Table of Contents
ToggleE-commerce has experienced exponential growth over the past decade, and with it, e-commerce logistics have evolved dramatically. As customers demand faster delivery times, increased visibility into order status, and a seamless shopping experience, businesses must adapt their fulfillment strategies to meet these expectations.
One critical way companies are staying ahead is by leveraging data to drive smarter e-commerce logistics solutions.
Data for Smoother E-Commerce Logistics Handling
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management lies at the heart of any successful e-commerce logistics operation. By analyzing sales patterns, historical data, and seasonal trends, businesses can make informed decisions about stocking levels, reducing instances of both understocking and overstocking, thus improving e-commerce sales.
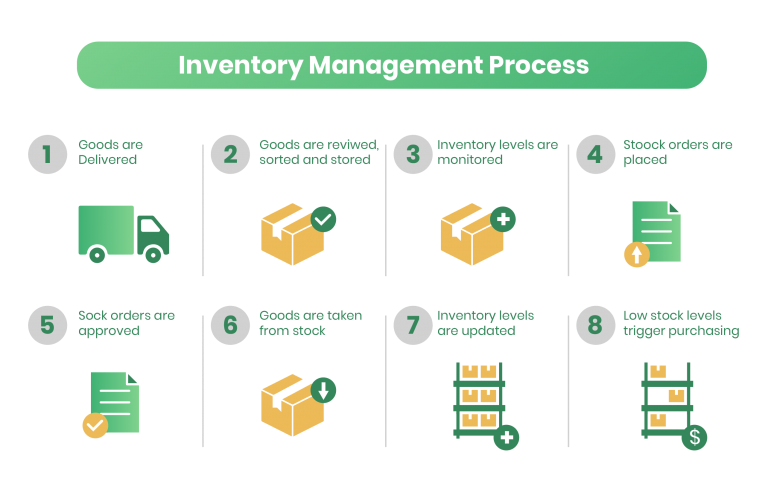
Image Source: Advotics
Implementing real-time inventory tracking systems allows companies to monitor product availability across multiple channels, minimizing out-of-stock situations while preventing excess inventory buildup.
- Beyond Basic Forecasting: While analyzing sales patterns, historical data, and seasonal trends is foundational, modern systems go much deeper. They incorporate:
- Real-time Market Signals: Monitoring social media sentiment, competitor pricing fluctuations, search trends, and even weather patterns provides leading indicators of demand shifts.
- Promotional Impact Modeling: Predicting the precise uplift from marketing campaigns, discounts, or influencer partnerships prevents both overestimation leading to excess stock and underestimation causing missed opportunities.
- New Product Introduction (NPI) Forecasting: Leveraging data from similar product launches, category trends, and pre-order metrics to set realistic initial stocking levels for new items.
- The Power of Real-Time Visibility: Implementing robust real-time inventory tracking systems (utilizing RFID, advanced WMS integrations, IoT sensors) is non-negotiable. This granular visibility across all sales channels (website, marketplaces, physical stores if applicable) and fulfillment nodes (central DCs, regional hubs, 3PL warehouses, stores used for fulfillment) is critical. It prevents the infamous “available to promise” failures where a customer orders an item shown as in stock online, only to discover it’s actually allocated elsewhere or misplaced in a warehouse.
- Predictive Analytics & Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms move beyond simple extrapolation. They identify complex, non-linear demand patterns, predict the impact of external events (e.g., a viral TikTok review), and continuously learn and refine their forecasts. This enables:
- Dynamic Safety Stock Calculation: Adjusting buffer inventory levels automatically based on predicted demand volatility and supplier lead time reliability, rather than relying on static, often arbitrary, percentages.
- Automated Replenishment Triggers: Systems can proactively generate purchase orders or transfer requests based on forecasted depletion rates and predefined rules, minimizing human latency and error.
- Markdown Optimization: Predicting the optimal timing and depth of markdowns for slow-moving items to maximize recovery value and free up warehouse space and capital.
