Table of Contents
ToggleIn the dynamic realm of e-commerce, the availability of products on the digital shelf stands as a paramount factor in dictating the triumph of any online enterprise. Proficiently handling and sustaining optimal stock levels wields formidable influence over customer contentment, revenue generation, and the overarching prosperity of a business. This article will look into the profound significance of digital shelf stock availability for e-commerce ventures, the intrinsic connection between stock availability and customer satisfaction, the substantial repercussions of stockouts on e-commerce revenues, actionable strategies to enhance stock availability, and pivotal performance metrics for meticulously gauging and nurturing stock availability to yield unparalleled results.
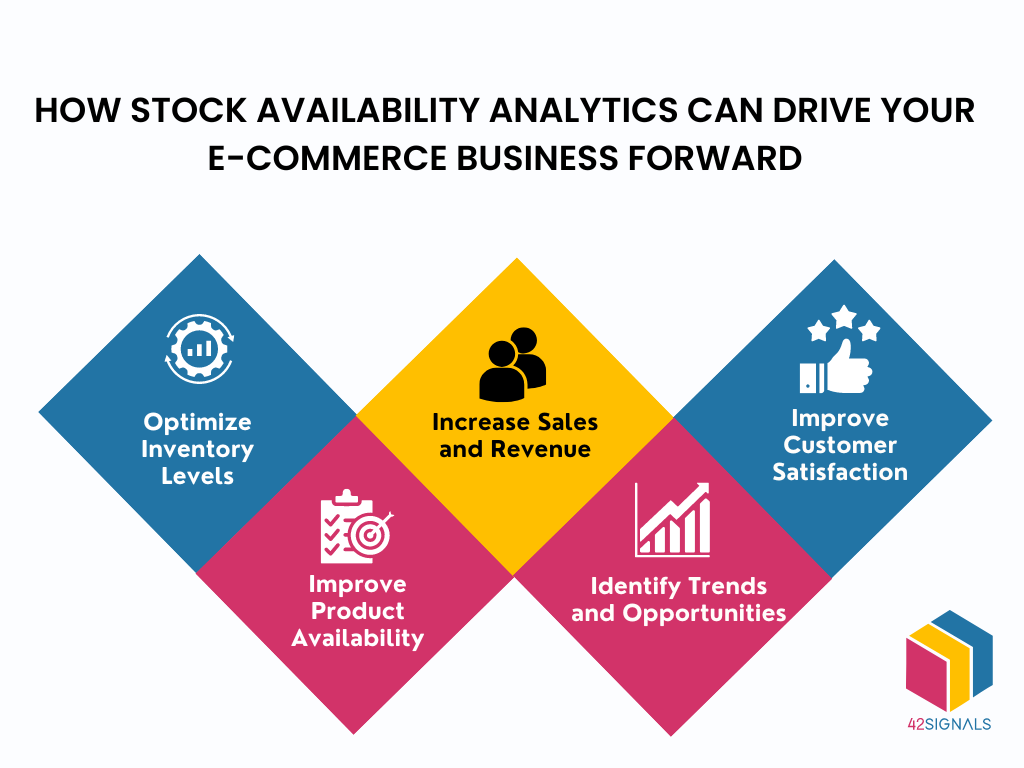
Understanding Digital Shelf Stock Availability
Stock availability in the digital realm embodies the lifeblood of e-commerce – it’s the heartbeat of product availability on your online storefront. It encompasses the vitality of your inventory, measuring not just the mere quantity of items in your stockroom but also the precision and immediacy with which your platform broadcasts this vital information to your customers. In the fiercely competitive world of online retail, precise and up-to-the-second stock availability is the linchpin that empowers retailers to exceed customer expectations, shield against inventory droughts, and elevate sales to unprecedented heights.
The Link Between Stock Availability and Customer Satisfaction
Stock availability and customer satisfaction are interlinked. Customers intending to make a purchase require the items to be in stock.
If a product is out of stock or unavailable, it can lead to frustration, disappointment, and even loss of trust in the business.
On the other hand, when customers can easily find and purchase the products they desire, it enhances their overall shopping experience and increases their satisfaction. Happy and satisfied customers are more likely to make repeat purchases, recommend the business to others, and contribute to positive online reviews and word-of-mouth marketing.
