Table of Contents
ToggleShopping by voice is taking off! This new way to shop, called voice commerce, lets you use your voice commands on smart speakers or smartphones. Think of it as talking to a helpful assistant, like Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri, to buy things. While voice commerce is still fresh, it is growing fast.
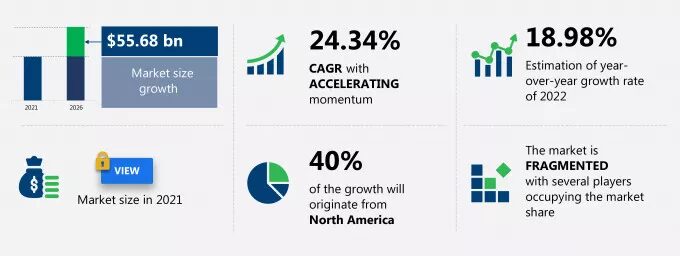
Image Source: Technavio
Statistics indicate that voice sales could reach $60 billion in 2024. However, most transactions currently tend to be for simpler items, highlighting the technology’s early market penetration stage. The trend is driven by increasing consumer comfort with technology and the hands-free convenience it offers, marking a potential shift in future shopping behaviors.
Voice Commerce and Its Current Market
The Death of Friction: Voice Commerce as the Ultimate Convenience Engine
Traditional e-commerce relies on screens, keyboards, and clicks—a process riddled with micro-frictions: typing errors, menu navigation, payment forms, and decision fatigue. Voice commerce eliminates these barriers by leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and AI-driven contextual understanding. The result? A conversational shopping experience mirroring human interaction.
Key Drivers of Convenience:
- Speed & Efficiency
- Voice searches are 3.7x faster than typing (Google).
- Example: “Reorder my usual coffee beans” processes an order in 5 seconds vs. 2+ minutes via app.
- Hands-Free & Eyes-Free Operation
- Critical for multitasking parents, drivers (via car systems), or users with mobility impairments.
- Domino’s saw 50% of voice orders come from customers cooking or cleaning.
- Hyper-Personalization
- Voice assistants (like Alexa or Google Assistant) learn preferences over time:
“Add to my cart” leverages past purchase data, size/color preferences, and delivery defaults.
- Voice assistants (like Alexa or Google Assistant) learn preferences over time:
Applications of Voice Commerce
Voice commerce has found noteworthy applications in various sectors, reshaping the shopping experience. Key areas include:

Image Source: FivedofTwelve
1. Hands-Free Household Replenishment: The Subscription Economy Revolutionized
The Mechanics of Habit Formation
Voice-activated reordering transforms tedious chores into automated rituals. When a user says “Alexa, order Tide Pods,” behind-the-scenes AI:
- Cross-references purchase history for size/variant
- Checks inventory against Amazon’s real-time supply chain
- Applies saved payment/shipping preferences
- Confirms delivery before checkout
Why Consumers Adopt:
- Procter & Gamble found 68% of voice replenishment users are busy parents reducing “mental load”
- Dollar Shave Club cut churn 22% by adding voice reordering to its subscription model
2. Voice-First Food Services: Speed as the Ultimate Currency
The 30-Second Transaction
Domino’s voice ordering via Google Assistant completes sales in 19 seconds vs. 2.5 minutes via app. Key drivers:
- Pre-set “Easy Order” profiles (saved pizzas, payment, addresses)
- Voice-AI cross-sell (“Add garlic bread for $3 more?”)
Market Impact:
- Starbucks’ voice orders via mobile grew 31% faster than app-only in 2023
- Uber Eats’ voice feature reduced misorders by 63% through confirmation dialogues
Innovation Frontier:
- McDonald’s Drive-Thru AI: Voice agents upsell “Would you like apple pie with that?” boosting average ticket by 18%
- “Multi-Vendor Menus”: Say “Order pad thai for 4” → AI compares local Thai restaurants by price/delivery time
3. Accessibility: Democratizing Commerce Through Voice
Breaking Physical Barriers
- Motor Disabilities: Walmart’s voice app enables wheelchair users to shop without manual navigation
- Visual Impairment: Target’s voice interface reads product details/prices aloud (screen-reader compatible)
- Cognitive Conditions: Simplified commands help Alzheimer’s patients maintain independence
Inclusive Design Wins:
- Amazon’s “Show and Tell” helps blind users identify products by holding items to camera + voice query
- CVS Pharmacy: 37% of voice prescription refills come from seniors avoiding complex apps
4. Automotive Voice Commerce: The $48B In-Car Opportunity
The Dashboard Marketplace
GM’s Marketplace platform lets drivers:
- “Pay for gas at Shell Station 12” (location-aware)
- “Order Starbucks ahead at Exit 203” (ETA-synced)
- “Renew my parking permit” (document scanning via car camera)
Safety-Driven UX:
- Voice reduces distracted driving – Hyundai’s system shortens interaction time by 7x vs. mobile
- Mercedes’ natural language processing understands fragmented commands (“Uh… coffee… near here?”)
