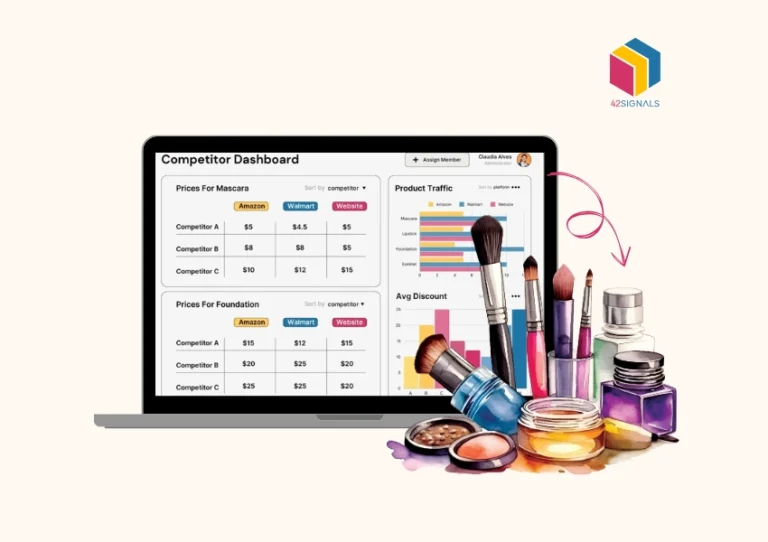
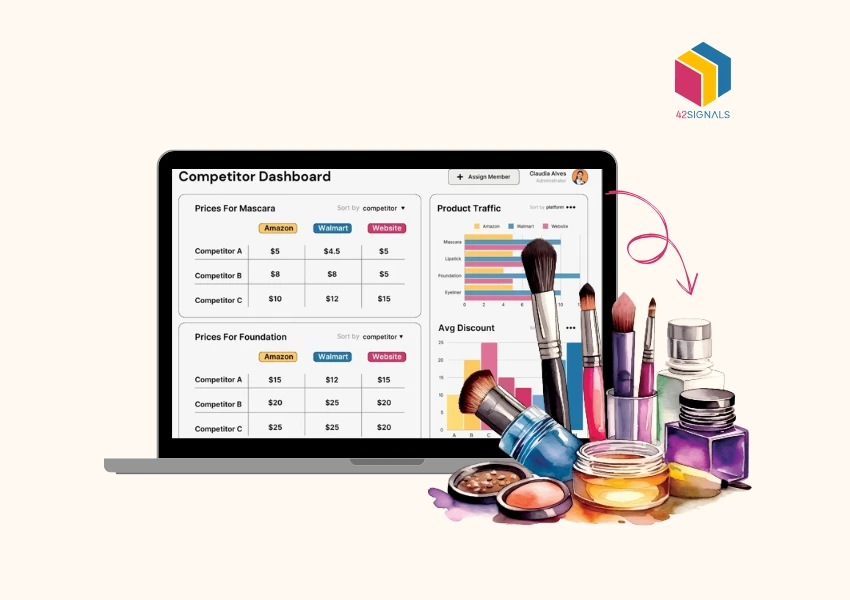
Today, where competition is intense and rapid technological advancements continuously reshape business landscapes, companies face the challenge of maintaining profitability while upholding brand value. One critical strategy for achieving this balance is the implementation and monitoring of Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies. MAP monitoring has become an essential tool for businesses seeking to protect their brand integrity, ensure fair competition, and maintain healthy profit margins.
Let’s understand the essentials of monitoring your MAP, its importance, and how businesses can effectively implement and manage these strategies.
Understanding Policies for MAP Monitoring
A Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policy is a set of guidelines established by a manufacturer that dictates the lowest price at which a retailer can advertise a product. It is important to note that MAP policies do not control the actual selling price of a product; instead, they regulate the advertised price. This distinction is crucial, as antitrust laws in many jurisdictions, particularly in the United States, prohibit manufacturers from setting fixed resale prices.
