Today, people expect immediate access to services, whether it’s hailing a ride, streaming entertainment, or even ordering food. This growing demand for instant gratification has led to the birth of a new retail model that is revolutionizing the way we shop—Quick Commerce or Q-Commerce.
To understand how to make it work, let’s explore what Q-Commerce is, its rise, and how dark stores and digital shelf analytics are driving its growth.
What is Q-Commerce?
Quick Commerce, often abbreviated as Q-Commerce, represents a natural progression from traditional e-commerce.

Image Source: Delivery Hero
While e-commerce focuses on the convenience of shopping from the comfort of your home with delivery times that might range from a few days to a week, Q-Commerce takes this convenience to the next level by offering rapid, on-demand delivery, often within 10 to 30 minutes.
At its core, Q-Commerce is built on speed and immediacy. It caters to consumers who need products—such as groceries, personal care items, or household essentials—delivered almost instantaneously.
The growing demand for immediate access to everyday products is reshaping the retail landscape, with companies developing logistics and technological solutions to fulfill these urgent needs.
How Quick Commerce is Taking Over the Retail Industry?
Several factors are driving the rise of quick commerce, and at the heart of it is the shift in consumer expectations. Today’s consumers not only expect convenience but also speed, and Q-Commerce has positioned itself perfectly to meet this demand.
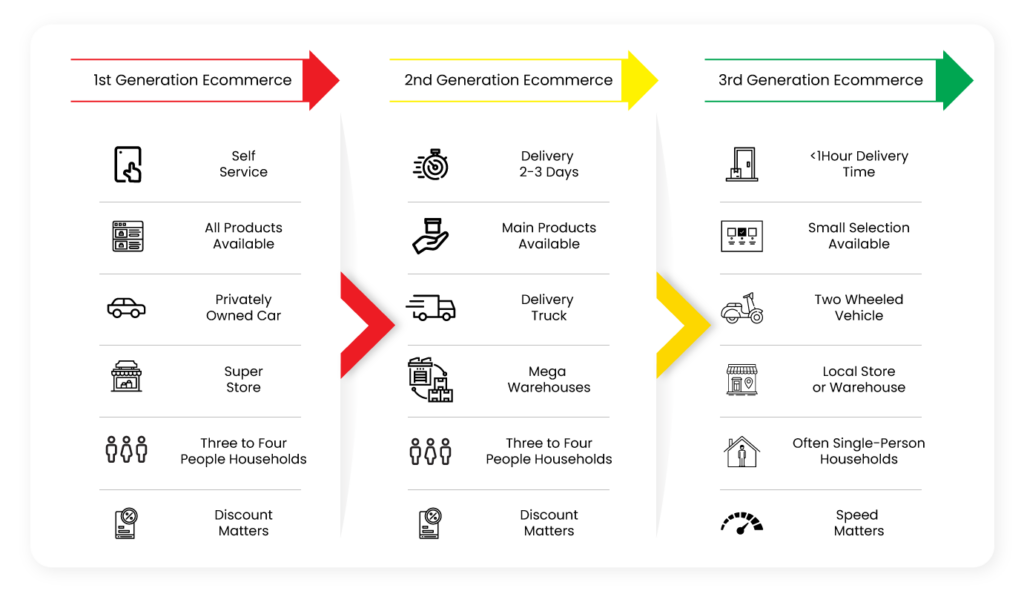
Image Source: Codilar
Whether it’s urban professionals too busy to visit a store, parents juggling family responsibilities, or anyone else in need of last-minute purchases, the promise of ultra-fast delivery is extremely appealing.
This shift has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which made doorstep delivery more than a convenience—it became a necessity.
With many people avoiding crowded stores, Q-Commerce offered a safe, efficient alternative. Startups and established retailers alike recognized this trend and began investing heavily in the infrastructure required to make quick commerce a reality.
How Does Quick Commerce Work?
At first glance, quick commerce might seem like a logistical miracle—how can a business deliver products within minutes of an order being placed? The answer lies in a combination of cutting-edge technology, well-designed operational models, and a new type of retail space known as dark stores.