Revenue Impact:
- BMW DriveStore: In-car voice purchases average $127/transaction (vs. $84 mobile)
- ExxonMobil: Voice-fuel payments increased loyalty app usage by 41%
5. Hyper-Personalization: The AI Psychologist
Beyond “Customers Also Bought”
Sephora’s voice AI tracks:
- Past purchases (“You bought Summer Fridays lip balm in June”)
- Local weather (“High UV today – add sunscreen?”)
- Beauty trends (“Try ‘clean girl’ aesthetic with these 3 items”)
Data-Driven Loyalty:
- Netflix-style Algorithms: Kroger’s voice system knows “Order weekly veggies” means organic kale + bell peppers
- Mood-Based Commerce: Spotify x Starbucks partnership suggests “Feeling stressed? Order chamomile tea” during mellow playlists
Conversion Metrics:
Personalized voice prompts achieve 23% higher conversion than generic prompts (MIT Sloan Study)
6. Voice-First Customer Service: The End of Hold Music
Frictionless Resolution Architecture
Bank of America’s Erica handles:
- “Dispute $57 charge from Amazon” → Instantly flags fraud
- “When’s my mortgage due?” → Pulls personalized statement
- “Send $50 to Mom” → Verifies via voice biometrics
Cost-Saving Impact:
- Delta Airlines: Voice support reduced call center volume by 31%
- Best Buy: 68% of voice-tracked returns avoid store visits
The AI-Human Handoff:
When voice bots detect frustration (user sighs), they:
- Apologize authentically (“I’m sorry this is frustrating”)
- Summarize issue for human agent
- Seamlessly transfer with context
The Psychology of Convenience: Why Voice Commerce Wins Loyalty
Convenience isn’t just functional—it’s emotional. Voice commerce taps into:
- Reduced Cognitive Load: No need to compare options visually; users trust the assistant to curate (e.g., “Find me a vegan pizza under $20”).
- Instant Gratification: One-step commands like “Buy now” trigger dopamine via immediacy.
- Barrier-Free Reordering: 65% of voice shoppers use it for routine replenishment (e.g., pet food, diapers).
Case Study: Tide’s Voice Strategy
Tide’s Alexa skill lets users reorder detergent via voice. By integrating with Amazon’s Subscribe & Save, they reduced churn by 12%—proving convenience locks in recurring revenue.
Adapting to the Changing Consumer Behavior Driven by Voice Technology
Voice technology’s rise is making shopping and searching by voice even more irresistible for consumers. It’s essential that e-commerce platforms adapt and improve their strategies through the implementation of natural language processing and machine learning technologies to effectively optimize content for extended, converse search inquiries via voice commands. Doing so enhances the user experience for voice searchers and boosts sales opportunities.
Moreover, businesses are recommended to implement voice commerce functionalities, enabling customers to make purchases via voice instructions on intelligent speakers and portable gadgets. Personalization is key; voice assistants can suggest products based on purchase history and preferences. Ensuring robust security measures for voice transactions to build consumer trust is also vital.
In adapting to this shift:
- Optimize for conversational voice search
- Integrate voice commerce capabilities
- Personalize the shopping experience
- Implement strong security for voice transactions
Optimizing Your E-commerce Platform for Voice Search Capability
E-commerce businesses must adapt to the rising trend of voice commerce. Here’s how to optimize:

1. NLP Implementation: Decoding the Human Query
Beyond Keyword Matching
Traditional search relies on lexical analysis; voice NLP requires intent mapping. When users ask:
“Where can I buy allergy-friendly flowers near me today?”