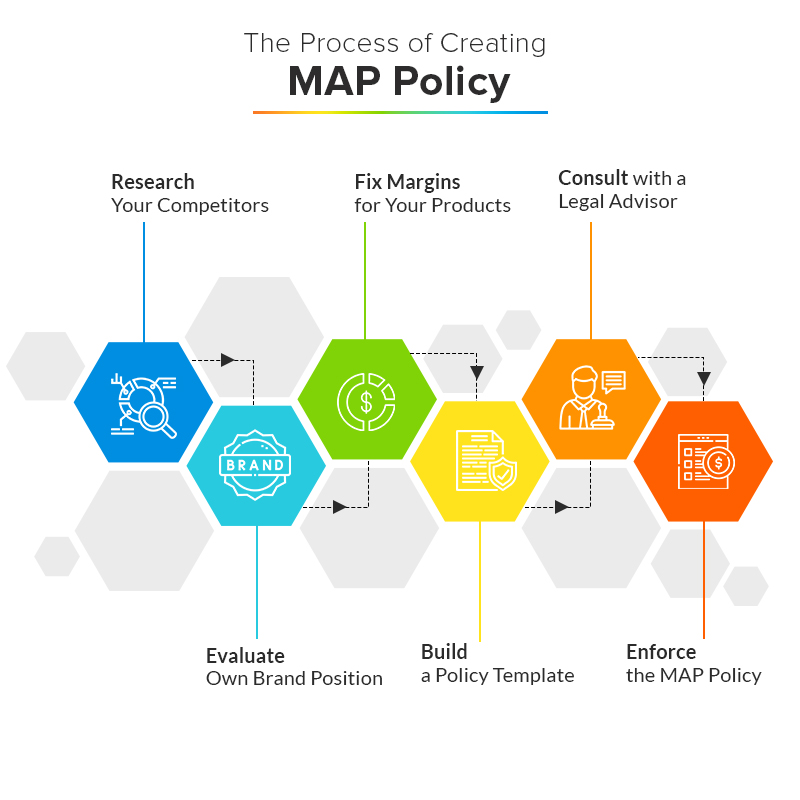
Image Source: Metrics Cart
MAP policies aim to ensure that all retailers operate on a level playing field when it comes to advertising, preventing larger retailers from using aggressive discounting strategies to undermine smaller competitors. By establishing a minimum advertised price, manufacturers help maintain the perceived value of their products and protect the brand’s reputation.
Why MAP Monitoring Matters
Effective Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) monitoring isn’t just a compliance task; it’s a fundamental strategic imperative for manufacturers and brands operating in competitive markets. Vigilant enforcement safeguards critical aspects of your business ecosystem:
1. Brand Integrity
The Core Issue: Your advertised price is a direct signal of your brand’s positioning. Consistent undercutting of the MAP erodes the perceived quality, exclusivity, and premium status you’ve worked hard to build.
Consequence of Neglect: When consumers see your flagship product heavily discounted across numerous platforms, it triggers a “race to the bottom” in their minds. The product becomes associated with bargain bins and constant sales, diminishing its aspirational value. Luxury and premium brands are particularly vulnerable, as deep discounting shatters the illusion of exclusivity.
Strategic Impact: Rigorous MAP monitoring ensures consistent advertised pricing, reinforcing your brand’s intended market position (luxury, mid-tier, value) and protecting the substantial investment made in brand equity. It signals stability and confidence in the product’s worth.
2. Fair Competition
The Core Issue: Unchecked discounting primarily benefits massive retailers with vast economies of scale and loss-leader capabilities. They can absorb temporary margin hits to undercut smaller competitors who rely on fair margins to survive.
Consequence of Neglect: Smaller authorized retailers, including specialized boutiques and local businesses, are forced out of the market. This leads to channel consolidation, reduced consumer choice, and ultimately, less innovation and personalized service. It creates an environment where competition is solely based on price, not value-added services or expertise.
Strategic Impact: MAP policies, actively monitored and enforced, create a level playing field. It allows retailers of all sizes to compete fairly on service, expertise, customer experience, and loyalty programs – factors that often differentiate smaller players, rather than being crushed in a price war they cannot win. This fosters a diverse, healthy retail ecosystem crucial for long-term market stability.
3. Profit Margin Protection
The Core Issue: Chronic discounting pressures erode margins not just for the violating retailer, but for all retailers and the manufacturer. When MAP is ignored, competitors feel compelled to match the lower price to avoid losing sales, triggering a downward spiral.
