Navigating the complexities of stock availability is a cornerstone for triumph in the eCommerce industry. When customers go to a website to buy a specific product, if the item is out of stock, it can quickly sour the shopping experience.
Stock availability is an intricate dance of supply and demand rather than just having items on shelves; it’s about strategic alignment of inventory with market needs. Too much inventory can raise warehousing costs, reduce shelf life and lead to losses. Too little inventory can lead to inadequate supply and products being out of stock more often. Let’s look at stock availability in detail.

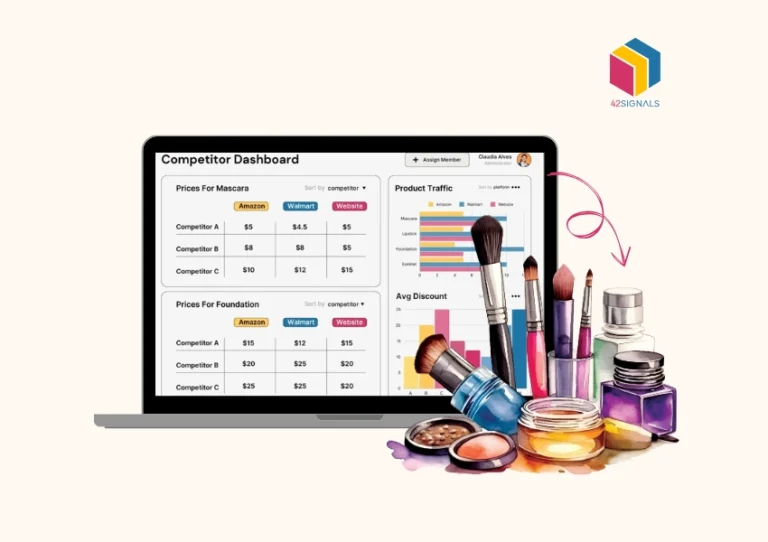
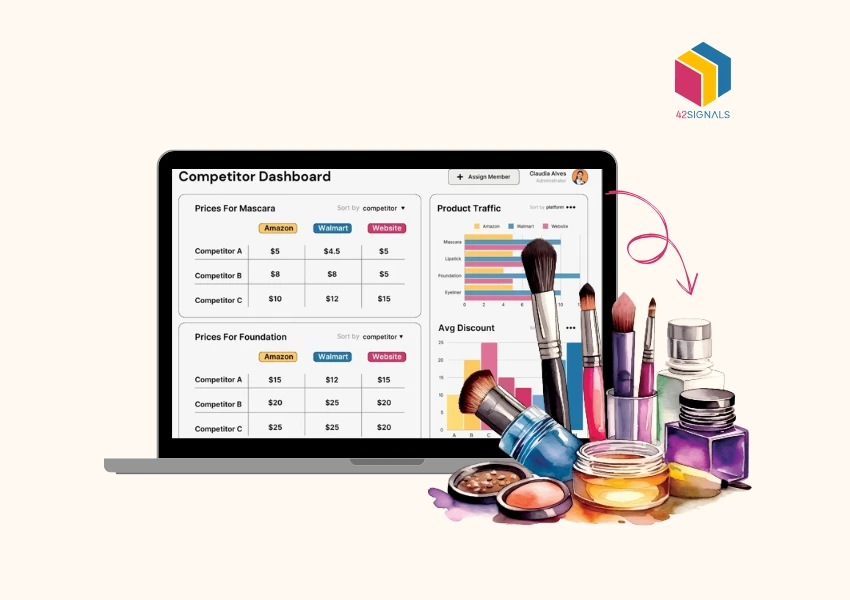
Image Source: Stock availability analytics | 42Signals
Understanding Stock Availability – The What
Stock availability is the strategic equilibrium between maintaining sufficient inventory to meet customer demand and avoiding excess that ties up capital or leads to waste. It’s not just about having products in a warehouse; it’s a dynamic process influenced by demand forecasting, supply chain agility, real-time inventory tracking, and lead time management. At its core, stock availability ensures that the right product is in the right place, at the right time, and in the right quantity.
