Table of Contents
ToggleMAP (Minimum Advertised Price) violations can have a significant impact on e-commerce brands. These violations occur when sellers advertise their products below the agreed-upon minimum price set by the brand. Not only do MAP violations devalue the brand and its products, but they can also lead to price erosion and damage relationships with authorized resellers. In this ultimate guide, we will explore the various aspects of detecting MAP violations on Amazon, the impact they have on brands, and effective strategies for combating these violations.
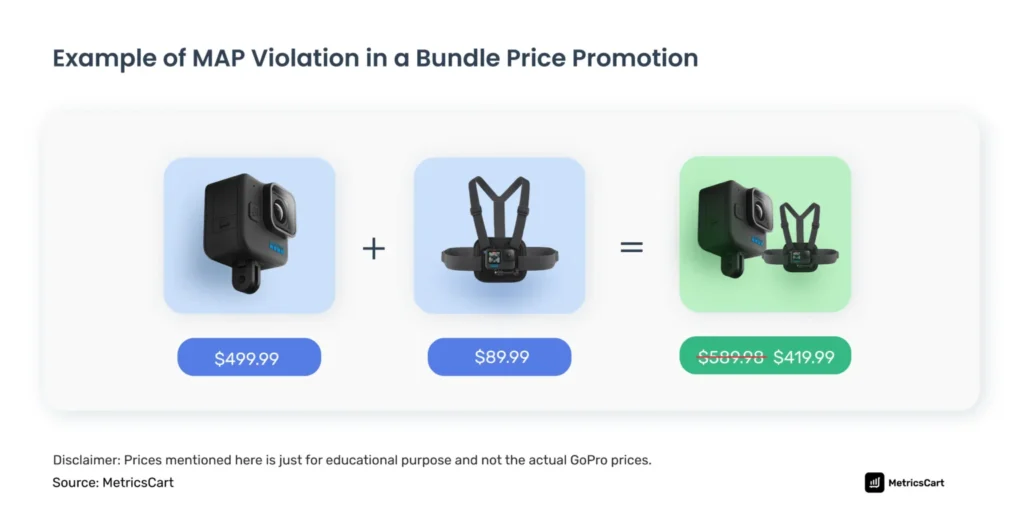
Image Source: Metrics Cart
Understanding MAP Violations
MAP policies are put in place by brands to maintain product value and protect their authorized resellers. These policies ensure that all sellers advertise products at or above a minimum price, thereby preventing price wars and maintaining a level playing field.
MAP violations on Amazon occur when sellers disregard these policies and advertise products below the agreed-upon minimum price. This not only affects the brand’s reputation but also puts authorized resellers at a disadvantage, as they are required to adhere to the set minimum price.
The Anatomy of a MAP Policy: More Than Just a Number
A MAP policy is a unilateral dictate from a brand to its resellers. It is crucial to understand that, in the United States, MAP is not a horizontal agreement between competitors (which would violate antitrust laws) but a vertical agreement between a manufacturer and its downstream retailers. The policy stipulates the lowest price a retailer can advertise the product for. It is vital to note the word “advertise”; the policy typically does not govern the final selling price at the checkout cart, allowing retailers some flexibility to offer discounts upon purchase.
A well-drafted MAP policy should be:
- Clear and Unambiguous: It must explicitly define what constitutes an “advertisement” (e.g., website listing, Amazon offer, Google Shopping ad, email promo, physical flyer).
- Comprehensive: It should cover all sales channels and all products, or clearly specify which products and channels are included.
- Consistently Applied: The brand must enforce the policy uniformly across all resellers to avoid claims of selective enforcement or discrimination.
- Legally Vetted: Given the delicate legal landscape, policies should be crafted or reviewed by legal counsel specializing in antitrust and trade law.
The Impact of MAP Violations on Amazon for Brands
MAP violations on Amazon can have a detrimental impact on brands, both in the short term and the long term. Let’s take a look at some of the key effects of MAP violations:
1. Brand Devaluation
Consistent discounting trains consumers to devalue your product. A high-quality product sold perpetually at a discount ceases to be a premium item in the consumer’s mind and becomes a commodity whose primary differentiator is price. This makes it incredibly difficult to ever raise prices again and attracts a more price-sensitive, less loyal customer base. Furthermore, luxury and premium brands rely on perceived exclusivity and value; rampant discounting shatters this image instantly.