Dark stores are one of the foundational pillars of quick commerce. These are retail outlets that are not open to the public but are set up solely to fulfill online orders.

Unlike traditional stores that must accommodate both in-person shoppers and online order processing, dark stores are optimized exclusively for picking, packing, and dispatching items as quickly as possible.
Their locations are carefully chosen, often in densely populated urban areas, to minimize delivery times.
These stores are usually stocked with a smaller, more curated inventory compared to large supermarkets.
The focus is on high-demand items that consumers are likely to need on short notice, such as groceries, toiletries, and over-the-counter medications.
Workers in these dark stores use digital tools, including digital shelf analytics, to keep track of inventory in real-time and ensure that the most popular products are always available.
Digital shelf analytics also plays a crucial role in predicting demand patterns. These tools analyze consumer data to determine which products are most likely to be ordered at any given time and location.

This helps companies stock their dark stores efficiently and minimize out-of-stock situations, ultimately ensuring faster order fulfillment.
What Is The Role of Dark Stores in Q-Commerce?
Dark stores are the hidden engines of Q-Commerce, and their strategic placement in cities is critical to meeting the delivery promise.
Because these stores are exclusively dedicated to processing online orders, they eliminate the delays associated with traditional brick-and-mortar stores, where customers and staff share the same space. With no need to cater to foot traffic, dark stores can optimize every aspect of their operations, from product layout to staffing.
The size of these stores varies depending on the population density and consumer demand in their service area.
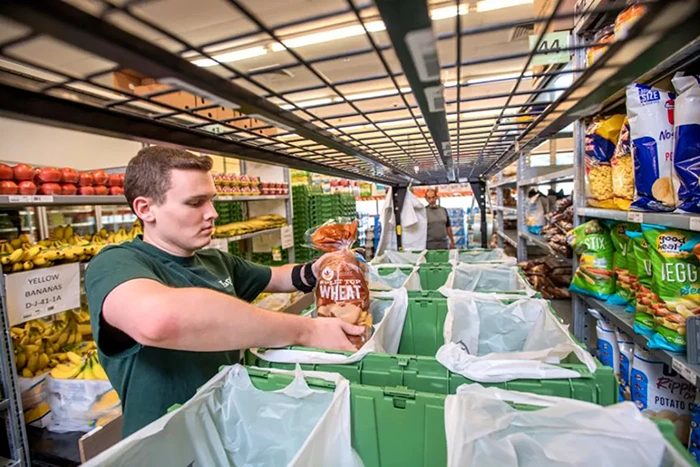

Image Source: CNN
Some are as small as a few thousand square feet, while others resemble large warehouses. Regardless of size, their primary function is to ensure that orders can be packed and dispatched within minutes.
The rise of dark stores has also led to advancements in automation. Some stores are experimenting with robots and other automated systems to further speed up the picking process.
The integration of technology not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces human error, which can be costly in an industry where speed and accuracy are paramount.
The Impact of Digital Shelf Analytics on Q-Commerce
One of the most significant challenges in Q-Commerce is maintaining a balance between stock availability and delivery speed.
If a customer orders a product that is out of stock, the entire promise of quick commerce is jeopardized.
Digital shelf analytics tools provide real-time data on inventory levels and help businesses make data-driven decisions about restocking and promotions.
For instance, if the data shows that a certain product is running low in a specific dark store, the system can trigger an automatic restock before the product sells out. In addition, digital shelf analytics can provide insights into consumer preferences, helping companies adjust their offerings to meet changing demands.
Moreover, these tools can be integrated with other technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict future demand trends
If the data indicates an increase in demand for certain products on weekends or during specific times of the year, the company can stock its dark stores accordingly. This level of predictive analytics not only improves efficiency but also enhances the customer experience by reducing the likelihood of out-of-stock situations.
Key Players in the Q-Commerce Space
Several companies are leading the charge in the quick commerce space, each leveraging dark stores and advanced technology to meet the growing demand for ultra-fast delivery. Some of the major players include Gorillas, Gopuff, and Flink, all of which have built their businesses around the concept of delivering everyday essentials in record time.
