Table of Contents
ToggleWith the increasing competition in the online marketplace, businesses are constantly seeking new ways to stand out from the crowd and provide a unique shopping experience for their customers. Enter visual commerce – a revolutionary approach that combines artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR) technologies to transform how consumers interact with products online.
What is Visual Commerce?
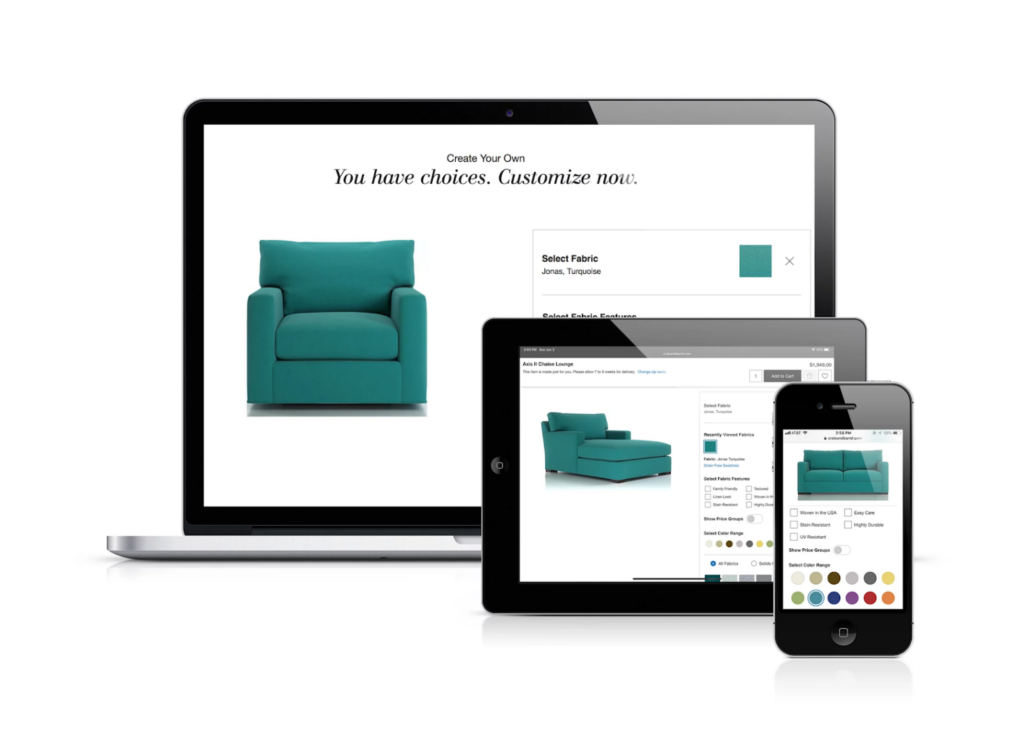
Image Source: Threekit
Visual commerce refers to the integration of rich media content such as images, videos, and interactive elements into e-commerce platforms. It aims to create immersive experiences that allow shoppers to engage more deeply with products before making a purchase decision.
By leveraging advanced AI algorithms and AR capabilities, retailers can now offer virtual try-on features, personalized product recommendations, and even 3D previews of items in one’s living space or wardrobe. These innovations have been shown to boost engagement levels, reduce return rates, and ultimately increase sales conversions.
One key aspect of visual commerce is its ability to bridge the gap between physical and digital environments. Traditionally, customers have relied heavily on tactile feedback when evaluating potential purchases. However, this sensory input is absent in online shopping scenarios, often leading to uncertainty and dissatisfaction post-purchase.

Image Source: Square
Through AI-powered image recognition technology, visual commerce enables users to upload photos of themselves or desired spaces and receive accurate suggestions based on color matching, style compatibility, and other factors. This not only helps customers make informed decisions but also fosters trust in the brand.
The Role of AI in Visual Commerce
Artificial intelligence serves as the backbone of visual commerce, driving innovations that make the shopping experience smarter and more personalized. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, such as product details, user preferences, and shopping behaviors, to generate accurate and tailored recommendations.
For instance, visual search technology allows users to upload a photo of a product they like, and the system will identify similar items available for purchase. This feature is particularly appealing to younger demographics who are accustomed to discovering products through social media platforms like Instagram or Pinterest.
Machine learning, a subset of AI, enhances this process by continuously refining its understanding of customer preferences. Over time, the system learns to predict what a user might be interested in based on their past interactions, leading to a highly personalized shopping experience. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also increases the likelihood of repeat purchases and brand loyalty.
Augmented Reality: Elevating the Shopping Experience
Augmented reality takes visual commerce to another level by providing experiential value to shoppers. For instance, furniture companies like IKEA and Wayfair leverage AR technology to let customers preview how pieces would look in their homes before buying them.
Similarly, cosmetics brands enable users to virtually apply makeup using smartphone cameras, thereby streamlining the decision-making process. Such applications significantly enhance customer satisfaction and encourage repeat business since they minimize the risk of purchasing ill-suited products.