2. Loss of Control over Prices
When a market devolves into a price war, innovation suffers. Brands are forced to cut costs—often at the expense of quality, materials, or R&D—to compete with their own discounted products. The entire business strategy shifts from value creation to cost-cutting, a race that is difficult to win and often ends with a diminished brand and inferior products.
3. Damaged Relationships with Resellers
Authorized resellers invest in marketing, customer service, product education, and inventory. They are brand ambassadors. When a rogue seller undercuts them on price without any of these overheads, it creates a “free-rider” problem. The authorized seller does all the work to build demand, while the violator reaps the sales. This leads to:
Stifled Innovation in Retail: When margins are crushed, resellers cannot invest in the value-added services that make their stores unique, such as expert staff, demonstrations, or exceptional warranty support.
Loss of Key Retail Partners: Frustrated authorized sellers will stop stocking, promoting, and supporting your brand. Losing a major brick-and-mortar retailer is often far more damaging than losing sales from a few unauthorized Amazon sellers.
Effective Strategies for Detecting MAP Violations on Amazon
To detect MAP violations on Amazon, brands need to implement robust strategies to monitor and identify instances of non-compliance. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Implement Automated Price Monitoring Software
This is non-negotiable for serious brands. Dedicated MAP monitoring tools use web crawlers to scan thousands of online retailers, marketplaces, and search engines 24/7. They provide:
- Real-time Alerts: Instant notifications via email or SMS when a violation occurs.
- Competitive Intelligence: Dashboards tracking not just your prices but also competitor pricing strategies.
- Historical Data: Reports showing pricing trends over time, which is invaluable for identifying repeat offenders and patterns.
- Seller Identification: Advanced tools go beyond the listing to help identify the entity behind the seller name, a critical step for enforcement.
2. Conduct Regular “Mystery Shopping” to Figure Out MAP Violations on Amazon
For high-value violations or to gather evidence for legal action, physically place orders from violating sellers. This confirms the final sale price and helps you gather intelligence on their operations (e.g., Where are they shipping from? Is the product authentic? Is it new or used?).
3. Monitor the Digital Supply Chain
Often, unauthorized sellers acquire products through legitimate means that violate your distribution agreements. They may source from:
- Diverters: Companies that buy excess inventory from authorized distributors or retailers in one region and sell it in another where they are not authorized.
- Liquidators: Entities that purchase customer returns or refurbished goods and sell them as new.
- Unauthorized Distributors: Wholesalers who have acquired your product but are not part of your official network.
Regular audits of your distributors’ sales records can help you identify leaks in your supply chain.
The Enforcement Lifecycle: From Detection to Resolution
Detection is only half the battle. A structured, documented enforcement process is key to finding any MAP violations on Amazon.
Step 1: Documentation and Evidence Gathering
The moment a violation is detected, take clear screenshots that include the URL, product, price, date, and time. This creates an irrefutable paper trail. Automated software often does this automatically.
Step 2: The Tiered Response Approach to Find MAP Violations on Amazon
Not all violations are equal. A first-time offender may have made an honest error, while a repeat offender is willfully destructive. Your response should be tiered:
- First Notice: A polite but firm educational email, informing the seller of the MAP policy and requesting immediate compliance. Include the evidence and a copy of the policy.
- Second Notice: A more formal warning, stating the potential consequences of continued violation (e.g., loss of authorized status, termination of supply).
- Final Notice and Escalation: For persistent violators, escalate to more severe actions. This includes reporting them to the marketplace (Amazon’s MAP violation report form is effective), pursuing legal action through a cease-and-desist letter, or terminating their relationship with your distributors.
Step 3: Leveraging Marketplace Relationships
Amazon and other major platforms do not enforce MAP policies directly, as it could imply collusion. However, they do enforce their own policies that dovetail with MAP enforcement. You can report MAP violations on Amazon based on:
- Intellectual Property Rights: If the violator is using your copyrighted images or trademarked logo without permission.
- Product Condition: If they are listing a product as “new” when it is actually used, refurbished, or defective.