- Distributed Inventory Strategies: Data underpins successful implementation of strategies like storing bestsellers closer to high-demand customer clusters or utilizing store inventory for online fulfillment (BOPIS/Ship-from-Store), significantly reducing shipping times and costs.
Additionally, predictive algorithms can forecast future demand, enabling organizations to prepare accordingly and avoid costly stockouts or markdowns.
Warehouse Optimization
Data analysis plays a crucial role in optimizing warehouse operations in e-commerce logistics.
Machine learning algorithms can determine optimal storage locations based on factors such as product velocity, dimensions, weight, and handling requirements.
This not only streamlines picking processes but also reduces travel time within the facility.
- Intelligent Slotting: Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets encompassing:
- Product Velocity (Pick Frequency): Fast-moving items are placed in easily accessible “golden zones” close to packing stations.
- Product Affinity (Frequently Bought Together): Items often ordered together are stored near each other to minimize picker travel for multi-item orders.
- Physical Characteristics: Dimensions, weight, fragility, and required storage conditions (e.g., temperature-controlled) dictate optimal bin or pallet locations, maximizing space utilization and handling safety.
- Seasonality & Promotions: Slotting dynamically adjusts based on anticipated demand surges for specific items.
- Workflow Orchestration: Data drives the entire order fulfillment process:
- Wave Planning Optimization: Grouping orders for picking based on factors like delivery deadlines, carrier cut-off times, destination zones, and item location proximity within the warehouse.
- Pick Path Optimization: Generating the most efficient travel route for pickers (or robots) through the warehouse for each wave or batch, significantly reducing “travel empty” time – often the largest time sink in picking.
- Labor Management: Using historical and real-time performance data to forecast staffing needs by shift and task, identify training opportunities, and optimize productivity through gamification or performance feedback loops.
- Automation Integration & Performance Monitoring: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), robotic picking arms, and automated sortation systems generate a wealth of performance data:
- Uptime & Utilization Metrics: Identifying bottlenecks or maintenance needs before they cause significant delays.
