in the market.
- Real-time market monitoring: E-commerce analytics tools provide real-time data on market conditions, allowing retailers to adjust their pricing strategies promptly.
- Predictive analytics: By utilizing advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, retailers can forecast future pricing trends and make data-driven pricing decisions.
Implementing Retail Pricing Analytics Strategies
Achieving success in implementing retail pricing strategies necessitates meticulous planning and precise execution.
Consider the following essential steps:
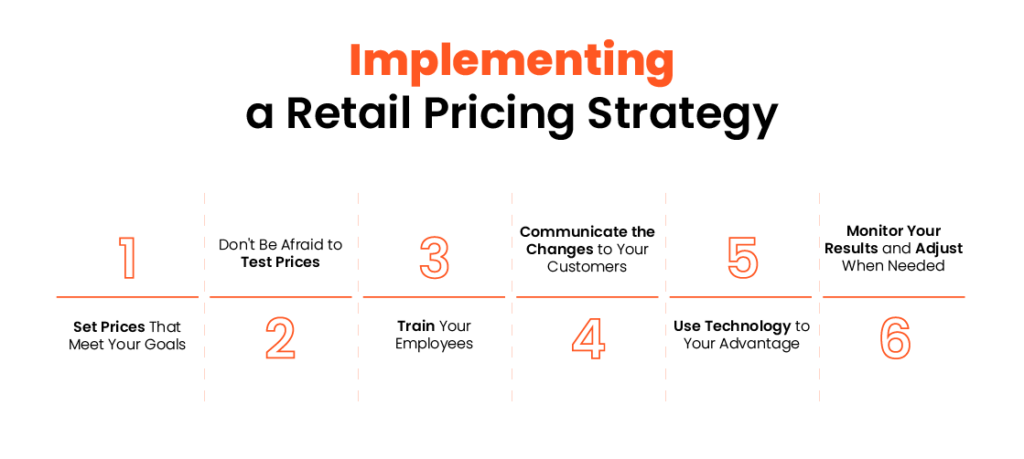
Image Source: Brandly
- Define Pricing Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals of your pricing strategy, whether the focus is on boosting sales, optimizing profits, or gaining a larger market share.
- Gather Data and Analyze: Collect relevant data on competitor pricing, market trends, and customer preferences. Analyze this data to identify patterns and insights that inform your pricing decisions.
- Develop Pricing Models: Develop pricing models that consider factors such as cost, demand, competition, and customer value perception. Test different pricing scenarios to identify the most profitable approach.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your pricing strategies and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review pricing data and market trends to stay ahead of the competition.
The Future of Pricing Analytics
As technology progresses, the future outlook for pricing analytics appears promising.
An example of dynamic pricing impact
Several trends are anticipated to shape the evolution of this field:
- Increased Incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven algorithms are poised to manage extensive sets of pricing data. It also helps with furnishing retailers with actionable insights and recommendations.
- Personalized Pricing: Retailers are expected to utilize customer data and AI algorithms to deliver tailored pricing based on individual customer preferences, purchasing history, and loyalty.
- Real-Time Pricing Adjustments: The evolution of advanced analytics tools empowers retailers to dynamically modify prices. Responding to factors such as inventory levels, customer demand fluctuations, and competitive pricing dynamics.
- Integration of Omnichannel Data: Retailers are expected to persist in integrating data from diverse channels. E-commerce platforms, physical stores, and mobile applications—enabling a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior and facilitating the optimization of pricing strategies across all channels.
Retail pricing analytics stands as a potent tool capable of significantly enhancing retailers’ profitability.
By harnessing appropriate technology and scrutinizing key metrics, retailers can formulate and execute effective pricing strategies.
Looking to boost your profits through retail pricing data? Look no further than 42Signals. Contact us at sales@42signals.com to book a FREE demo!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 4 pricing strategies?
- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy involves adding a fixed percentage markup to the cost of producing or acquiring a product or service. It is a straightforward approach that ensures a minimum profit margin but may not take into account market conditions or customer demand.
- Value-based Pricing: In this strategy, businesses set prices based on the perceived value of their products or services to customers rather than on production costs. By understanding what customers are willing to pay, companies can maximize revenue and differentiate themselves from competitors.
- Competitive Pricing: Companies using this strategy match or beat the prices of their closest competitors. While it helps maintain a competitive edge in the market, it may limit profits if margins are already thin.
- Dynamic Pricing: Also known as price discrimination, dynamic pricing adjusts prices based on factors such as time, location, and consumer behavior. Examples include surge pricing used by ride-sharing apps like Uber or fluctuating airfare prices seen on travel websites.
What are the 3 C’s of pricing strategy?
- Cost: Understanding the total cost involved in creating or delivering your product or service is essential when determining prices. Consider both variable costs (those associated with each unit produced) and fixed costs (overhead expenses).
- Customers: Knowing your target market and their preferences, needs, and willingness to pay plays a significant role in developing an effective pricing strategy. Conduct market research to gather insights about your ideal customers and tailor your pricing accordingly.
- Competitors: Analyzing the competition enables you to position yourself effectively within the market and identify opportunities to differentiate your offerings. Keep track of industry trends, competitor pricing tactics, and market conditions to make well-informed pricing decisions.