- Listing Quality: If their product page contains incorrect or misleading information.
Step 4: Legal Recourse for MAP Violations on Amazon
For the most egregious and damaging violators, legal action may be the final option. This can involve claims of trademark infringement, unfair competition, or tortious interference with business relationships. This is a complex and costly path and should only be pursued under the guidance of an attorney.
Key Indicators of MAP Violations
When monitoring for MAP violations on Amazon, there are certain key indicators that brands should look out for. These indicators can help identify potential violations and take appropriate action.
1. Consistently Low Prices
What It Looks Like:
This is the most straightforward violation. A seller, often with an obscure name, lists your product at a price 20%, 30%, or even 50% below the established MAP. This price remains static for days or weeks, making it easy to find but damaging while it lasts.
Underlying Causes:
- Grey Market Goods: The seller may have sourced products through unauthorized channels (e.g., from a liquidator, a foreign distributor, or by diverting inventory from a closeout sale). Their acquisition cost is significantly lower than that of an authorized reseller, allowing them to profit even while undercutting MAP.
- Inventory Dumping: A seller going out of business or liquidating inventory has no incentive to protect your brand’s pricing. Their goal is to convert stock into cash quickly.
- Counterfeit Products: In the most severe cases, consistently low prices can be a red flag for counterfeit goods. The inferior quality allows for a lower price point, devastating both your sales and your brand’s reputation.
- Market Dominance Strategy: A large, well-funded retailer might intentionally sell at a loss to drive smaller competitors out of the market for that product, establishing themselves as the sole seller before raising prices again.
Strategic Response:
Audit Your Supply Chain: Consistent low prices from multiple sellers often indicate a leak. Audit your authorized distributors and retailers to identify who might be selling excess inventory to unauthorized third parties and identify MAP violations on Amazon.
Investigate the Source: Use the seller’s information (if available) or conduct a “mystery buy” to determine the product’s origin and authenticity. Is it new, used, refurbished, or counterfeit?
Enforce Immediately: This type of violation requires a swift and direct response. Issue a formal cease-and-desist letter and report the listing to the marketplace for trademark infringement if they are using your images or if the product is inauthentic.
2. Rapid Price Changes
What It Looks Like:
You observe a seller’s price fluctuating wildly throughout the day. It might jump to the MAP-compliant price for an hour, only to drop 5-10% below MAP for the next several hours. This pattern repeats, keeping their average price below the minimum while making manual monitoring futile.
Underlying Causes:
- Repricing Software: This is almost always the work of automated algorithmic tools. Sellers use repricers to stay competitive. A careless or malicious seller can configure their repricer to always stay a certain amount below the Buy Box price or the lowest competitor, inevitably dragging it below MAP.
- Avoiding Detection: The seller is likely aware of the MAP policy but is gambling that rapid, temporary dips will go unnoticed by the brand’s monitoring systems, allowing them to win the Buy Box during those cheap periods without facing consequences.
Strategic Response:
Gather Pattern Evidence: Document the frequency of the changes. A log showing dozens of violations per day is powerful evidence when escalating to the seller’s上级或 marketplace platform.
Automated Monitoring is Essential: This tactic proves that manual price checks are obsolete. You need monitoring software that tracks price history 24/7 and captures screenshots as proof of the violation at specific times.
Target the Repricing Algorithm: In your communication with the seller, specifically prohibit the use of repricers that do not respect MAP. Demand that they configure their software to have a price floor set at your MAP.
3. Multiple Unauthorized Sellers
What It Looks Like:
Suddenly, your product listing is flooded with 10-20 new “just launched” seller accounts, all offering the product below MAP. Individually, they are small, but collectively they create a race to the bottom that crushes the price and pushes authorized sellers out of the Buy Box.
Underlying Causes:
- Distribution Leakage: This is a classic sign that your product has been diverted. An authorized distributor or retailer is likely selling large quantities of your product to a liquidator or a grey market wholesaler, who then resells it in bulk to these small, unauthorized sellers.
- Counterfeit Operations: Multiple new sellers can also indicate a coordinated counterfeiting effort, with different sellers operating from the same source of fake goods.