AR also helps reduce return rates, a significant challenge for e-commerce businesses. By giving customers a realistic preview of how a product will look or function in real life, AR helps eliminate doubts and ensures that what customers see is what they get.
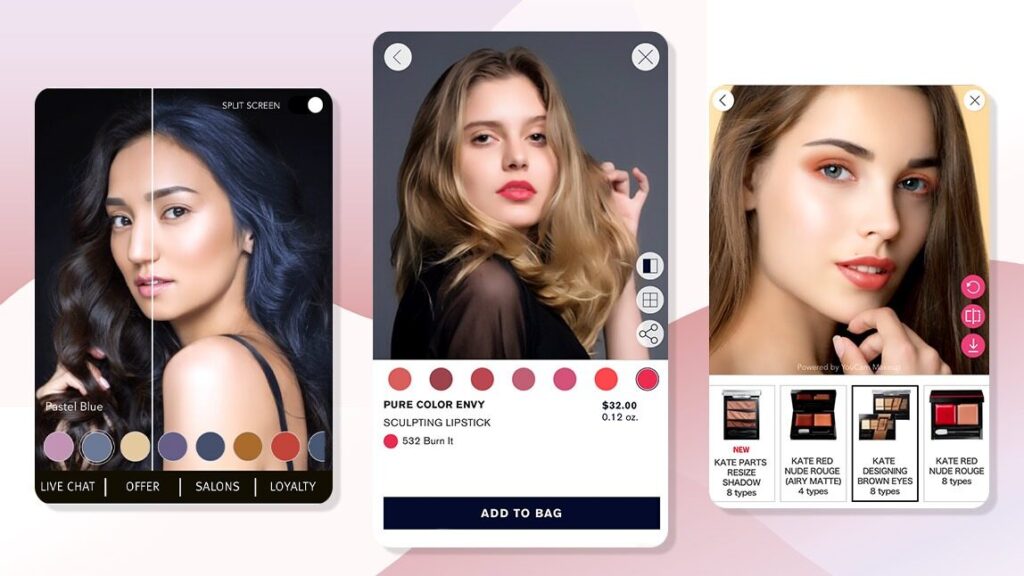
Image Source: Perfect Corp
Benefits for Businesses
The rise of visual commerce has far-reaching implications for both consumers and businesses alike. Brands can now craft compelling narratives around their offerings, fostering emotional connections with target audiences.
For businesses, visual commerce offers a significant competitive edge by enabling more engaging and interactive customer experiences. Studies show that consumers are more likely to purchase products that they can visualize or interact with. Retailers can also use the data generated from these interactions to fine-tune their marketing strategies and inventory planning.
Another significant advantage lies in the ability to deliver highly targeted marketing campaigns. Machine learning algorithms analyze user behavior patterns, preferences, and browsing history to generate tailored product recommendations.
As a result, customers benefit from relevant suggestions while brands enjoy higher click-through rates and conversion probabilities. Additionally, these intelligent systems continuously learn and adapt to individual tastes, ensuring that promotional materials remain fresh and engaging over time.
The Critical Role of 3D Product Models
At the heart of advanced visual commerce lies the 3D product model. Unlike static photographs, a 3D model is a digital asset that can be manipulated, customized, and integrated into various experiences. These models serve as the single source of truth for all visual content, from generating high-resolution still images from any angle to powering AR applications and interactive configurators.
For consumers, 3D models transform the browsing experience from passive observation to active exploration. They can rotate a product 360 degrees, zoom in to examine texture and stitching, and even disassemble a virtual product to understand its components. This level of inspection replicates the physical act of picking up and examining an item in a store, building confidence and reducing the anxiety associated with online purchases. For complex products like electronics or custom furniture, this interactive exploration is invaluable, providing a depth of understanding that dozens of static images cannot achieve.
Social Commerce and the Rise of Shoppable Media
Visual commerce has seamlessly merged with social media, giving birth to the powerful trend of social commerce. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Pinterest have become de facto discovery engines for products, and they have integrated native shopping features to capitalize on this. Shoppable posts, where users can tap on a tagged item in a photo or video to see details and purchase it without leaving the app, are a direct application of visual commerce principles.
This integration creates a frictionless path from inspiration to purchase. A user watching a makeup tutorial on TikTok can immediately buy the featured lipstick through a shoppable link. Someone browsing interior design inspiration on Pinterest can purchase a similar lamp they see in a pin. This immediacy is crucial in capturing the “want it now” impulse, dramatically shortening the sales funnel and turning social media platforms into powerful, direct-to-consumer storefronts.
Data and Analytics: The Unseen Engine
The interactivity of visual commerce generates a wealth of data that goes far beyond traditional e-commerce metrics. Businesses are no longer limited to tracking clicks and page views; they can now analyze how users interact with their products. This includes data points such as:
- Which products are most frequently rotated or zoomed in on? This indicates high consideration and interest.