The Impact of Stockouts on E-commerce Sales
Stockouts, or situations where a product is out of stock, can have a detrimental impact on e-commerce sales. When a customer encounters a stockout, they have limited options – they can either wait for the product to be restocked, choose an alternative product, or abandon the purchase altogether.
Many customers are time-sensitive and may not be willing to wait for the restocking of a particular product. This can result in missed sales opportunities and potentially lost customers to competitors. Furthermore, forcing customers to settle for an alternative product may not meet their exact needs or preferences, leading to a less satisfactory purchase experience.
Stock unavailability also has negative consequences for customer loyalty. Customers who encounter frequent stockouts may lose confidence in the e-commerce business, and they may start exploring other options to fulfil their shopping needs. This can significantly impact customer retention rates and overall business growth.
Strategies to Improve Digital Shelf Stock Availability
Stockouts on the digital shelf are more than just a minor inconvenience; they represent a critical failure point in the e-commerce customer journey, leading directly to lost sales, damaged brand reputation, diminished search ranking performance, and frustrated customers who may never return. Achieving and maintaining high stock availability requires a proactive, multi-faceted approach that extends far beyond basic inventory tracking. Building upon the foundational strategies, here’s an in-depth exploration of how to significantly improve digital shelf stock availability:
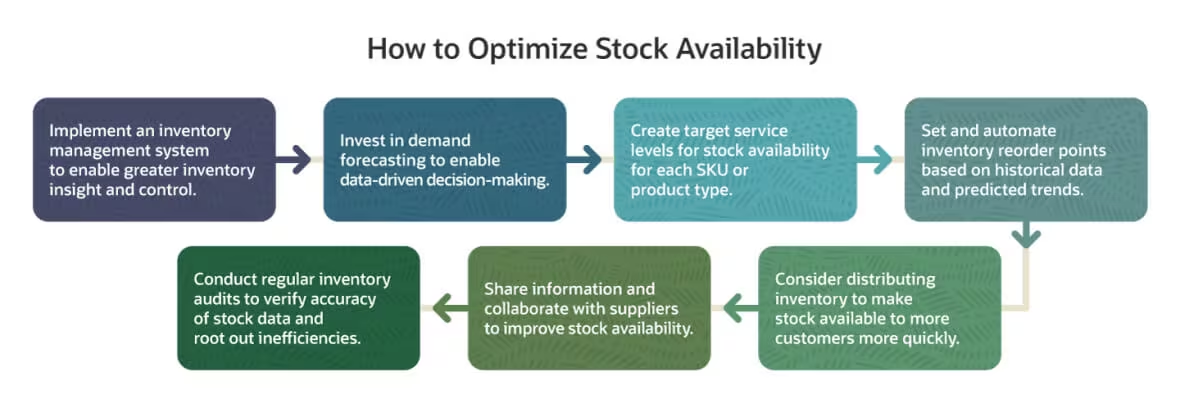
Image Source: NetSuite
1. Inventory management
- Advanced Demand Forecasting: Move beyond simple historical averages. Leverage sophisticated forecasting techniques:
- Statistical Modeling: Utilize time-series analysis (e.g., moving averages, exponential smoothing, ARIMA models) to identify trends and seasonality.
- Machine Learning (ML): Implement ML algorithms that incorporate a vast array of influencing factors: historical sales data, seasonality, promotions (planned and competitive), marketing campaigns (email, PPC), website traffic trends, social media sentiment, economic indicators, weather (for relevant products), and even competitor stockouts. ML models continuously learn and adapt, improving accuracy over time.
- Causal Forecasting: Explicitly model the impact of specific events like promotions, new product launches, or external events (e.g., a pandemic, major sporting event) on demand.
- Granularity: Forecast at the most granular level possible (SKU, channel, region) to account for localized demand variations.
- Dynamic Reorder Points (ROP) & Safety Stock Calculations: ROP shouldn’t be static. Dynamically adjust based on:
- Lead Time Variability: Factor in supplier reliability and transportation delays.
- Demand Variability: Higher volatility requires higher buffers.
- Desired Service Level: Define the target probability of avoiding a stockout (e.g., 95%, 98%) – higher levels necessitate more safety stock. Utilize formulas like
ROP = (Average Daily Demand * Lead Time) + Safety Stock, whereSafety Stock = Z-score * √(Lead Time * Demand Variance). Automate these calculations within inventory management systems.