- The “Waterfall” Effect: When one unauthorized seller appears and isn’t stopped, it signals to others that your brand is not actively enforcing its MAP policy, inviting more violators to join in.
Strategic Response for MAP Violations on Amazon:
Enforce Broadly: You must issue notices to all violating sellers simultaneously. Tolerating any of them undermines your authority. Report them en masse to the marketplace.
Trace the Source: A mystery buy from several of these sellers can be revealing. Check if the products have the same batch numbers, originate from the same geographic location, or have had their UPCs tampered with.
Plug the Leak: This is a critical step. Use the data from your investigation to confront the authorized partner who is leaking the inventory. This may involve enforcing your Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policy or changing your distribution agreement to include stronger penalties for diversion.
4. Unauthorized Bundles or Promotions
What It Looks Like:
A seller advertises your product at the correct MAP price but includes a “free gift,” a heavily discounted companion product, or a “add to cart for special discount” promotion that effectively lowers the final cost below the minimum advertised price and is a MAP violation on Amazon.
Underlying Causes:
- Circumventing the Policy: The seller is attempting a technicality. They argue that they are advertising the product at MAP, but the added value of the bundle constitutes a separate promotion. Most well-written MAP policies explicitly forbid this.
- Clearing Unrelated Inventory: A seller might bundle your hot-selling product with a slow-moving item from another brand to clear out their own stale stock.
- Gaining a Competitive Edge: This is a tactic used by sellers who want to appear compliant on the surface while still offering a more attractive “deal” than competitors who are following the rules.
Strategic Response:
Treat it as a Violation: In your communications, make it clear that bundling and unauthorized promotions are a violation of the policy’s spirit and letter. Demand immediate cessation of the promotion.
Define “Advertisement” in Your Policy: Your MAP policy must be explicitly worded to cover any promotional tactic that effectively reduces the product’s price, including:
- Bundling with other products
- “Free gift with purchase” offers
- Coupon codes (advertised on the listing or automatically applied at checkout)
- Loyalty points that can be redeemed for cash
- “Add to cart to see price” mechanisms
Monitor the Entire Customer Journey: Enforcement requires checking not just the listing price, but also going through the checkout process to see if a coupon is auto-applied, or checking the seller’s other pages for promotional codes.
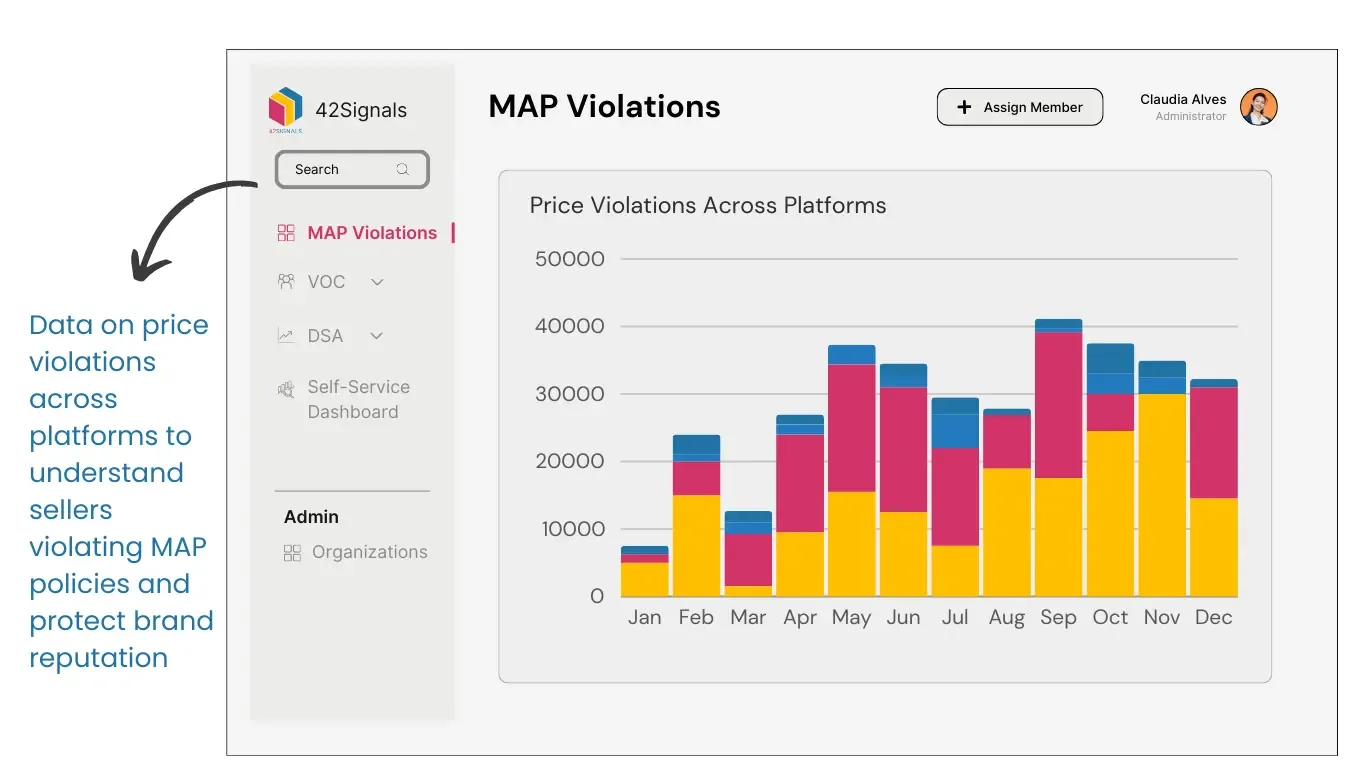
Utilizing Monitoring Tools and Software to Combat MAP Violations on Amazon
Monitoring tools and software can be invaluable resources for brands looking to combat MAP violations on Amazon. Ecommerce analytics tools like 42Signals, automate the monitoring process and provide insights into pricing trends and potential violations.