- What specific features or colors do users select in a configurator? This provides direct insight into consumer preferences for product development and inventory planning.
- At what point in an AR try-on do users drop off? This can help identify usability issues or points of decision paralysis.
This behavioral data is a goldmine for retailers. It allows them to optimize product pages, refine marketing messaging, make informed decisions about which products to promote, and even influence future design and manufacturing cycles. By understanding not just what customers buy, but what they look at and how they engage, businesses can create a truly customer-centric strategy.
Challenges and Future Prospects in Visual Commerce
Despite its numerous benefits, visual commerce is not without its challenges. For one, implementing AI and AR technologies requires significant investment in both infrastructure and expertise. Businesses must ensure that their platforms are capable of handling complex algorithms and large-scale data processing.
Another challenge is the need for high-quality visuals. Customers expect sharp, realistic images and videos that accurately represent the product. This demands investment in professional photography, videography, and 3D modeling.
Privacy concerns also come into play, as AI-driven personalization relies on collecting and analyzing user data. Businesses must strike a balance between offering a personalized experience and respecting customer privacy.
Looking ahead, the future of visual commerce is undoubtedly promising. With advancements in AI and AR technologies accelerating at breakneck speeds, we can expect increasingly sophisticated implementations aimed at enhancing user experiences further. For example, wearable AR devices could provide seamless shopping experiences, allowing users to browse, try on, and purchase products directly from their surroundings.
Additionally, integration with other emerging technologies, such as blockchain, could revolutionise the way visual commerce operates. Blockchain could ensure transparency and security in transactions, while also enabling features like digital ownership of virtual goods.
Expanding the Definition of V-Commerce
V-commerce, or virtual commerce, takes the principles of e-commerce into entirely digital realms. Beyond traditional online shopping, v-commerce includes activities like purchasing virtual goods in video games, shopping in VR environments, and engaging with brands in metaverse platforms.
As the metaverse continues to grow, v-commerce is set to become an integral part of the digital economy. Imagine attending a virtual fashion show where you can purchase outfits for your avatar or even yourself in real life. These experiences blur the line between physical and digital shopping, creating new opportunities for brands to connect with tech-savvy audiences.
The Metaverse and the Next Frontier in Visual Commerce
The emergence of the metaverse represents the ultimate expression of visual commerce. In these persistent, shared virtual worlds, the principles of visual commerce are not just an enhancement but the very foundation of interaction. Consumers are no longer browsing a website; they are inhabiting a digital space where brands can create flagship stores, showrooms, and experiential events.
For example, an automotive company could host a virtual test drive on a simulated race track, allowing users to experience the performance and interior of a new model. A luxury fashion house could launch an exclusive, digital-only clothing line for avatars, creating a new revenue stream and a powerful branding tool. This deep level of immersion fosters a sense of community and belonging, turning customers into brand advocates within these digital landscapes. The line between content, community, and commerce becomes seamlessly blurred, offering a glimpse into the future of retail where experience is the primary product.
The Power of Storytelling and Emotional Connection
At its core, visual commerce is a powerful tool for storytelling. A static image of a sofa is just a product. A 3D model that you can place in your own living room is an illustration of potential. But a video that shows a family gathering around that same sofa, or an AR experience that lets you see how the fabric looks in your specific lighting, tells a story about your life with that product. This emotional resonance is invaluable.
By using rich media to contextualise products within a lifestyle or narrative, brands can forge deeper connections with their audience. A customer isn’t just buying a tent; they are buying the promise of adventure, which is sold through stunning videos of the tent in majestic landscapes and interactive features that let them explore its weatherproof capabilities. This emotional investment significantly increases the perceived value of the product and strengthens brand loyalty far beyond what a list of specifications could achieve.
Conclusion on Visual Commerce
As we move forward, it is evident that visual commerce will continue shaping the future of e-commerce.
With advancements in AI and AR technologies accelerating at breakneck speeds, we can expect increasingly sophisticated implementations aimed at enhancing user experiences further.
Ultimately, embracing visual commerce could prove instrumental in driving growth and success within the competitive landscape of online retail.
If you liked this article, read our other insightful articles to boost e-commerce sales.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of V-commerce?
V-commerce, or virtual commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services in a virtual environment. One common example of v-commerce is purchasing digital items within video games or online worlds, such as skins, weapons, or other customization options for avatars. Another example could be shopping in a virtual reality (VR) store where customers can browse products and make purchases while immersed in a simulated environment using a headset and controllers. Essentially, any transaction that takes place in a digitally created space falls under the umbrella of v-commerce.
What is virtual commerce?
Virtual commerce, also known as v-commerce, is a type of e-commerce that involves buying and selling goods and services through digital channels, often in a simulated or virtual environment. This can include transactions conducted on websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, or even within virtual reality experiences. Virtual commerce allows businesses to reach new audiences and offer unique experiences that may not be possible in traditional brick-and-mortar stores. It also enables consumers to shop from anywhere at any time, with access to a wider range of products than they might find in their local area.