- Throughput Analysis: Measuring units processed per hour/minute to gauge system efficiency and capacity limits.
- Exception Handling: Tracking errors or jams to identify systemic issues and improve system design or procedures.
- ROI Calculation: Precisely measuring the productivity gains and cost savings achieved by automation investments.
- Layout & Capacity Planning: Data analysis informs warehouse design changes, expansion decisions, and peak season preparation by modeling different scenarios based on forecasted volumes, SKU proliferation, and process changes.
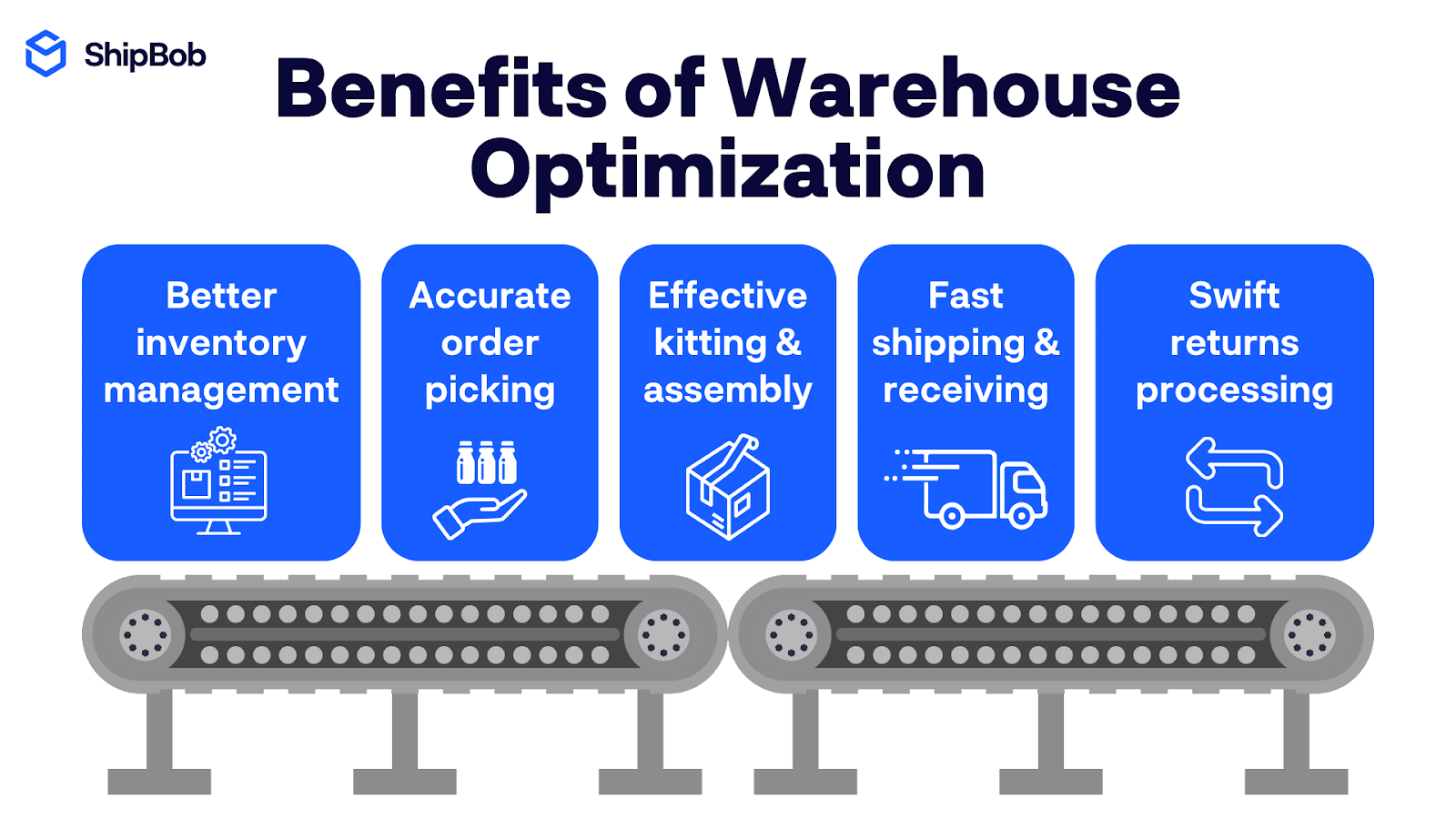
Image Source: ShipBob
Moreover, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotics equipped with sensors generate valuable performance metrics, helping managers identify bottlenecks, improve workflow efficiency, and reduce labor costs.
Transportation Planning
Leveraging data enables businesses to create more efficient transportation plans in their e-commerce logistics planning, resulting in reduced shipping costs and quicker deliveries.
- Advanced Routing & Carrier Selection: Sophisticated Transportation Management Systems (TMS) leverage vast datasets to:
- Dynamic Route Optimization: Continuously recalculating the most efficient routes in real-time, factoring in live traffic congestion, road closures, weather disruptions, fuel costs, and driver Hours of Service (HOS) regulations. This goes far beyond simple point-to-point distance.
- Intelligent Carrier Allocation: Automatically selecting the optimal carrier and service level (e.g., ground, expedited, LTL, FTL) for each shipment based on cost, transit time reliability, destination, package characteristics, and negotiated contracts. This includes comparing real-time spot market rates.
- Consolidation Opportunities: Identifying shipments going to the same geographic area that can be combined into full truckloads (FTL) or more efficient Less-Than-Truckload (LTL) configurations, dramatically reducing per-unit shipping costs.
- Multi-Modal Optimization: Evaluating and seamlessly integrating different transportation modes (air, ocean, rail, truck, parcel) based on real-time data is crucial, especially for international or long-haul domestic shipments:
- Cost/Transit Time Trade-offs: Analyzing the balance between the higher speed/cost of air freight versus the lower cost/longer transit of ocean or rail for specific lanes and inventory needs.