- These tools track pricing data across multiple selling channels and provide analytics to identify MAP violations.
- They allow brands to monitor their competitors’ pricing strategies to identify any violations or undercutting.
In conclusion, MAP violations on Amazon can have a significant impact on brands, but with effective strategies and the use of monitoring tools and software, brands can detect and combat these violations.
By taking proactive measures to protect their brand and maintain control over pricing, brands can stay competitive and ensure the long-term success of their Amazon marketplace presence.
To know more about how 42Signals can aid your business, contact us at sales@42signals.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do violations stay on Amazon?
Violations on Amazon do not have a publicly defined expiration period. Minor issues, such as incorrect product data, may be resolved quickly and have minimal long-term impact. However, serious or repeated violations can stay on your seller account indefinitely and negatively affect your account health. Amazon tracks all policy violations through the Account Health Dashboard, and multiple unresolved issues can put your account at risk of suspension.
How many violations to get banned on Amazon?
There’s no fixed number of violations that trigger a ban on Amazon. Instead, Amazon evaluates a seller’s Account Health Rating (AHR), which is influenced by:
- The severity of the violation (e.g., counterfeit products are treated more seriously than a missing image).
- The number of unresolved issues.
- Whether the seller takes corrective action in a timely manner.
A seller with frequent or high-impact violations (like intellectual property complaints or safety issues) and no corrective steps may face account suspension or permanent deactivation after just a few violations.
Does Amazon use MAP tracking?
Amazon does not enforce Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies on behalf of brands. While MAP pricing is a common practice among manufacturers, Amazon generally allows third-party sellers to set their own prices—even below the MAP—unless it violates Amazon’s Fair Pricing Policy (which is designed to prevent price gouging or misleading pricing).
To monitor MAP violations, brands must use third-party tools or join Amazon Brand Registry, which offers some visibility into who is selling your products and how. But enforcement still rests with the brand, not Amazon.
How to report violations on Amazon?
To report a violation on Amazon, follow these steps:
- For counterfeit, copyright, or trademark infringement:
Go to Amazon’s Report Infringement form and submit details. - For listing issues or MAP concerns:
Use the “Report incorrect product information” link on the product listing page, or reach out through Seller Support if you’re a registered brand. - If you’re a Brand Registry member:
Use the Brand Registry dashboard to report policy violations, unauthorized sellers, or listing manipulation.
Amazon typically reviews these reports and may take action depending on the nature and evidence provided.