For example, during peak seasons like Black Friday, a retailer must balance aggressive demand forecasts with supplier lead times to prevent stockouts while avoiding post-holiday surplus. Poor stock availability manifests in two extremes: stockouts, which frustrate customers and erode trust, and overstocking, which incurs storage costs, markdowns, or waste (e.g., perishable goods). Key components include:
The Crucial Role of Stock Availability – The Why
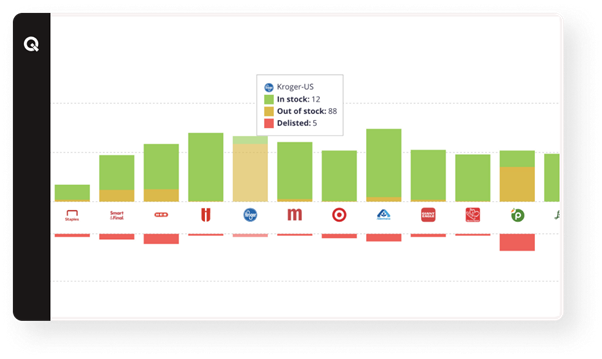
Image Source: Commerce IQ
Stock availability isn’t merely a logistical concern; it’s the backbone of customer satisfaction and business growth. The longer products are out of stock, customers lose confidence and trust in that brand, sending them elsewhere to competitors.
This experience, if unchanged, can lead to high customer attrition rates and significant losses in revenue. Let’s look at the reasons why stock availability is such a crucial component to success –
1. Enhancing Customer Experience
Timely order fulfilment is instrumental in cultivating customer satisfaction and allegiance. Imagine a customer ready to purchase a birthday gift—encountering an “out of stock” message not only derails their plans but often triggers negative reviews or social media backlash. Conversely, reliable availability fosters trust. For example, Amazon’s “Buy Now” button thrives on its reputation for consistent stock, reducing cart abandonment and earning repeat business.
2. Maximizing Sales Opportunities
Every stockout represents a missed revenue opportunity. Apparel brands, for instance, lose approximately $1.75 trillion globally annually due to poor inventory management (McKinsey). Conversely, optimized stock levels enable brands to capitalize on trends. When Stanley’s Quencher tumbler went viral, proactive inventory scaling allowed them to meet demand, driving a 275% revenue surge in 2022.
3. Cultivating Brand Reliability
Consistency breeds loyalty. Brands like Toyota, famed for “Lean Manufacturing,” balance minimal inventory with high availability, reinforcing their reputation for dependability. In eCommerce, 68% of customers prioritize retailers with real-time stock visibility (SAP), showcasing how transparency builds credibility.
4. Streamlining Operations
Efficient stock management reduces holding costs and waste. Zara’s agile supply chain, which refreshes inventory biweekly, minimizes overstock while responding swiftly to trends. Similarly, Walmart’s cross-docking system slashes storage time, cutting costs by 10–15%. Advanced tools like RFID tagging and predictive analytics further refine accuracy, reducing human error.