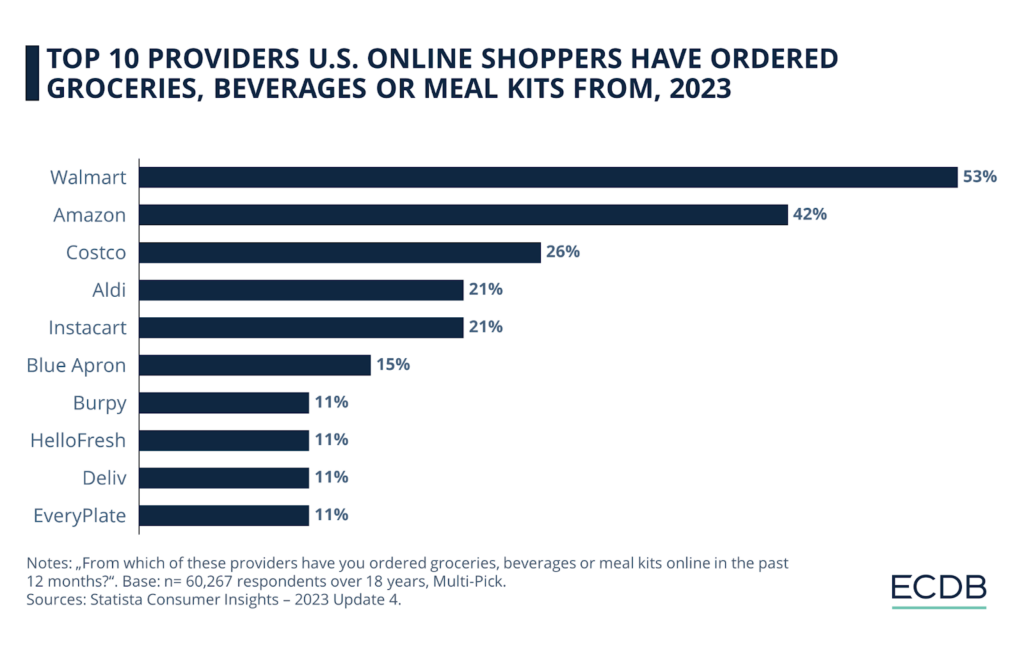
Image Source: Ecommerce DB
These companies typically operate in major cities where there is a high concentration of consumers who value convenience and speed.
In addition to these specialized startups, larger e-commerce platforms and retailers are entering the Q-Commerce space as well. For instance, companies like Amazon and Walmart are experimenting with faster delivery options to remain competitive.
By building their own network of stores or partnering with third-party logistics providers, these giants are aiming to capture a share of the rapidly growing quick commerce market.
The Future of Quick Commerce
As Q-Commerce continues to gain momentum, several trends are likely to shape its future. One significant trend is the expansion of product categories available for ultra-fast delivery.
While Q-Commerce initially focused on groceries and essential items, consumers are beginning to expect quick delivery for a wider range of products, from clothing to electronics.
Companies that can efficiently expand their product offerings without compromising on delivery speed will likely emerge as leaders in this space.
Another trend is the increased use of automation and artificial intelligence to streamline operations. As companies continue to optimize their dark stores and delivery networks, we can expect to see more automation in both the picking process and the delivery itself.
For example, autonomous delivery vehicles or drones could eventually become a common sight in cities, reducing delivery times even further.
Sustainability will also be a critical consideration as Q-Commerce scales. The environmental impact of rapid deliveries—such as increased packaging waste and higher emissions from delivery vehicles—may lead to a push for more eco-friendly solutions.
This could include using electric delivery vehicles, optimizing delivery routes to reduce carbon footprints, and finding ways to minimize packaging waste.
Conclusion
Q-Commerce is more than just a trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how consumers expect to shop and receive their products.
The growing category and the insurgence of new companies in the domain bodes well for the businesses looking to grow in this and adjacent industries.
To stay ahead in this rapidly evolving market, leverage 42Signals to track digital shelf performance, monitor competitor activity, and optimize your strategy for maximum growth. Schedule a demo now!