Consequences of Neglect: Squeezed margins force cuts elsewhere: reduced investment in product innovation, diminished marketing budgets, lower-quality customer support, and pressure on supplier relationships. Retailers lose the ability to fund value-added services. Ultimately, product quality or availability may suffer.
Strategic Impact: Effective MAP monitoring acts as a vital margin firewall. By preventing destructive price erosion, it preserves the necessary profitability for manufacturers to fund R&D, marketing, and warranty support, and for retailers to invest in staff training, store experience, and sustainable operations. This stability benefits the entire value chain and ensures the product’s long-term viability.
4. Channel Harmony
The Core Issue: Retailers who diligently invest in your brand, adhere to guidelines, and uphold the MAP feel betrayed and demotivated when they see others blatantly undercutting advertised prices without consequence.
Consequence of Neglect: Resentment builds among compliant partners. They become less likely to participate in cooperative marketing programs, provide prime shelf space, or advocate strongly for your brand. Channel conflict escalates, damaging crucial manufacturer-retailer relationships and hindering collaborative growth efforts.
Strategic Impact: Consistent MAP monitoring and swift, fair enforcement demonstrate respect for your authorized partners. It builds trust and loyalty. Compliant retailers are more inclined to collaborate on exclusive launches, joint promotions, in-store displays, and co-marketing campaigns, creating a unified and powerful brand presence in the market. It signals that you value and protect their investment in your brand.
5. Consumer Perception
The Core Issue: Inconsistent advertised pricing creates confusion, suspicion, and hesitation among consumers. They question the product’s true value (“Is it overpriced normally, or is the discount genuine?”), The retailer’s legitimacy and the brand’s control over its distribution.
Consequences of Neglect: Consumers may delay purchases, endlessly searching for a “better deal,” or become skeptical of the product’s quality/authenticity if found at drastically different prices. This erodes trust in both the retailer and the brand. For premium products, it directly undermines the justification for the higher price point.
Strategic Impact: MAP monitoring ensures advertised price consistency. This fosters consumer confidence in the product’s inherent value proposition. Shoppers feel reassured they are getting a fair deal regardless of where they shop (authorized channels), reducing purchase friction and “showrooming.” It reinforces the brand’s message of quality and reliability, leading to more confident and faster purchasing decisions.
Without a systematic, technology-driven MAP monitoring program, policies become merely suggestions. Sporadic checks are ineffective against sophisticated or transient violators. Investing in robust monitoring demonstrates a serious commitment to protecting your brand’s health, your partners’ businesses, and the product’s long-term profitability and perception in the marketplace. It transforms your MAP policy from words on paper into a powerful strategic asset.
Implementing Effective MAP Monitoring
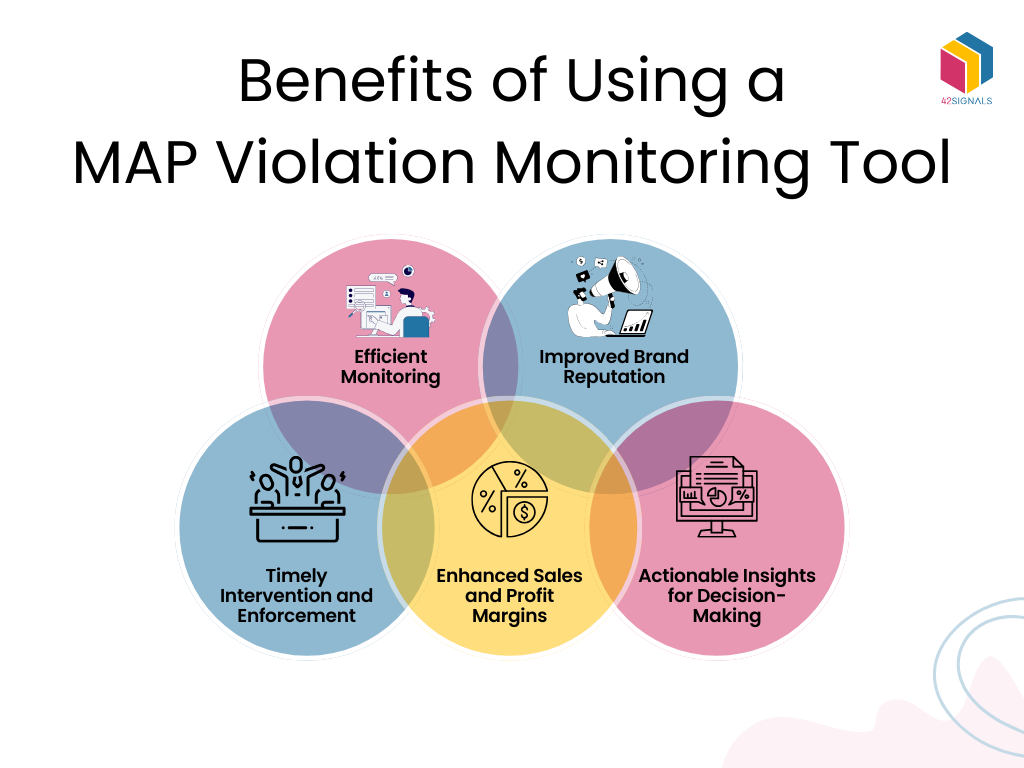
Successful MAP monitoring involves several key steps that businesses must follow to ensure compliance and address violations promptly.
1. Develop a Clear MAP Policy
Before monitoring can begin, manufacturers must establish a clear and comprehensive MAP policy. This policy should outline the minimum advertised price for each product and specify the consequences of non-compliance. It is crucial to communicate the policy clearly to all retail partners and obtain their acknowledgment of the terms.