- Visibility Across Modes: Gaining end-to-end shipment tracking even when multiple carriers and modes are involved, ensuring proactive exception management.
- Port & Terminal Congestion Prediction: Using data to anticipate delays at key hubs and proactively reroute shipments or adjust schedules.
- Network Design & Parcel Spend Management: Data analysis is critical for strategic decisions:
- Optimal Warehouse Location: Modeling different distribution network configurations to minimize total transportation costs and transit times to the majority of customers.
- Parcel Invoice Auditing & Negotiation: Analyzing carrier invoices in detail to identify billing errors, assess accessorial charge patterns, and leverage data-driven insights to negotiate better contracts based on actual shipping profiles and volumes.
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Measuring emissions associated with different routes and modes to support sustainability goals and reporting.
Furthermore, multi-modal transport options – combining different modes of transportation such as air, sea, rail, and road freight – can be evaluated based on real-time data, ensuring timely and cost-effective deliveries.
Last-Mile Delivery
The final leg of the supply chain, known as “last-mile” delivery, often poses significant challenges for e-commerce logistics planning due to its complexity and high operational expenses.
However, innovative data-driven solutions are emerging to address these issues.
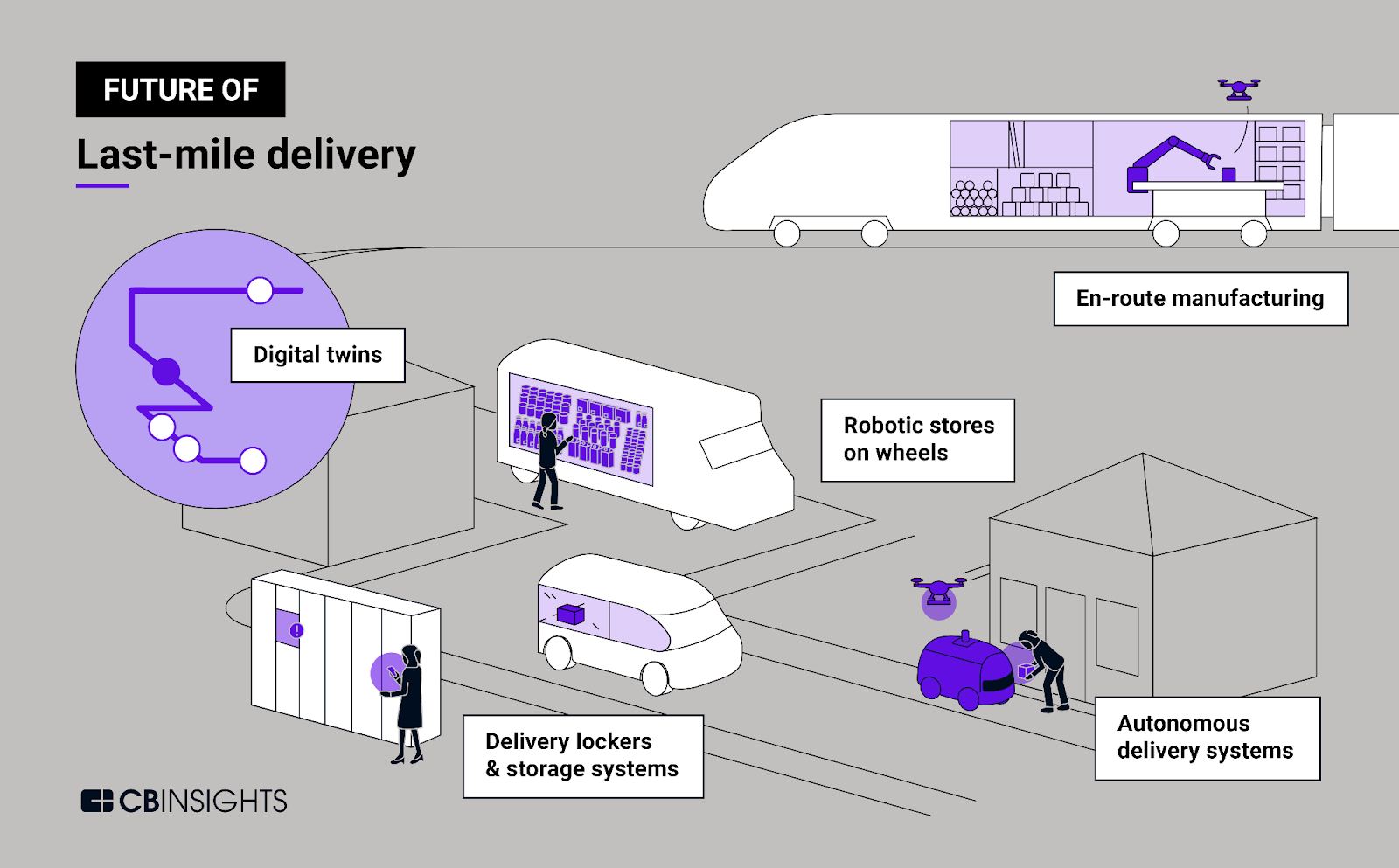
Image Source: CB Insights
- The Challenge Amplified: Beyond complexity and cost, last-mile faces urbanization challenges (traffic, parking, density), the “Amazon effect” of expecting same/next-day delivery, and the need for extreme flexibility (time windows, delivery instructions, alternative locations).
- Geo-Analytics & Dynamic Routing: Sophisticated tools analyze layers of data:
- Historical Traffic & Travel Times: Building accurate time-of-day and day-of-week models for specific streets and neighborhoods.
- Demographic & Customer Density: Understanding where high-value customers or high-volume delivery clusters are located.
- Delivery Constraints: Incorporating customer preferences (safe places, delivery windows), building access restrictions, and parking availability.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Dynamically rerouting drivers based on live traffic, weather events, or unexpected delays (like a customer not answering the door). This maximizes the number of successful delivery attempts per hour.