- Multi-Echelon Inventory Optimization (MEIO): For businesses with complex supply chains (e.g., multiple warehouses, distribution centers, stores fulfilling online orders), MEIO software optimizes stock allocation across the entire network. It determines where to hold inventory (central DC vs. regional hubs vs. stores) and how much to hold at each level to minimize total costs while meeting service level targets across all sales channels.
- ABC Analysis & Cycle Counting: For stock availability prioritize management effort. Classify SKUs based on value and velocity (A-items: High value/velocity, B-items: Medium, C-items: Low). Apply tighter controls and more frequent cycle counts to A-items. Regular, smaller cycle counts are more efficient and accurate than massive annual physical inventories, ensuring system data reflects reality.
- Inventory Accuracy as a KPI: Treat inventory record accuracy (e.g., 98%+ target) as a critical operational metric. Root cause analysis for discrepancies (theft, damage, mis-shipments, system errors) is essential.
2. Transparent communication
- Real-Time, Granular Visibility: Invest in systems that provide true real-time (or near real-time) inventory visibility at the most granular level required (e.g., specific warehouse bin location, store shelf). This is the bedrock of an accurate digital shelf display.
- Beyond “In Stock” / “Out of Stock”: Implement nuanced statuses:
- Low Stock: Warn customers when quantities are limited (e.g., “Only 3 left!”), creating urgency and managing expectations.
- Pre-Order: For items with known future arrival dates, capture demand early.
- Backorder with ETA: If an item is temporarily unavailable but a reliable restock date is known, clearly communicate this ETA. Allow customers to order with full transparency.
- Available at Nearby Store: For omnichannel retailers, show local store stock availability and enable options like BOPIS (Buy Online, Pickup In-Store) or ship-from-store.
- Discontinued: Clearly mark items no longer being restocked.
- Proactive Alerts: Allow customers to sign up for “Back in Stock” notifications via email or SMS. This captures intent and brings customers back.
- Impact on Search & Filters: Ensure out-of-stock items are automatically suppressed or deprioritized in site search results and category filters (unless a customer specifically chooses to view them). Displaying unavailable products frustrates users.
- Cart Reservations: Implement robust systems that temporarily reserve inventory when an item is added to a cart for a defined period (e.g., 10-30 minutes), preventing overselling during the checkout process. Handle abandoned carts effectively to release stock promptly.
3. Supplier partnerships
Build strong relationships with suppliers to ensure timely replenishment of stock. Collaborate closely with suppliers to align inventory levels with demand forecasts and minimize the risk of stockouts.
- Data Sharing & Joint Planning: Move beyond transactional relationships. Share detailed demand forecasts, promotional plans, and sales data with key suppliers through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), APIs, or collaborative platforms. Engage in Sales & Operations Planning (S&OP) or Integrated Business Planning (IBP) processes with suppliers.
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI): For strategic suppliers, consider VMI models where the supplier monitors your inventory levels (via system access) and is responsible for initiating replenishment orders based on agreed-upon min/max levels. This shifts ownership and leverages supplier expertise.
- Consigned Inventory: Hold supplier-owned stock in your fulfillment centers. You only pay (or the inventory is only counted as yours) when it sells. This reduces your inventory carrying cost and risk while improving availability.
- Reliability Metrics & SLAs: Establish clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with suppliers:
- On-Time In-Full (OTIF): Measures the percentage of orders delivered complete and on the promised date.
- Lead Time Consistency: Track the variance in actual vs. promised lead times.
- Quality Acceptance Rate: Minimize delays caused by rejecting defective shipments.
- Collaborative Improvement: Use performance data to identify root causes of delays and work jointly on improvement plans.
- Supplier Diversification & Risk Mitigation: Avoid over-reliance on single suppliers or geographic regions. Develop backup sources for critical items. Assess supplier financial health and operational resilience.
4. Implement safety stock
Maintain a buffer stock, also known as safety stock, to account for unforeseen fluctuations in demand or delays in the supply of stock availability. This helps mitigate the risk of stockouts during peak periods or other unexpected circumstances.
- Calculating with Precision: As mentioned under Inventory Management, safety stock isn’t guesswork. Use statistical methods considering:
- Demand Uncertainty (σd): Standard deviation of forecast error.
- Lead Time Uncertainty (σL): Standard deviation of lead time variation.
- Service Level Factor (Z): Derived from the desired probability of no stockout (e.g., Z=1.65 for 95% service level).
- Formula:
Safety Stock = Z * √( (Average Lead Time * σd²) + (Average Demand² * σL²) )(This accounts for both demand and lead time variability).