When developing a MAP policy, manufacturers should consider factors such as:
- Product Categories: Different product categories may require distinct MAP pricing strategies based on factors like market demand, competition, and brand positioning.
- Geographic Variations: Prices may need to be adjusted for different regions to account for local market conditions and cost structures.
- Seasonality: Certain products may experience fluctuations in demand due to seasonal factors, necessitating temporary adjustments to MAP pricing.
2. Utilize Advanced Monitoring Tools
Monitoring MAP compliance manually is an arduous task, especially for businesses with a vast network of retail partners and an extensive product range. To streamline this process, companies should invest in advanced MAP monitoring tools and software.
These tools can automatically track advertised prices across various online and offline platforms, providing real-time alerts when violations occur. By leveraging technologies such as web scraping, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, businesses can efficiently identify and address pricing discrepancies.
3. Establish a Violation Resolution Process
Once a MAP violation is detected, it is essential to have a well-defined process for addressing the issue. Manufacturers should work collaboratively with retailers to resolve violations promptly and amicably. This process should include:
- Notification: Inform the retailer of the violation and provide evidence of the infraction.
- Education: Offer guidance and support to retailers to help them understand the importance of MAP compliance and the potential consequences of non-compliance.
- Correction: Allow the retailer a reasonable timeframe to correct the advertised price to comply with the MAP policy.
- Escalation: If the violation persists, consider escalating the issue by imposing penalties, such as withholding promotional support or terminating the retailer relationship.
4. Foster Collaborative Relationships
Building strong, collaborative relationships with retail partners is vital for effective MAP monitoring. Manufacturers should engage in open communication with retailers, providing them with the necessary resources and support to comply with MAP policies.
Regular meetings, training sessions, and workshops can help foster a culture of compliance and collaboration. By demonstrating a commitment to mutual success, manufacturers can encourage retailers to prioritize adherence to MAP guidelines.
5. Monitor Multiple Channels
In today’s omnichannel retail environment, monitoring MAP compliance across multiple platforms is essential. Online marketplaces, social media, and mobile apps have become significant channels for advertising and selling products. Manufacturers must ensure that their MAP policies extend to these digital channels, as well as traditional brick-and-mortar stores.
Advanced monitoring tools can help businesses track advertised prices across diverse channels, allowing them to identify violations in real time and take appropriate action.
Challenges in MAP Monitoring
While monitoring your MAP offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that businesses must navigate.
1. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
MAP policies must be carefully crafted to comply with legal and regulatory requirements. Antitrust laws vary by jurisdiction, and businesses must ensure that their policies do not violate these laws. Legal counsel should be consulted to review MAP policies and ensure they are enforceable and compliant.