- Alternative Delivery Models: Data enables and optimizes new approaches:
- Crowdsourced Delivery Platforms: Matching available local couriers (or even gig economy drivers) with nearby deliveries in real-time, offering flexibility and speed, especially for local retailers or urgent orders. Data ensures fair pricing, reliable driver ratings, and efficient matching.
- Pickup Points (PUDO) / Lockers: Analyzing customer locations and behavior to strategically place secure pickup points (in stores, transit stations, standalone lockers) where they offer maximum convenience and reduce failed home delivery attempts. Data determines optimal density and location.
- Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs): Placing small, automated warehouses deep within urban centers, enabled by data predicting hyper-local demand patterns to stock the right ultra-fast-moving items for immediate delivery.
- Autonomous Vehicles & Drones: While still evolving, their deployment and route planning will be entirely reliant on complex real-time data processing for navigation, obstacle avoidance, and delivery coordination.
- Predictive ETAs & Proactive Communication: Leveraging real-time driver location, traffic data, and historical performance to provide customers with highly accurate Estimated Time of Arrivals (ETAs) via SMS or app notifications, significantly enhancing transparency and reducing customer anxiety (and WISMO calls – “Where Is My Order?”).
Returns Management
An effective returns process is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction, yet a massive pain point in e-commerce logistics.
Analyzing return rates, reasons, and patterns helps businesses pinpoint potential areas for improvement throughout the entire buying journey – from product descriptions and images to packaging materials and delivery speeds.
- Understanding the “Why”: Deep analysis of return data is paramount:
- Return Reason Codes: Categorizing and quantifying reasons (size/fit issues, damaged, not as described, changed mind, defective) to identify root causes.
- Product-Level Analysis: Pinpointing specific SKUs with abnormally high return rates warranting investigation into quality, description accuracy, or imagery.