- Dynamic Adjustment: Continuously recalculate safety stock levels based on updated demand forecasts, actual lead times, and observed variability. Seasonality and promotional periods often require temporary increases.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Recognize that safety stock ties up capital and incurs holding costs (storage, insurance, obsolescence). Optimize the buffer size by balancing the cost of holding extra inventory against the cost of a stockout (lost profit, lost customer lifetime value, expedited shipping costs, brand damage).
- Strategic Placement: Hold safety stock at the optimal location within the supply chain network (e.g., near high-demand regions) as determined by MEIO principles.
5. Monitor and adjust
Continuously monitor stock levels, demand patterns, and inventory turnover rates. Regularly analyze data to identify trends, make informed decisions, and adjust stock levels accordingly.
- Real-Time Dashboards: Implement centralized dashboards providing real-time visibility into critical metrics across all channels and locations:
- Stockout Rate: % of SKUs unavailable when ordered.
- Inventory Turnover: How quickly stock sells (Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory Value).
- Days of Supply (DOS): Current inventory level / forecasted average daily sales.
- Forecast Accuracy: Measured by Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) or Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD).
- Sell-Through Rate: Units sold / units received over a period.
- On-Time Delivery (to Customer & from Supplier).
- Root Cause Analysis of Stockouts: Don’t just note a stockout; investigate relentlessly:
- Was it a forecasting error? (Underestimated demand, missed trend)
- A supply failure? (Supplier delay, quality rejection, transportation issue)
- A system failure? (Inventory sync error, incorrect safety stock setting, delayed PO placement)
- A process failure? (Goods received but not put away promptly, theft)
- A/B Testing & Scenario Planning: Test different forecasting models, safety stock levels, or replenishment strategies. Use simulation tools to model the impact of potential disruptions (supplier failure, demand spike) and plan mitigation strategies.
- Cross-Functional Alignment: Stock availability isn’t just a warehouse or procurement issue. Ensure tight alignment between:
- Merchandising: Providing accurate product lifecycle info (launches, discontinuations), promotion plans.
- Marketing: Sharing campaign details and expected demand impact.
- Sales: Providing channel-specific insights and feedback.
- Finance: Ensuring adequate funding for inventory investment and optimizing working capital.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize integrated platforms:
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Central hub for financials, inventory, orders.
- WMS (Warehouse Management System): Optimizes warehouse operations and inventory movement accuracy.
- OMS (Order Management System): Orchestrates order routing, fulfillment, and inventory visibility across channels/locations.
- Advanced Planning Systems (APS): Dedicated software for sophisticated demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and replenishment planning.
- PIM (Product Information Management): Ensures consistent and accurate product data (including availability) syndicated across all digital shelf touchpoints (website, marketplaces, social commerce).
- API Integrations: Seamlessly connect all systems for real-time data flow.
Measuring and Monitoring Stock Availability for Optimal Results
To effectively manage stock availability, e-commerce businesses need to measure and monitor relevant metrics. Key metrics to consider include:
- Stockout rate: Measure the percentage of times a product is not available when a customer attempts to purchase it. This metric provides insight into the frequency of stockouts and helps identify areas for improvement.
- Fill rate: Calculate the percentage of customer orders that are completely fulfilled from available stock. A high fill rate indicates robust stock availability, while a low fill rate suggests potential stock management issues.
- Lead time: Measure the time it takes from placing an order with a supplier to the product’s arrival in the warehouse. This metric helps identify any delays in replenishing stock and allows for proactive management of inventory levels.
- Inventory turnover rate: Calculate the number of times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific period. A high inventory turnover rate indicates efficient stock management, while a low rate may suggest excess stock or slow-moving products.
- Customer feedback: Regularly collect and analyze customer feedback regarding stock availability. Keep an eye on customer reviews, ratings, and comments to gain insights into potential stock-related issues and identify areas for improvement.
By regularly monitoring these metrics and taking proactive measures to address any stock availability challenges, businesses can improve their customer experience.
In conclusion, digital shelf stock availability is a critical aspect that can make or break an e-commerce business. It directly influences customer satisfaction, sales performance, and customer loyalty.
E-commerce analytics platforms like 42Signals provide aid in managing inventory levels, understanding out-of-stock products and patterns among other features.
To know more about our product or for a demo, contact us at sales@42signals.com