2. Global Market Complexities
For businesses operating in international markets, MAP becomes even more complex. Different countries have varying regulations regarding pricing policies, and manufacturers must adapt their strategies accordingly. Cultural differences and varying consumer expectations also play a role in shaping MAP policies for global markets.
3. Identify Unauthorized Sellers with MAP Monitoring
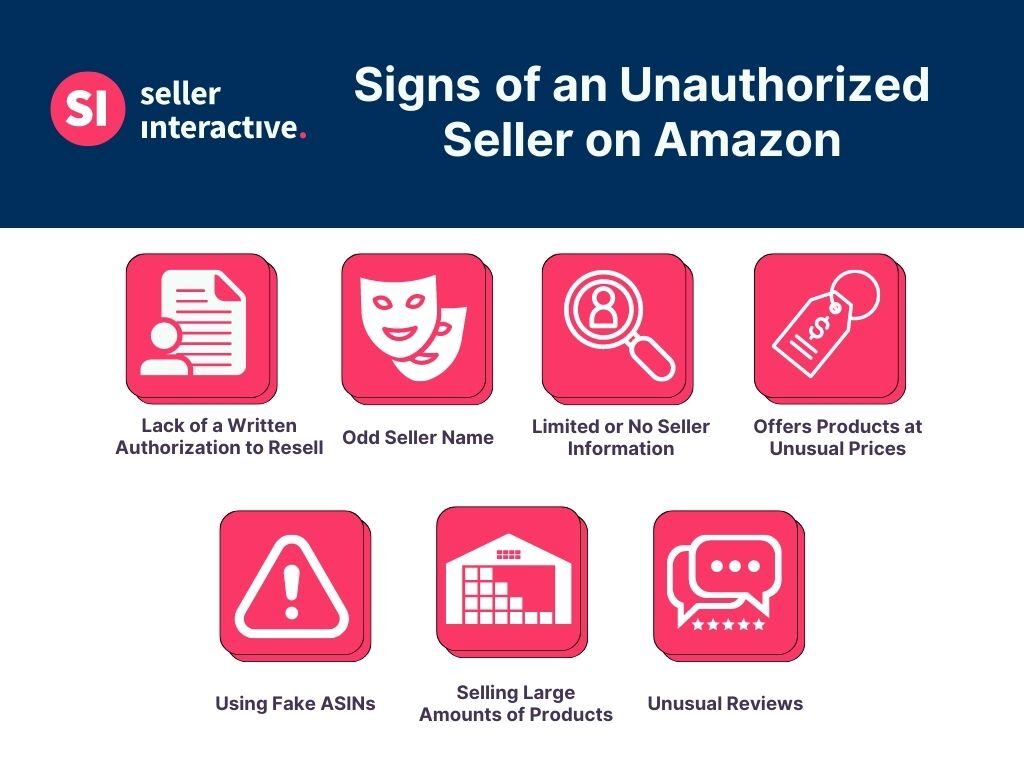
Image Source: Seller Interactive
The rise of online marketplaces has made it easier for unauthorized sellers to advertise products at prices below the MAP guidelines. Identifying and addressing these unauthorized sellers can be challenging, but it is essential for maintaining brand integrity and protecting authorized retail partners.
Manufacturers may need to collaborate with platform operators to remove unauthorized listings and take legal action against repeat offenders.
4. Dynamic Pricing
The increasing prevalence of dynamic pricing strategies, where prices fluctuate based on demand and supply conditions, poses a challenge for MAP monitoring. Manufacturers must strike a balance between allowing flexibility in pricing and ensuring compliance with MAP policies.
Advanced monitoring tools can help identify patterns in dynamic pricing and alert manufacturers to potential violations.
Conclusion | Final Takeaways in MAP Monitoring
As the retail landscape continues to evolve, businesses must remain vigilant in their MAP violation efforts, adapting to changing market conditions and consumer expectations.
By prioritizing MAP compliance, companies can build trust with consumers, foster long-term relationships with retail partners, and secure their position as leaders in their respective industries.
To effectively implement a full-suite MAP tracking system for your brand, schedule a demo with us today.