- Customer Segmentation: Identifying return patterns by customer segment (new vs. loyal, geographic region, acquisition channel).
- Process Friction Points: Tracking where delays or complications occur in the return authorization, shipping label generation, carrier pickup/drop-off, warehouse processing, and refund issuance.
- Proactive Prevention: Insights drive action upstream:
- Enhanced Product Pages: Using return data to improve sizing charts, add more realistic images/videos (including user-generated content), provide detailed materials information, and refine product descriptions to set accurate expectations.
- Personalized Recommendations: Algorithms can flag items with higher return likelihood for specific customers (e.g., based on past return behavior for similar items) and suggest alternatives or prompt double-checking sizing before purchase.
- Packaging Optimization: Data on damage-related returns informs investments in more protective or right-sized packaging solutions.
- Optimizing Reverse Flow: Data streamlines the return journey:
- Automated Return Authorization (RMA): Systems can instantly approve low-risk returns based on rules (customer history, item value, reason code), speeding up the process.
- Intelligent Return Routing: Directing returned items to the optimal location (e.g., nearest warehouse for fast restocking, refurbishment center, liquidation partner, or even donation facility) based on item value, condition, and restocking potential. This minimizes handling costs and maximizes recovery value.
- Restocking Efficiency: Tracking the time and cost involved in inspecting, testing, repackaging, and relisting returned items to identify inefficiencies.
- Liquidation Optimization: Using data to determine the best channel (outlet store, secondary marketplace, bulk liquidation) for unsellable returns to maximize recovery.
- Customer Experience & Loyalty: Easy returns, powered by data-driven simplicity (pre-printed labels, easy drop-off, quick refunds), build significant trust and encourage repeat purchases, even if the initial purchase was returned.
Armed with this insight, companies can take proactive measures to minimize unnecessary returns, enhance product quality, and refine marketing strategies.

Image Source: Webinterpret
Conclusion on E-commerce Logistics
As consumer demands continue evolving, so too will the need for advanced data analytics in e-commerce logistics.
To remain competitive, e-commerce enterprises must leverage every available resource – particularly actionable digital shelf insights derived from comprehensive data analysis – to inform strategic decision-making and stay one step ahead of new developments in the e-commerce space.
For e-commerce analytics solutions, get in touch with us at sales@42signals.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What is e-commerce logistics?
E-commerce logistics refers to the coordination and management of all activities involved in delivering orders placed online to customers. This includes everything from receiving and processing orders, picking and packing items, managing inventory levels, selecting carriers and shipping methods, tracking packages, handling returns and exchanges, and communicating with customers throughout the delivery process.
What is the role of logistics in commerce?
Logistics plays a critical role in commerce by ensuring that goods and services move efficiently and effectively from suppliers to customers. Logistics encompasses a wide range of activities, including transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfillment, packaging, and distribution.
What do you mean by e-logistics?
eLogistics or e-commerce logistics, also known as “electronic” or “digital” logistics, refers to the integration of digital technologies into logistics operations. This can include automating manual tasks, using real-time data analytics to inform decision-making, implementing AI and machine learning algorithms to predict and prevent disruptions, and leveraging mobile devices and cloud computing to enable remote monitoring and control.
What are the 4 major types of logistics?
While there are many different ways to categorize logistics functions, one common framework divides them into four main areas:
a. Procurement logistics: This involves sourcing raw materials and components from suppliers, negotiating contracts, scheduling deliveries, and managing inventory levels.
b. Production logistics: This focuses on managing the flow of materials and parts through manufacturing facilities, coordinating production schedules, and ensuring quality standards are met.
c. Distribution logistics: This entails storing finished goods, preparing orders for shipment, selecting appropriate carriers, and arranging transportation modes.
d. Reverse logistics: This deals with returning defective or unwanted products, repairing or refurbishing items, disposing of waste, and recycling materials. Each of these logistics types requires specialized knowledge, skills, and resources, and must be carefully managed to achieve optimal results.