The NLP engine must decode:
- Entities: Flowers (product), allergy-friendly (attribute), today (time)
- Intent: Local purchase (transactional)
- Context: Urgency (same-day), health constraint
2. Conversational Keywords: The Long-Tail Revolution
Optimizing for How People Speak
Voice searches are 30% longer than text queries. Optimize for:
- Question Framing: “How to fix a leaking toilet” vs. “plumbing repair”
- Colloquialisms: “Sneakers” (57% voice) vs. “athletic shoes” (43% text)
- Procedural Phrases: “Steps to…” “Can you show me…”
3. Site Speed: The 0.5-Second Rule
Why Speed is Non-Negotiable
- 53% of voice search users abandon sites taking >2s to load (Google)
- Voice assistants prioritize pages with <1.3s FCP (First Contentful Paint)
4. Mobile Responsiveness: Designing for Thumbless Interaction
Voice-First UX Principles
- Hands-Free Navigation:
- “Scroll down” voice commands → Anchor link hotspots
- Audio-Optimized Content:
- Convert size charts to audio summaries (“Medium fits 38-40 inch chest”)
- Zero-Tap Checkout:
- Auto-fill forms via voice profile integration
Staples’ Mobile Voice UX:
- Voice-filtered category navigation (“Show me wireless keyboards under $50”)
- Reduced checkout steps from 5 to 2 for voice users
5. Voice-First Customer Service: The End of Hold Music
Frictionless Resolution Architecture
Bank of America’s Erica handles:
- “Dispute $57 charge from Amazon” → Instantly flags fraud
- “When’s my mortgage due?” → Pulls personalized statement
- “Send $50 to Mom” → Verifies via voice biometrics
Cost-Saving Impact:
- Delta Airlines: Voice support reduced call center volume by 31%
- Best Buy: 68% of voice-tracked returns avoid store visits
The AI-Human Handoff:
When voice bots detect frustration (user sighs), they:
- Apologize authentically (“I’m sorry this is frustrating”)
- Summarize issue for human agent
- Seamlessly transfer with context
Voice Commerce Trends
As voice technology advances, several key trends are shaping voice commerce:
• Increase in Voice Search
Consumers are increasingly using voice assistants for online search, hinting at a future where voice search optimization is crucial for e-commerce success.
• Personalized Shopping Experiences
Voice assistants are becoming more sophisticated, offering personalized recommendations based on previous interactions, which enhances user engagement.
• Seamless Integration with IoT
The integration of voice commerce with Internet of Things (IoT) devices is allowing for smoother and more innovative shopping experiences, like reordering groceries through a smart fridge.
• Enhanced Security Measures
As voice commerce grows, so does the need for robust security. Biometric voice identification and multi-factor authentication are becoming standard.
• Natural Language Processing Improvements
Continuous improvements in NLP are enabling more accurate and human-like interactions, reducing the gap between virtual and in-person shopping experiences.
• Expansion Beyond Retail
Voice commerce is extending into new sectors such as banking, travel, and healthcare, indicating its potential for widespread industry adoption.
Future-Proofing Your Business with Ongoing Innovations
As e-commerce changes rapidly, these strategies will help your business succeed in the long run:
- Smart Glasses: Visual AR + voice commands (e.g., “Show me reviews for these shoes”).
- Car Dashboards: Voice grocery orders during commutes (Volvo x Amazon partnership).
- Metaverse Integration: Virtual voice shopping in digital worlds (e.g., Meta’s voice-enabled avatars).
Brands Must:
- Build voice-first loyalty programs (e.g., “Use 500 points for free shipping”).
- Leverage predictive analytics to anticipate needs before the user speaks.
- Treat voice as a relationship channel—not a transactional tool.
Key Takeaway: Voice Commerce as Invisible Infrastructure
These use cases reveal voice commerce isn’t a feature – it’s becoming ambient infrastructure. As Google’s VP of Commerce put it:
“We’re building a world where commerce flows through conversation. Your fridge orders milk before you notice it’s empty. Your car pays for parking while you focus on driving. That’s not future tech – it’s rolling out now.”
Brands that master contextual anticipation and zero-friction fulfillment will dominate the next decade of consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is voice commerce?
Voice commerce refers to the process of using voice commands—through devices like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri—to search for, order, and purchase products online. Instead of typing or tapping on a screen, customers can simply say what they want, and the assistant handles the transaction. It makes shopping faster, hands-free, and more natural, especially for repeat or low-consideration purchases like groceries or household supplies.
What is the future of voice commerce?
The future of voice commerce looks promising as smart speakers and AI-powered voice assistants become more widely used in households. It’s expected to integrate deeper into everyday shopping routines, offering personalized recommendations, subscription renewals, and even voice-based payments with improved security. Over time, brands will optimize product listings for voice search SEO, making sure their products are discoverable when consumers shop by speaking rather than typing.
What is the e-commerce voice process?
The e-commerce voice process is the step-by-step journey of completing a transaction through a voice assistant:
- Activation – The user wakes the device (e.g., “Hey Google” or “Alexa”).
- Search – The shopper makes a request, like “Find running shoes under $100.”
- Recommendation – The assistant reads back results, often prioritizing best sellers or Prime-eligible products.
- Selection & Confirmation – The shopper confirms the choice with a simple command.
- Payment & Checkout – Payment details (stored securely in the assistant’s ecosystem) are processed, and the order is placed.
This process eliminates manual browsing and creates a more conversational shopping experience.
What are the 4 types of e-commerce?
The four main types of e-commerce are:
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Companies sell directly to individual customers (e.g., Amazon, Netflix).
- B2B (Business-to-Business): Transactions between businesses, such as wholesalers selling to retailers (e.g., Alibaba).
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Consumers sell to other consumers via platforms like eBay, OLX, or Facebook Marketplace.
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business): Individuals provide products or services to businesses, such as freelancers on platforms like Upwork or content creators working with brands.