Strategic Approaches to Stock Availability Management – The How
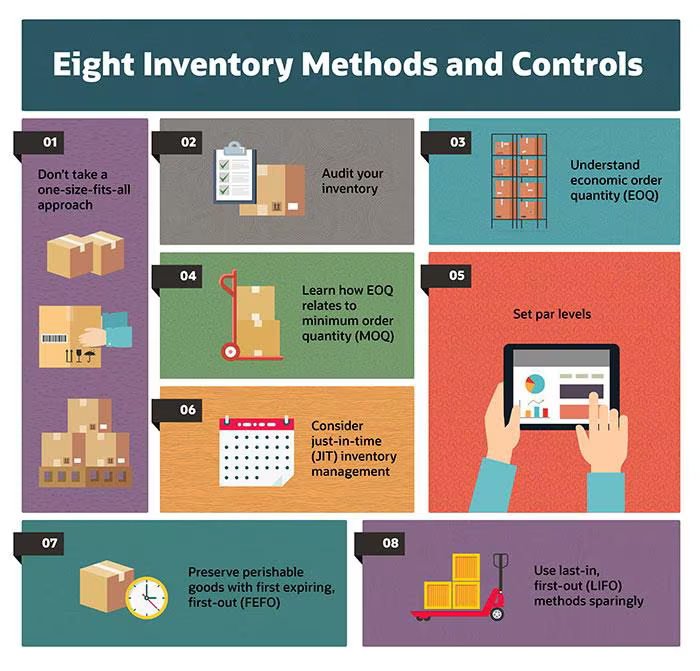
Image Source: NetSuite
Being such a volatile and dynamic component of the eCommerce supply chain, stock availability management comes with its challenges. This could be inaccurate demand forecasting, supply chain disruptions, fluctuations in market needs, unforeseen events, and their impact (like Covid-19), to name a few.
These challenges in stock availability must be top of mind when looking at optimal inventory management. A few solutions are –
1. Advanced Inventory Solutions
Deploy cutting-edge systems for seamless stock tracking and analysis. Solutions like 42Signals allow users to predict and identify out-of-stock situations beforehand, enabling proactive inventory management.
For instance, IoT-enabled sensors in Amazon’s warehouses provide real-time visibility into stock levels, while cloud-based platforms like TradeGecko unify multichannel sales data to prevent oversights.
2. Predictive Demand Analysis
Gone are the days of relying on gut feelings or static spreadsheets. Predictive demand tools like 42Signals combine AI with real-time data (e.g., web traffic, competitor pricing) to forecast demand with surgical precision. While seasonal peaks (e.g., holiday toys) follow predictable patterns, viral products—like the 2023 Stanley Cup craze—require agility. Brands like Shein thrive by analyzing TikTok trends to adjust production in 2–3 days.
3. Strengthening Supplier Networks
A resilient supplier network is the unsung hero of stock availability. Take inspiration from Toyota, which treats suppliers as partners, sharing production schedules and co-developing contingency plans. Strategies include:
Supplier Scorecards: Grade vendors on metrics like on-time delivery (e.g., Dell’s 98% threshold).
Collaborative Platforms: Use tools like SAP Ariba for real-time order tracking and communication.
Buffer Agreements: Negotiate safety stock commitments for high-risk items (e.g., semiconductor chips).
Case Study: During the 2021 Suez Canal blockage, Home Depot’s pre-vetted alternate suppliers prevented delays, avoiding $2B in lost sales.
4. Supply Chain Diversification
Mitigate risks by broadening supply sources. Plan A, Plan B, and Plan C; when the first plan or system falls through it serves well to have backup measures in place. This could mean alternate shipping companies, raw material suppliers, and so on.
Relying on a single supplier or route is a recipe for disaster. Diversification involves:
Geographic Spread: Source from multiple regions (e.g., Apple’s mix of Chinese, Indian, and Vietnamese manufacturers).
Dual Sourcing: Partner with backup suppliers for critical components (e.g., Tesla’s lithium battery suppliers).
Logistics Redundancy: Engage multiple carriers (e.g., FedEx + UPS) and ports to avoid bottlenecks.
Example: After floods disrupted Thai hard drive production in 2011, Western Digital diversified to Malaysia, cutting recovery time by 60%.
5. Adaptive Warehouse Strategies
Implement flexible approaches like JIT for optimal inventory levels. A just-in-time (JIT) inventory system is a management strategy that has a company receive goods as close as possible to when they are actually needed. Such systems allow for reduced inventory costs while not derailing production schedules.
Conclusion
Stock availability metrics can be the missing piece to the puzzle that propels your business forward. With this data, gauging the demand and supply of products becomes easier and more accurate.
If you’re interested in exploring this solution, contact us for more information.